It’s hard to ignore the ubiquity of the internet of things (IoT). Even if you’re one of those holdouts that doesn’t own consumer IoT devices such as a smart speaker, internet-connected thermostat, or a smart watch, industrial IoT (IIoT) devices—a subset of the IoT landscape—are already playing a part in your daily life. From the delivery of water and electricity, to manufacturing, to entertainment such as amusement park rides, IIoT devices are part of more industries than not, and have been for some time. Gartner recently estimated that there were 4.8 billion IIoT assets in the world at the end of 2019, and expects that number will grow by 21 percent in 2020.

The biggest issue faced in many operational technology (OT) environments, which host IIoT assets, isn’t just this growth, but also dealing with older industrial control systems (ICS) that have sometimes been in operation as long as 30 years. Many of these assets have been connected to the network over the years, making them susceptible to attacks. These legacy devices were often deployed on flat networks, at a time when the need for security took a back seat to other priorities, such as high availability and performance.
The discovery of vulnerabilities in these systems doesn’t always mean that patches are, or even can be, rolled out to fix them. Patching many of these IIoT assets means taking them offline—something that’s not always an option with critical infrastructure or production lines that rely on high availability. So patches are often not applied, and vulnerabilities stack up as devices age, leaving attackers with a large swath of exploits to attempt in the pursuit of compromising IIoT assets.
And the number of vulnerabilities discovered in IIoT devices is growing, as is evident in research carried out by Cisco Talos’ Security Research Team, whose mission is to discover vulnerabilities before the bad guys do. During their look back at 2019, Talos pointed out that they published 87 advisories about vulnerabilities in IoT and ICS devices—by far the largest category for the year. In fact, there were 23 percent more advisories published in this space than there were for desktop operating systems, the second largest category, and historical mainstay targeted by attackers.
This isn’t all that surprising in a field that’s growing this fast. But it’s worth considering how adding new assets into a network, as well as securely maintaining the OT network where assets reside, presents new challenges and naturally increases the attack surface.
So, if you’re using IIoT assets in your business, what sorts of threats do you need to look out for? And how do you protect your devices?
Getting in
The good news is that most IIoT assets aren’t directly exposed to the internet, meaning attackers must rely on other methods to get to them. In essence, the same techniques used in other attacks are used to get to IIoT assets.
The most common vector for compromise—email—certainly applies here. An attacker can attempt to gather information about engineers, plant managers, and developers that have access to IIoT systems and specifically target them with phishing emails. Compromising a computer owned by any of these users can be the most direct path to compromising IIoT assets.
Unpatched systems, simple or default device passwords, and relaxed remote access policies for maintenance contractors all offer attackers avenues of approach. Weaknesses in any of these can provide ways for an attacker to move laterally and gain access.
The reality is that IIoT-specific threats are not that common of an occurrence. There are threats that have attacked general IoT devices en mass, such as Mirai and VPNFilter. And there are threats like Stuxnet, which specifically targeted PLCs. Of course such highly targeted threats are cause for concern. But it’s far more likely that an IIoT device will be compromised and reconfigured by an attacker than be compromised by a trojan or a worm.
Scorching the earth
Let’s say an attacker sets their sights on bringing a particular business to its knees. He or she begins by crafting an enticing phishing email with a malicious PDF and sends it to HR in the guise of a job application. The employee responsible for monitoring job enquiries opens the PDF, effectively compromising the computer.
The attacker works his or her way laterally through the network, monitoring network traffic and scanning compromised systems, looking for logins and authentication tokens. Without multi-factor authentication enabled for access, they encounter few issues in doing so. The attacker eventually manages to compromise a domain controller, where they deploy malware using a Group Policy Object (GPO), successfully compromising the entire IT network.
Due to poor segmentation, the attacker manages to eventually work his or her way to the OT network. Once in, the attacker performs reconnaissance, flagging the IIoT assets present. The attacker identifies vulnerable services in the assets, exploits them, and knocks them offline.
Production grinds to a halt and the business is effectively shut down.
Defense with an arm behind your back
So how do you defend your IIoT assets and the OT network as a whole against attacks, especially for high-availability assets that can’t readily be brought down to patch?
