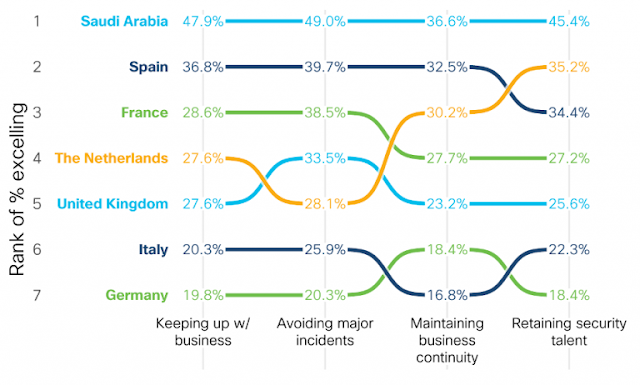
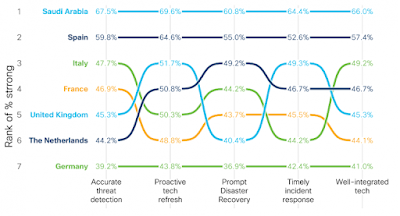
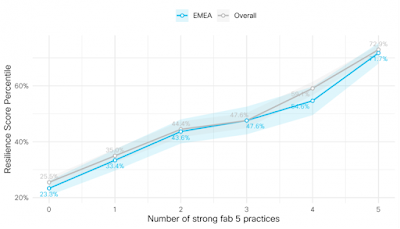
It’s a multicloud world!
Today applications are no longer restricted to the boundaries of a data center; applications are deployed everywhere – this change brings a need for a solution that can provide end-to-end visibility, control, policy management, and ease of management.
Market Trend
Organizations are embracing the power of the public cloud because it provides agile, resilient, and scalable infrastructure, enabling them to maximize business velocity. A recent study shows that 82% of IT leaders have adopted hybrid cloud solutions, combining private and public clouds. Additionally, 58% of these organizations are using between two and three public clouds1, indicating a growing trend towards multicloud environments. As organizations lean further into multicloud deployments, security teams find they are playing catch up, tirelessly attempting to build a security stack that can keep up with the agility and scale of their cloud infrastructure. Teams also face a lack of unified security controls across their environments. By definition, cloud service provider security solutions are not designed to achieve end-to-end visibility and control in the multicloud world, hardening silos and creating greater security gaps. Organizations need a cloud-agnostic solution that unifies security controls across all environments while securing workloads at cloud speed and scale.
Cisco Multicloud Defense is a highly scalable, on-demand “as-a-Service” solution that provides agile, scalable, and flexible security to your multicloud infrastructure. It unifies security controls across cloud environments, protects workloads from every direction, and drives operational efficiency by leveraging secure cloud networking.
Secure cloud networking can be broken down into three pillars:
- Security: Provides a full suite of security capabilities for workload protection
- Cloud: Integrates with cloud constructs, enabling auto-scale and agility
- Networking: Seamlessly and accurately inserts scalable security across clouds without manual intervention
One of the key benefits of Cisco Multicloud Defense is not only its ability to unify security controls across environments but enforce those policies dynamically. With dynamic multicloud policy management, you can:
- Keep policies up to date in near-real time as your environment changes.
- Connect continuous visibility and control to discover new cloud assets and changes, associate tag-based business context, and automatically apply the appropriate policy to ensure security compliance.
- Power and protect your cloud infrastructure with security that runs in the background via automation, getting out of the way of your cloud teams.
- Mitigate security gaps and ensure your organization stays secure and resilient.
Another key benefit of Multicloud Defense is how it adds enforcement points (PaaS) in both distributed and centralized architectures.
Cisco Multicloud Defense Overview
Cisco Multicloud Defense uses a common principle in public clouds and software-defined networking (SDN) which decouples the control and data plane, translating to the Multicloud Defense Controller and the Multicloud Defense Gateways.
