Sunday, 20 March 2022
Private 5G Delivered on Your Terms
Thursday, 21 October 2021
Secure and Simplify Your Programmable Edge and Industrial Sensors
The Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard provides operations teams with a centralized, cloud-based dashboard to securely deploy, monitor, and troubleshoot device connectivity. Using this secure connectivity as a foundation, that same dashboard then enables you to extract, transform, govern and deliver data from IoT edge devices to the cloud with Cisco Edge Intelligence, install and manage your containerized edge applications and to deploy a broad range of industrial IoT sensors with Cisco Industrial Asset Vision.
Create templates and test remote access with the Edge Device Manager Sandbox
Extract all your IoT sensor data via MQTT with Industrial Asset Vision
Simplify IoT Edge-to-Multi-Cloud Data Flow with Cisco Edge Intelligence
Thursday, 23 September 2021
Cisco teams up with Meshtech and launches Application Hosting for brand-new Asset Tracking IoT portfolio
Application Hosting on the Catalyst 9100 series access points allows organizations of all sizes to run IoT applications from the edge. As organizations integrate and deploy IoT services across their networks, the ability to optimize workflows, streamline IoT application changes, and simplify critical processes right out of the box, is essential. This includes having the ability to monitor IoT deployments end-to-end, as well as ongoing device and IoT network management. This is precisely why Cisco is developing integrations with vendors like Meshtech.
Cisco and Meshtech deliver seamless integration
Meshtech, based in Norway, develops IoT solutions that are used in smart buildings, healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and more. Its portfolio includes a suite of sensors, asset monitoring, and control systems that are used for environmental monitoring, asset tracking, and usage analytics.
Read More: 300-715: Implementing and Configuring Cisco Identity Services Engine (SISE)
With Cisco’s Application Hosting capabilities, Meshtech devices communicate directly with the Cisco Catalyst access point. Application Hosting doesn’t replace the Meshtech application but rather it eliminates the need for additional hardware while adding additional device management features.
IT teams retain the same visibility into key performance indicators across Meshtech sensors including humidity levels, movement, and temperature. With Application Hosting, they gain additional visibility and control on the Cisco platform. This includes the status of IoT devices, placement of sensors, as well as the ability to push application updates. Together, the integrated solution provides advanced visibility, control, and support across the application lifecycle.
How it works
Easy deployment and management
Thursday, 19 August 2021
Simply Faster than the Rest, Cisco Wi-Fi 6 + Multigigabit Switching
Wow, that’s exciting!
But would you be surprised?
The fact is, technology is advancing so fast that before we can adjust to the current innovation, a better version is already available. Just look at where we were with virtual reality, self-driving cars, and IoT smart homes only a few years back. The point is, our expectation for what is possible has never been higher, and as a technology fanatic, life is good!
But while we’re busy geeking out, let’s not forget that all this upcoming innovation requires an equally powerful network infrastructure to support it. For example, let’s look at 8K VR gaming, a technology that’s right around the corner and will require a minimum of 1 Gbps for gameplay and above 2 Gbps for an optimal experience. With a growing thirst for technology to provide a more HD, a more next-gen, and a more seamless experience, we can expect that the required data consumption will skyrocket as well.
The question is no longer whether innovation is coming but if your network can handle it.
Next Level Wireless Speeds with Multigigabit Switching
Wi-Fi 6, with all its glory, has been the star of the networking show since the launch of Cisco’s Catalyst wireless access point (AP) product line. From our flagship Catalyst 9130 Access Point boasting a ridiculous max PHY of 5.37 Gbps down to the small Catalyst 9105, they’re truly the gold standard of enterprise wireless.
But what if I told you there is a way to further enhance their already incredible prowess?
By simply combining Cisco Catalyst APs with Catalyst Multigigabit Switching, we can witness what can only be described as network performance at its finest. A bold statement, but I can prove it by showing you the throughput numbers tested within Cisco’s wireless lab using a Catalyst 9130 Wi-Fi 6 AP on software version 17.5.1 and a Catalyst 9300 multigigabit switch.
Numbers Speak for Themselves
But first, let’s take a step back; if we connect a Catalyst 9130 AP to a gigabit switch, the 5.38 Gbps max PHY is actually significantly bottlenecked as the throughput capabilities become limited from the wired side. With this topology, we achieved an average throughput of just below 1 Gbps using the IxChariot performance testing tool.