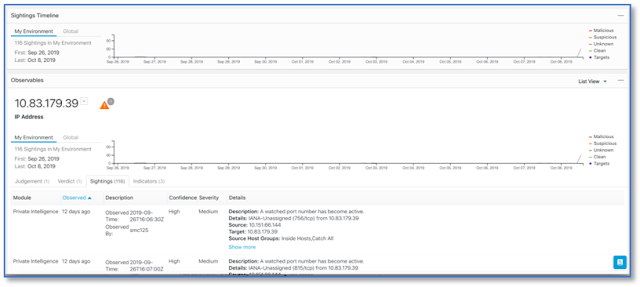
Network monitoring is often the most effective step you can take. However, it’s important to passively monitor the traffic when it comes to IIoT assets. Active monitoring, where traffic is generated and sent through the network specifically to observe its behavior, can result in an increased load on the network, causing disruptions to device performance and even causing them to fail. In contrast, passive scanning listens to the traffic, fingerprinting what it sees, rather than introducing new traffic into the OT environment.
Keeping a current inventory of assets on the network is also very important in protecting the IT and OT networks. Passive monitoring can help to identify assets on the network, including errant and rogue devices. With a comprehensive list of devices, you can create policies for asset groups.
It’s also very important to segment your networks. Having a complete asset inventory and policies in place will help when figuring out how to segment your IIoT assets and the OT network. While this may not prevent a determined attacker from crossing the boundaries between different areas of the network, it can slow them down, providing more time to respond in the case of an attack. Explore implementing zones and conduits
as discussed in ISA99 and IEC 62443 within your organization.
However, it’s worth noting that many IIoT assets leverage broadcast and multicast network communications, where one or more devices will send traffic to all other devices on the network. This can pose a challenge when aggressively segmenting a network. To address this, having a complete inventory of assets on the network is important. Strong dataflow mapping is also helpful when it comes to knowing which assets are talking to each other and how they interact as a whole.
Patching IIoT assets as soon as possible after a vulnerability is discovered is highly recommended. But if it isn’t possible to take a device offline to patch, then visibility becomes critical. It’s important to know what assets you have and the network layout to identify what absolutely must be patched. It may also be worth exploring IIoT redundancy within your network, allowing you to take one device down while others pick up the load during maintenance cycles.
Being able to detect IIoT traffic anomalies is also very helpful. Look for behavior that falls outside of what is expected, such as two IIoT assets talking to each other that shouldn’t be, unplanned firmware updates, unexpected configuration changes, or other anomalies.
Finally, threat hunting is a great way to look for and weed out threats within your OT environment. Proactively looking for bad actors doing bad things, building playbooks, and automating them will go a long way to improve your security posture.
Easing the burden
Protecting IIoT assets is arguably one of the more difficult tasks in security. There are a wide variety of devices, many of which operate in a very tailored manner and don’t respond well to disruption that could be caused by many security processes and procedures.
Fortunately, there are a number of Cisco Security products that can help.
◉ Cisco Cyber Vision gives OT teams and network managers full visibility into their industrial assets and application flows. Embedded in Cisco industrial network equipment, it decodes industrial protocols to map your OT network and detect process anomalies or unwanted asset modifications.
◉ Identity Services Engine leverages the asset inventory built by Cisco Cyber Vision to create dynamic security groups and automatically enforce segmentation using TrustSec.
◉ ISA3000 is a ruggedized industrial firewall appliance you can deploy in harsh environments to enforce zone segmentation, detect intrusions, and stop network threats.
◉ Stealthwatch is a security analytics solution that uses a combination of behavioral modeling, machine learning, and global threat intelligence to detect advanced threats. Integrated with Cisco Cyber Vision, this visibility extends deep within the IIoT infrastructure.
◉ AMP for Endpoints can be used to protect engineering workstations within the OT environment.
◉ Duo’s multi-factor authentication can be used to prevent an attacker from gaining access to systems on the network as a they attempt to move laterally.
◉ Cisco Email Security can detect targeted phishing emails aimed at IIoT operators and others, preventing malicious payloads from reaching their intended target.
Ultimately, a layered approach will provide the best security. For instance, Cisco Cyber Vision can automate visibility of industrial devices and secure operational processes. Integrated with Cisco’s security portfolio, it provides context for profiling of industrial devices in Stealthwatch, and maps communication patterns to define and enforce policy using granular segmentation via with ISE.