The Multicloud Defense Gateway(s) are delivered as Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) in AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). These gateways are delivered, managed, and orchestrated by a SaaS-based Multicloud Defense Controller.
Figure 1: Cisco Multicloud Defense Overview
- Multicloud Defense Controller (Software-as-a-Service): The Multicloud Defense Controller is a highly reliable and scalable centralized controller (control plane) that automates, orchestrates, and secures multicloud infrastructure. It runs as a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and is fully managed by Cisco. Customers can access a web portal to utilize the Multicloud Defense Controller, or they may choose to use Terraform to instantiate security into the DevOps/DevSecOps processes.
- Multicloud Defense Gateway (Platform-as-a-Service): The Multicloud Defense Gateway is an auto-scaling fleet of security software with a patented flexible, single-pass pipelined architecture. These gateways are deployed as Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) into the customer’s public cloud account(s) by the Multicloud Defense Controller, providing advanced, inline security protections to defend against external attacks, block egress data exfiltration, and prevent the lateral movement of attacks.
Multicloud Defense Gateways
In the Cisco Multicloud Defense solution, organizations can use the controller to deploy highly scalable and resilient Egress Gateways or Ingress Gateways into their public cloud account(s).
Egress Gateway: Protect outbound and east-west traffic. The egress gateway provides security capabilities like FQDN filtering, URL filtering, data loss prevention (DLP), IPS/IDS, antivirus, forward proxy, and TLS decryption.
Ingress Gateway: Protects inbound traffic and provides security capabilities like web application firewall (WAF), IDS/IPS, Layer-7 protection, DoS protection, antivirus, reverse proxy, and TLS decryption.
Note: Multicloud Defense Gateways are an auto-scaling fleet of instances across two or more availability zones, providing agility, scalability, and resiliency.
Figure 2 shows security capabilities of the ingress and egress Multicloud Defense Gateway.

Figure 2: Cisco Multicloud Defense Gateway
The gateway uses a single pass architecture to provide:
- High throughput and low latency
- Reverse proxy, forward proxy, and forwarding mode
- Flexibility in selecting relevant advanced network security inspection engines, including TLS decryption and re-encryption, WAF (HTTPS and web sockets), IDS/IPS, antivirus/anti-malware, FQDN and URL filtering, DLP
Security Models
This solution provides a flexible way for security insertion in the customer’s infrastructure using three highly scalable and automated deployment models (centralized, distributed, and combined).
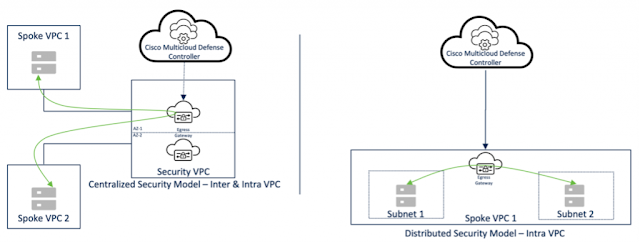
Centralized security model
In the centralized security model, the Multicloud Defense Controller seamlessly adds gateways in the centralized security VPC/VNet/VCN. In this architecture, ingress and egress traffic is sent to a centralized security VPC/VNet/VCN for inspection before it is sent to the destination. This architecture ensures scalability, resiliency, and agility using cloud deployment best practices.
Figure 3 shows egress and ingress gateways in a security VPC/VNet/VCN.
- For scalability, autoscaling is supported.
- For resiliency, auto-scaled instances are deployed in multi-availability zones.

Figure 3: Centralized Security Model
In a centralized security model, gateways are deployed in a hub inside the customer’s cloud account. However, customers can choose to have multiple hubs across accounts/subscriptions.
Distributed security model
In the distributed security model, the Multicloud Defense Controller seamlessly adds gateways in each VPC/VNet/VCN. In this architecture, ingress, and egress traffic stays local in the VPC/VNet/VCN.