Tuesday, 10 November 2020
Experience the Future with Cisco and the Internet of Things
It’s the year 1950, and I’m asking you what you imagine technology would be in 70 years; what would you say? My guess is you proceed to list out some science-fiction-like answers such as the existence of space exploration programs, maybe artificial intelligent robots, or perhaps the invention of some all-knowing neural network that enlightens humankind through accessible information. While such ideas may have been on the cusp of science-fiction at the time, it’s incredible to realize that we are in the generation where many of these innovations not only exist but are customer-ready today!
Oh, and by the way, remember that “all-knowing neural network” you had mentioned? This is what we presently refer to as the internet and, of course, is what you are using to access this blog at this very moment. Despite how much of a technological breakthrough the internet was during its invention in 1983, it has become such an everyday tool, and it just doesn’t spark the same excitement as it once did.
Let me be that unwarranted catalyst and re-ignite that internet excitement by introducing a new generation of internet-powered technology. A generation of technology that can harness the limitless knowledge of the internet and engrain it into inanimate objects connecting us in a way never thought possible. I am referring to the Internet-of-Things (IoT), a technological innovation spearheaded by Cisco and its state-of-the-art Application Hosting on the Catalyst Access Points (AP) platform.
What is the Internet of Things?
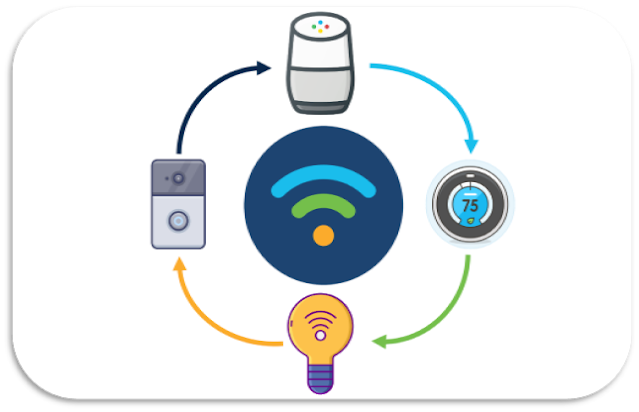
The Internet-of-Things is a concept where a wireless network is leveraged for communication with smart devices to accomplish tasks in a more simplified, efficient, and often automated manner. In fact, many IoT products probably have already found their way into your home already. These products come in all shapes and sizes, but some examples could be a voice-activated speaker such as an Amazon Alexa, a mobile application-controlled thermostat such as a Nest Thermostat, a motion-activated doorbell camera such as the August Doorbell Cam, or more excitingly, a voice triggered music playing salt dispenser such as the SMALT!
Other than the salt-dispenser (which actually exists), these are all products that, due to their simplicity and usefulness, have become seamlessly integrated into many of our lives.
Cisco’s Internet of Things Solution
What about the IoT Application itself?
The marketplace of IoT Technology
Monday, 24 August 2020
Simplify IoT Edge-to-Multi-Cloud Data Flow with Cisco Edge Intelligence
Connect assets at the edge to multi-cloud application destinations
Cisco recently made its brand new IoT data orchestration software – Edge Intelligence – publicly available. Edge Intelligence (EI) connects assets at the edge to multi-cloud application destinations securely, reliably and consistently.
The software integrates nicely with Cisco’s industrial networking and compute devices, which means that it already runs on some IOx capable devices (IR829, IR809, IC3000 and more to come very soon!). But today, you can get EI as a SaaS, where the user can manage assets, data policies, and data destinations via a centralized UI that enables remote deployment at scale.
How it works
Tuesday, 14 July 2020
Get Started with IoT and Prepare for DEVIOT Certification
Where do you even start with IoT?
Chances are if you have come this far reading this blog, you have made up your mind to embark upon the journey to equip your arsenal with more skills and knowledge regarding IoT.
You certainly own a smart device, don’t you? Great! Then you are already a part of the IoT world. How? If you are using Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, then you are already into IoT as these are some of the fundamental protocols that apply to IoT. There are many other protocols and standards which you should know about while deep-diving into the IoT world. Since IoT is adapted in so many different markets, each market or application has its own suitable IoT protocol that aligns to their requirements.
