Wireless connections are ubiquitous and have become a part of our daily lives. But planning and then maintaining a Wi-Fi network, optimized for today’s radio coverage and capacity requirements, may not be a daily or even yearly task for an otherwise seasoned network administrator.
While wireless technologies are ubiquitous, they still interact with the physical environment. Architecting the best coverage for a specific environment depends on many different factors like obstacles (walls, doors, windows), building geometry and materials as well as the number of users and intended usage. Looking across verticals demonstrates a wide range in complexity that can be encountered within different environments. For example, covering a moderate sized Enterprise Office space could be as simple as correctly placing some APs with omni-directional antennas, while covering a high ceiling warehouse means directional antennas to cover the space and more engineering to get it right. The challenge is that RF, unless visualized somehow, is invisible. Seeing the RF in enough context to determine the correct angles, power, coverage, and capacity needs requires good tools.
Our new solution
Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer changes the overall planning and maintenance experience for network operators. It provides a visual 3D immersive experience that simplifies many of the aspects of the processes mentioned above. At the same time its deep analysis ensures insights into the key success factors required.
Typical workflow for a new site looks like this:
◉ Planning, laying out the deployment at scale and analyzing the proper placement.
◉ Deployment of the equipment and on-boarding the site.
◉ Coverage validation, ensuring that the coverage meets the designed requirements.
◉ Tuning of the network configurations to optimize the coverage and capacity.
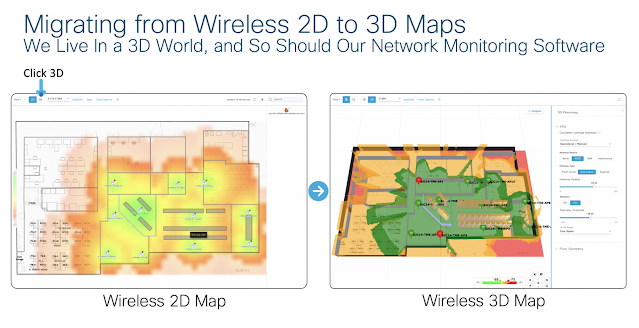
Adding the floor map to the management server to monitor static 2D heat maps.
Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer allows the user to perform these planning and deployment operations remotely on their laptop well before ever placing products on the floor space. Post deployment, the Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer correlates the existing telemetry data along with the predictive results to provide a unified view of everything needed to dynamically monitor the complex interactions occurring daily on the network. This drastically reduces the OPEX needed for the same operations, while providing a simplified and intuitive user experience.
Solution building blocks
Here are the main components of the solution
Figure 1 – 3D Analyzer Solution Building Blocks
Cisco Wireless Network is the overall network infrastructure consisting of APs, sensors, switches, wireless controllers, Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) and other network resources. It is needed to provide the edge services for the client devices.
Cisco DNA Center is the single point in the system that provides Day 0 with automation of provisioning and on-boarding tasks to life cycle monitoring/management and analysis. It also imports floor maps of the customer buildings.
Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer is a web-app that runs on the network administrator’s browser. Moreover, it connects to Cisco DNA Center through https. The system uses state of the art 3D visualization and General-Purpose GPU technologies to build predictive models of the floorspace’s wireless environment. It allows the user to have 3D visual representations of the network coverage, its capacity, and many related insights on the same.
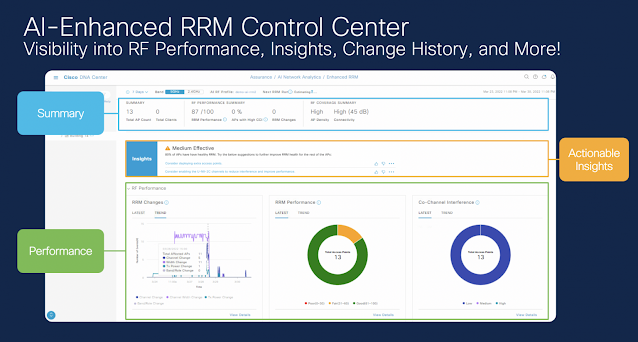
Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer brings the wealth of wireless telemetry data already available in Cisco DNA Center and combines this with the powerful context that the interactive 3D model can provide. The analyzer not only allows the user to see all this information in context, but also allows the powerful analysis engine to combine thousands of data points and provide actionable conclusions. The system minimizes the manual tuning, requiring a site visit, to optimize the network. The systems, using over-the-air measurements, allows verification of proper operations or gives clear indications on what will require some tuning, not just on Day 0, but for the life cycle of the deployment to Day n.
How does it work?
The Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer provides both Life Cycle Management and Planning within an immersive 3D operational experience.
Planning
Given a CAD or Ekahau Project file, that contains data regarding walls and materials, the app generates a 3D model of the environment and uses predictive modeling to display the RF coverage from the floor to the ceiling. Input for the model relies on telemetry available to accurately describe the current power, channels, and even antenna coordinates dynamically to render the environment. The powerful analysis engine looks at the millions of interactions between the access points, client devices, sensor APs, and the described physical environment across the 3D floor area. The 3D Analyzer can dynamically identify and isolate for view any service level issues discovered.
