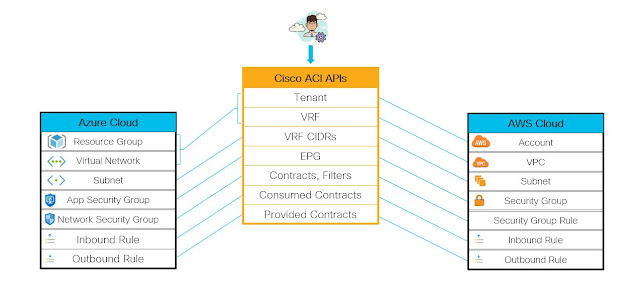
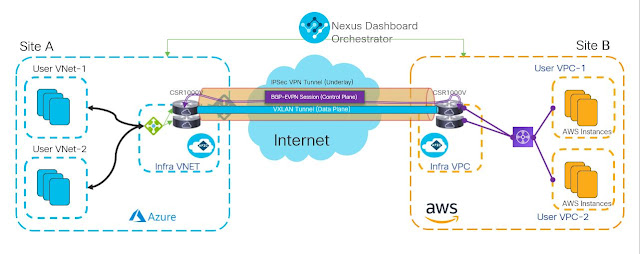
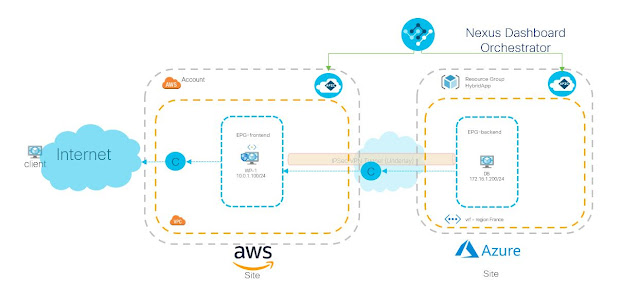
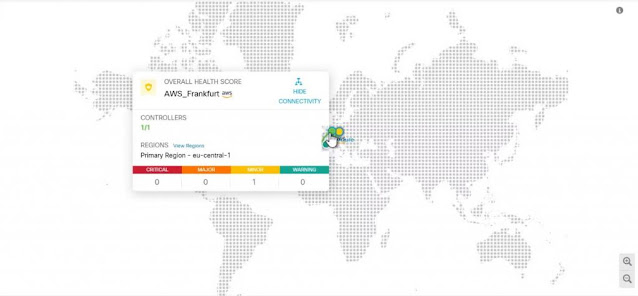
What is Cisco 300-710 SNCF Exam?
Cisco 300-710 SNCF exam measures an applicant's knowledge of Cisco Firepower Threat Defense and Firepower, comprising integrations, policy configurations, deployments, management, and troubleshooting. In this exam, you will learn how to carry out advanced Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW), and Next-Generation Intrusion Prevention System (NGIPS) features, comprising file type detection, network intelligence, network-based malware detection, and intense packet inspection.
How to Prepare for Cisco 300-710 SNCF Exam?
- The thing you should be familiar with is that the exam questions incorporate several topics; that's why your preparation for the exam should be adequate. Thus, before scheduling your CCNP Security 300-710 SNCF certification exam, get the list of exam syllabus topics.
- To get the most productive preparation, begin with the Cisco official website especially. Here you'll find the most appropriate study material for exam preparation. Cisco provides classroom training, e-learning, practice tests, study groups.
- Find online platforms that provide training courses for Cisco exams. On these platforms, you'll get the details on the exam from the top IT specialists.
- Perform Cisco 300-710 SNCF Practice Tests. The most updated and authentic practice tests will make your revision process smooth. Time management is essential in Cisco exams. No matter how much you have soaked up the concepts, it would all be worthless if you cannot output your knowledge in the assigned time. So make sure to time every exam you do and check whether you can finish answering all questions in time.
Things to Know About Cisco CCNP Security Certification
Job Opportunities
After getting CCNP Security certification, one can qualify for various jobs like Systems Engineer, Security Engineer, Network administrator, Network engineer, Network designer, Consulting systems engineer, Technical solutions architect, Network manager Job positions. CCNP Security certified professionals have high job availability than non-certified professionals.
High Salary
Cisco CCNP Security-certified professionals make at least ten percent more than their non-certified peers. The possibility to get high salary raises and can avail of fantastic job opportunities.
Skill Acknowledgment
Cisco CCNP Security certified notices that you had achieved excellent knowledge and skills in networking. Earning a certification from a renowned organization like Cisco indicates that one has acquired the best skills. Technology is an essential part of our lives today. If you want to advance in your career, it is best to stay updated with the latest technology and trends, precisely what Cisco CCNP certification does.
CCNP Security Certification Add Value to Your CV
CV is the only thing that talks about your education, skills, work experience, the knowledge that one has accomplished in their life. Once your CV is added with the Cisco CCNP Security certification, you will be ready to work with the leading organizations. The organizations believe that such professionals will be an asset to the organization and lead the organization to the top.
Great Confidence Builder
Cisco CCNP Security certification builds up the self-confidence to ace the interview for a new dream job. The knowledge and skills that have been achieved through certifications build the confidence to work with the latest technology.
Growth At Work
When it comes to finding a job in IT or computer networking, then earning Cisco CCNP Security certification puts you on the top of the list for promotion or career advancements. Cisco certified professionals will receive better job opportunities while switching the organization. They will be qualified for the positions that have high growth in the future, as IT is a dynamic world, and the skills they hold will need the update.
Opportunity to Work Globally
The Cisco certifications are globally recognized and offer better job opportunities to work in India, Dubai, Algeria, the USA, UK, and Australia.
Conclusion
Earning CCNP Security certification is not a walk in the park; if the applicant is hard working, no one can come in between their victory. Thus, sitting for the CCNP Security certification exam will pave the way towards this certification. Note that every organization wants to employ Cisco certified professionals to make their networks run efficiently. Take into consideration the benefits you'll get and start your preparation process for the 300-710 SNCF exam.