Consider the MQTT protocol. It has gained popularity in industries such as Supply Chain & Logistics, and Healthcare because of its lightweight properties and simplicity. Check out Cisco DevNet Intro to IoT Technologies – Protocols, Tools, and Software Module to learn about this protocol with a hands-on DevNet Learning Lab!
There are many resources you can find by visiting the DevNet IoT Dev Center to get you started with IoT. You’ll find introductory topics such as:
◉ how to develop applications using Cisco IOx
◉ getting started with Cisco Kinetics Gateway Management Module (GMM)
You can take advantage of these resources and more to get familiar with cutting edge Cisco IoT technologies.
Get prepared for an IoT professional certification
In the webinar, you’ll get an overview of the Cisco Certified DevNet Specialist, IoT Certification Exam. We’ll cover some ground on the topics the exam enlists, and what percentage of questions are to be expected from each module. We will also talk about some resources which will be useful to help you prepare for this certification exam.
See what my fellow Dev Advocate Jock Reed has to say about this certification, along with a short breakdown of the exam topics here.
There has never been a better time to get certified
Online, proctored exams are now delivered in most countries around the globe now. Thus, now is the ideal time to prepare for and earn your professional certification.
Please join me for the webinar on July 21st at 8:00 AM PDT. Register Now!
See you all there!
Friday, 3 July 2020
Three requirements to securely connect your industrial network
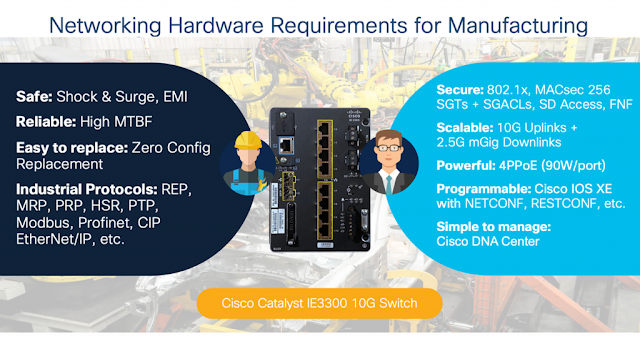
The first step is to converge to a single IP network. Network convergence is a proven formula for pulling together all the data in your environments. Cisco has been helping hundreds of thousands of organizations to converge their voice, video, data, and IoT networks to a single IP network. We’ve been doing this for over 30 years, and we know it works. A single network is easy to manage and operate and reduces your total cost of ownership. However, the primary challenge with a converged network is that it needs to be secure. There are three elements you need to securely connect an industrial network: 1) purpose-built hardware, 2) digitally signed and authentic security software, and 3) extensible architectures.
1. Choosing the right hardware
Start with the right hardware. For industrial internet of things (IIoT), the network hardware must satisfy the requirements of both the operational technology (OT) department and the IT department. At a high level, OT runs point on operations and understands how the organization produces its goods or services. IT connects the network and wants to make sure it’s done securely. OT and IT each have different priorities, goals, and concerns, yet the hardware has to meet both sets of requirements.
2. Selecting the right software
3. Architectural integrations
How Cisco can help
Tuesday, 16 June 2020
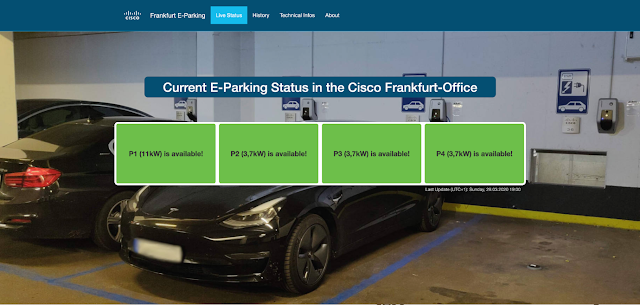
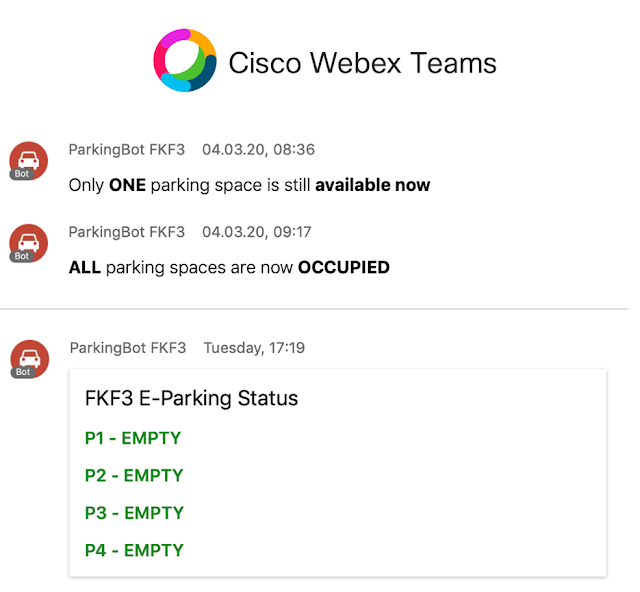
Smart Parking: A Cisco IoT Solution with LoRaWAN
Do you know the feeling? When you’re in a large parking garage and looking for an empty parking space? You are circling around with your car. Perhaps you’re late! You know there’s an empty spot somewhere. But where?!