Based on direction, traffic flow is inspected by egress or ingress gateways. This deployment ensures scalability, resiliency, and agility using cloud deployment best practices.
Figure 4 shows egress and ingress gateways in each VPC/VNet/VCN.
- For scalability, autoscaling is supported.
- For resiliency, auto-scaled instances are deployed in multi-availability zones.
Figure 4: Distributed Security Model
Combined security model (Centralized + Distributed)
This security model uses centralized and distributed models. In this case, some flows are protected by gateways deployed in the security VPC/VNet/VCN, and some flows are protected by gateways in the VPC/VNet/VCN.
Based on the traffic flow, traffic is inspected by egress or ingress gateways. This deployment ensures scalability, resiliency, and agility using cloud deployment best practices.
Figure 5 shows egress and ingress gateways in a centralized security VPC/VNet/VCN in addition to gateways deployed in the application VCPs/VNets/VCNs.
- For scalability, autoscaling is supported.
- For resiliency, auto-scaled instances are deployed in multi-availability zones.
Figure 5: Centralized + Distributed Security Model
Use-cases
Egress security
Figure 6 shows egress traffic protection in a centralized and distributed security model.
- In the centralized security model, traffic is inspected by gateways deployed in the security VPC/VNet/VCN.
- Gateways are auto-scale and multi-AZ aware.
- In the distributed security model, traffic is inspected by gateways deployed in the application VPC/VNet/VCN.
Figure 6: Egress traffic flow
Ingress security
Figure 7 shows ingress traffic protection in a centralized and distributed security model.
- In the centralized security model, traffic is inspected by gateways deployed in the security VPC/VNet/VCN.
- In the distributed security model, traffic is inspected by gateways deployed in the application VPC/VNet/VCN.
- Gateways are auto-scale and multi-AZ aware.
Figure 7: Ingress traffic flow
Segmentation (east-west)
Figure 8 shows intra and inter-VPC/VNet/VCN traffic protection in a centralized and distributed security model.
- In the centralized security model, intra and inter-VPC/VNet/VCN traffic is inspected by gateways deployed in the security VPC/VNet/VCN.
- In the distributed security model, intra-VPC/VNet/VCN traffic is inspected by gateways deployed in the application VPC/VNet/VCN.
- Gateways are auto-scale and multi-AZ aware.
Figure 8: Segmentation (East-West) traffic flow
URL & FQDN filtering for egress traffic
URL & FQDN filtering prevents exfiltration and attacks that use command-and-control. The Multicloud Defense Gateway enforces URL & FQDN-based filtering in a centralized or distributed deployment model.
- URL filtering requires TLS decryption on the gateway.
- FQDN-based filtering can be enforced on encrypted traffic flows.
Figure 8: URL & FQDN filtering for cloud egress
Coming soon: Multicloud Networking use cases
In our upcoming release (2HCY23), we are adding a set of Multicloud Cloud Networking use cases that enable secure connectivity — bringing all cloud networks together.
Multicloud Networking: Cloud-to-Cloud Networking
An egress gateway with VPN capability provides a secure connection to other cloud infrastructures. The egress gateway is delivered as-a-Service and provides resiliency and autoscaling. This architecture requires deploying the egress gateways with VPN capability “ON.” These gateways use IPsec connectivity for a secure interconnection.
Figure 9: Cloud-to-Cloud Networking (IPsec)
Multicloud Networking: Site-to-Cloud Networking
An egress gateway with VPN capability provides a secure connection to on-premises infrastructure. This architecture requires deploying the egress gateways with VPN capability “ON” in security VPC/VNet/VCN and a device at the data center edge for IPsec termination.
Figure 10: Site-to-Cloud Networking (IPsec)
Conclusion
It is a multicloud world we live in, and organizations need a cloud-agnostic solution that unifies security controls across all environments while securing workloads at cloud speed and scale. With Cisco Multicloud Defense, organizations can leverage a simplified and unified security experience helping them navigate their multicloud future with confidence.
Source: cisco.com