There’s a Cisco IoT solution for that
Well, there is a Cisco IoT solution for that which we implemented for our e-parking spaces in our Cisco office in Frankfurt, Germany. There, we have 4 parking spaces where you can charge your e-car. That’s good, but 4 spaces are too few to meet demand, and can be occupied quite fast. To solve the problem we implemented a solution using LoRaWAN parking sensors. The solution helps our visitors and employees with the following:
Website
The website is where the user can check live data on what parking spaces are empty and occupied.
Thursday, 11 June 2020
Why 5G is Changing our Approach to Security
5G technology will introduce advances throughout network architecture such as decomposition of RAN, utilizing API, container-based 5G cloud-native functions, network slicing to name a few. These technological advancements while allowing new capabilities, also expand the threat surface, opening the door to adversaries trying to infiltrate the network. Apart from the expanded threat surface, 5G also presents the security team with an issue of a steep learning curve to identify and mitigate threats faster without impacting the latency or user experience.
What are Some of the Threats?
Virtualization and cloud-native architecture deployment for 5G is one of the key concerns for service providers. Although virtualization has been around for a while, a container-based deployment model consisting of 5G Cloud Native Functions (CNFs) is a fresh approach for service providers. Apart from the known vulnerabilities in the open-source components used to develop the 5G CNFs, most CNF threats are actually unknown, which is riskier. The deployment model of CNFs in the public and private cloud brings in another known, yet the widespread problem of inconsistent and improper access control permissions putting sensitive information at risk.
5G brings in network decomposition, disaggregation into software and hardware, and infrastructure convergence which underpins the emergence of edge computing network infrastructure or MEC (Multi-Access Edge Compute). 5G Edge computing use cases are driven by the need to optimize infrastructure through offloading, better radio, and more bandwidth to fixed and mobile subscribers. The need for low latency use cases such as Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) which is one of several different types of use cases supported by 5G NR, requires user plane distribution. Certain 5G specific applications and the user plane need to be deployed in the enterprise network for enterprise-level 5G services. The key threats in MEC deployments are fake/rogue MEC deployments, API-based attacks, insufficient segmentation, and improper access controls on MEC deployed in enterprise premises.
5G technology will also usher in new connected experiences for users with the help of massive IoT devices and partnerships with third-party companies to allow services and experiences to be delivered seamlessly. For example, in the auto industry, 5G combined with Machine Learning-driven algorithms will provide information on traffic, accidents and process peer to peer traffic between pedestrian traffic lights and vehicles in use cases such as Vehicle to Everything (V2X). Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) in these use cases are a very critical part of the 5G threat surface.
What are Some of the Solutions to Mitigate Threats?
Critical infrastructure protection: Ensure your critical software, technologies, and network components such as Home Subscriber Server (HSS), Home Location Register (HLR), and User Defined Routing (UDR) are secured with the right controls.
Cisco Secure Development Lifecycle: Being cloud-native and completely software-driven, 5G uses open source technologies. Although this is critical for scalability and allowing cloud deployment integrations, vulnerabilities from multiple open-source applications could be exploited by attackers. To reduce the attack surface, service providers need to verify the 5G vendor-specific secure development process to ensure hardened software and hardware. We offer security built into our architectural components. Our trustworthy systems’ technology includes trust anchor, secure boot, entropy, immutable identity, image signing, common cryptography, secure storage, and run-time integrity.
Vendor Assessment (security): It’s critical to validate the vendor supply chain security, secure your organization’s development practices from end to end, and employ trustworthy products. You must also be vigilant when it comes to continuously monitor hardware, software, and operational integrity to detect and mitigate infrastructure and service tampering. Sophisticated actors are looking to silently gain access and compromise specific behavior in the network. These attackers seek to take control of network assets to affect traffic flows or to enable surveillance by rerouting or mirroring traffic to remote receivers. Once they have control, they might launch “man-in-the-middle” attacks to compromise critical services like Domain Name System (DNS) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificate issuance.
Secure MEC & Backhaul: 5G edge deployments will supply virtualized, on-demand resource, an infrastructure that connects servers to mobile devices, to the internet, to the other edge resources and operational control system for management & orchestration. These deployments should have the right security mechanisms in the backhaul to prevent rogue deployments and right security controls to prevent malicious code deployments and unauthorized access. As these MEC deployments will include the dynamic virtualized environments, securing these workloads will be critical. Cisco workload protection, will help service providers to secure the workloads. Cisco’s Converged 5G xHaul Transport will provide the service providers with the right level of features for secure 5G transport.
Cisco Ultra Cloud Core allows the user plane to support a full complement of inline services. These include Application Detection and Control (ADC), Network Address Translation (NAT), Enhanced Charging Service (ECS), and firewalls. Securing the MEC would require multiple layers of security controls based on the use case and the deployment mode. Some of the key security controls are:
• Cisco Security Gateway provides security gateway features along with inspections on GTP, SCTP, Diameter, and M3UA.
• Secure MEC applications: Securing virtualized deployments on the MEC and centralized 5GC requires a smarter security control rather than just having firewalls, be it hardware or virtualized. Cisco Tetration provides multi-layered cloud workload protection using advanced security analytics and speedy detections.
• Secure MEC access: Securing user access to MEC can be catered by utilizing the Zero Trust methodology, which is explained in greater detail below.
Utilizing zero trust security controls during 5G deployment is critical for service providers. This is particularly important in the deployment phase where there will be multiple employees, vendors, contractors, and sub-contractors deploying and configuring various components and devices within the network. The old method of just providing a VPN as a security control is insufficient, as the device used by the configuration engineer might have an existing malicious code that might be deployed within the 5G infrastructure. This whitepaper gives you more insights on how zero trust security could be applied to 5G deployments.
End to End Visibility: 5G brings in distributed deployments, dynamic workloads, and encrypted interfaces like never before. This requires end-to-end visibility to ensure proper security posture. Advanced threat detection and encryption methods can identify malware in encrypted traffic without requiring decryption. And because latency is very important in 5G, we can’t use traditional methods of distributed certificates, decrypting traffic, analyzing the data for threats, and then encapsulating it again, as this adds too much latency into the network. Cisco Stealthwatch is the only solution that detects threats across the private network, public cloud, and even in encrypted traffic, without the need for decryption.
Tuesday, 5 May 2020
Cisco’s AI/ML can make your Wi-Fi 6 upgrade a success
Wi-Fi 6 has some new features that are useful in resolving what used to be unsurmountable problem areas in a wireless network. The first step is to understand these new Wi-Fi 6 features and the wireless challenges that they resolve.
As you are sitting at home reading this, you could be analyzing your campus wireless network for areas where Wi-Fi 6 can add the most bang for your buck. Wi-Fi 6 has some new features that are useful in resolving what used to be unsurmountable problem areas in a wireless network. Your Cisco DNA Center Assurance dashboard has AI/ML features that can allow you to find these areas!
The first step is to understand these new Wi-Fi 6 features and the wireless challenges that they resolve:
Poor performance in highly congested areas: OFDMA in Wi-Fi 6, allows multiple clients to transmit simultaneously in order to increase capacity in highly congested areas.
Poor uplink performance on mobile devices: Uplink sub-channelization in Wi-Fi 6 provides mobile devices greater radio transmit power without consuming more battery power. This provides mobile devices better Wi-Fi performance in challenging conditions.
High radio interference: The Wi-Fi 6 OFDMA uplink map creates a synchronization that leads to less interference in between clients and in between access points. Additionally, OFDMA allows clients to transmit on small channels at greater power making them much less susceptible to interference from other wireless devices.
The IoT small packet problem: IT teams with large concentration of IoT devices (manufacturing, process control, video surveillance, etc.) are very familiar with the packet processing bottleneck that access points can become. Modern Wi-Fi 6 chipsets solve this with powerful quad-core 2.2GHz processors that can process three times more packets than most 802.11ac access points and twelve times as much as most 802.11n access points. This processing power, combined with a well-designed access point data-forwarding mechanism, has the potential to eliminate most of the issues you used to have supporting IoT devices.
Now let’s look at how you can use the AI/ML in Cisco DNA Center to quickly locate areas in your campus network that fit these challenging conditions.
Congested areas
Areas where mobile devices struggle
Areas of high interference
Interference is a difficult problem to diagnose in wireless networks because the symptoms of interference can vary. Users can experience long onboarding times, slow app performance, and difficulty connecting to the cloud. The good news is that the AI Network Analytics feature in Cisco DNA Center will automatically identify interference and alert you on the “Top 10 Issues” window, right on the front page of the dashboard.
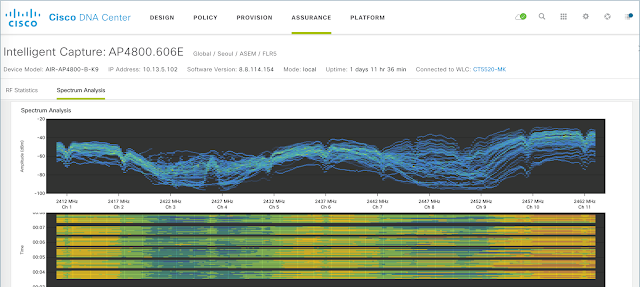
So, if you have seen these alerts on your home screen, it would be a good idea to see if Wi-Fi 6 can help mitigate this interference. If you go to the AI/ML “Trends and Insights” menu you can sort access points based on levels of interference. This can give you a list of your worst offenders. Click on one of the access points and look for the “Intelligent Capture” tool at the top of the window. This tool uses your network access points to perform complex packet, frame, and spectrum analyses.
Inside of the Intelligent Capture window, click on spectrum analysis and watch as the software begins to monitor the wireless traffic for interference severity and duty cycle. The waves show you the channels where the interference is located and how this is affecting the duty cycle of that particular access point. This is a very comprehensive test that will scan all of the available wireless channels with traffic from your actual network at that location.
Intelligent Capture lets you drill down on this and identify the percentage of channel utilization for this access point, other access points, and even non-Wi-Fi interference. The image to the right is a screen capture from the output of a spectrum analysis at 2.4 GHz (I cut the screen to be able to enlarge the image). Channels 1 and 2 have high levels of interference but channels 3 and 4 do not. If you find that interference is limited to one or two of the Wi-Fi channels, you can configure your access point to operate outside of these channels. However, if the interference is running across all channels you have a great candidate for a Wi-Fi 6 upgrade. The OFDMA synchronization in Wi-Fi 6 will greatly minimize any self-interference (interference between your own network devices and access points), and your Wi-Fi 6 clients will be able to transmit on a more narrow, more powerful radio channel giving them added robustness against internal or external interference.
A mere 20 Mbps of M2M data can take almost half of your access point’s capacity!
The IoT small packet problem
IT teams that operate networks for manufacturing, process control, mining, and digital cities are quite familiar with the IoT small packet problem. It has long been a thorn in the side of Wi-Fi networks used for machine-to-machine (M2M) connectivity and video surveillance. The issue is that these types of communication use small payloads of data in high frequency. Most forms of M2M encapsulate their data in 64-Byte UDP packets, while most normal IP file transfers use larger 1,500-Byte packets. A Wi-Fi access point is limited in the number of packets per second (PPS) that the imbedded chipset can process. Imagine a Wi-Fi chipset capable of processing 30,000 PPS. For normal 1,500-Byte data packets, this device is capable of transferring 360 Mbps (30,000*1500*8). But, for 64-Byte packets the maximum throughput drops to only 45 Mbps. More importantly, 20 Mbps of M2M data can take almost half of my access point’s capacity!