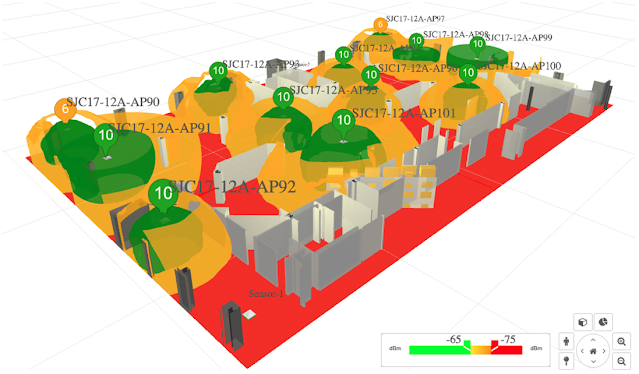
Figure 2 – Planning Prediction (iso-surfaces view)
Maintenance
Unlike a traditional static 2D heat map, the Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer also correlates real time data from the network. This is possible through the Cisco DNA Center telemetry and the Catalyst stack architecture, sensors, and assurance data. It allows correlation of the predictive results with the actual measured ground truth in the 3D floor map. This not only provides visual assurance of the accuracy, but a dynamic way to alert to harmful changes in the physical world. The 3D environment is augmented with the access points’ runtime health score as well as other critical data at multiple levels within the “virtual reality”. See the health scores below inside the colored tear drops.
Figure 3 – Prediction and Measurement (point cloud view)
Also please note that available sensor measurements are also integrated into the overall big picture of your network. Sensors are shown above in the circles labeled S.
The below chart illustrates the main data flows driving the 3D Analyzer’s view of the physical world. It’s a lot of correlation, and an unprecedented view of the network’s context.

The Cisco Catalyst network provides live data to Cisco DNA Center, which is drawn on by Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer. Using the floor maps, actual inventory HW models and current configurations, the app can generate the predictions and their correlation with the live data, providing a full 3D context rich visualization environment.
Key use cases
Here are a few use cases that Cisco believes brings new efficiencies and accuracy to your view of the network.
Visual insights
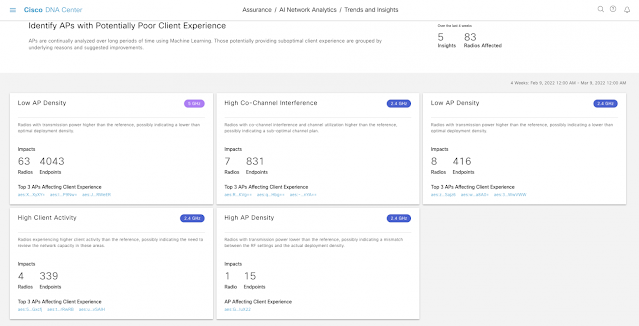
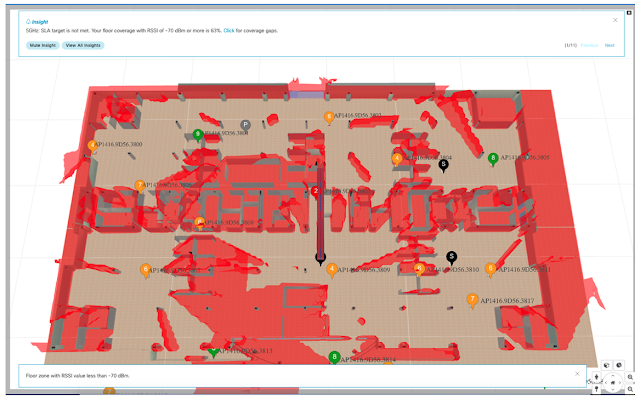
The Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer correlates the predicted data along with telemetry inputs, analyzes the results, and provides insights into the networks behavior. In the example below, the system detected that 67% of the floor’s RSSI coverage falls below the user-configured KPI (Key Performance Indicator) of -70dBm. With a single mouse click on the Insight, the environment is configured instantly to highlight the exact location of deficiency, instantly providing a clear and actionable view.
Figure 4 – Visual Insights
Detection of Channel Interference
On a wireless network, interference is the opposite of performance. By changing the view to “interference” the visualization now highlights areas where the network interferes with itself. In addition, the APs and Channel selections responsible are highlighted clearly to quickly provide context and identify the source.
The 3D analyzer not only detects and alerts to these issues, but it also allows the administrators to safely model solutions in real time without making changes to the configurations in the physical world.
Figure 5 – Co-Channel Interference Detection
The system can detect multiple types of interferences (co-channel, adjacent-channel, neighbor), together with interferences coming from other floors. Here is a multi-floor 3D representation of coverage that could create interference.
Figure 6 – Multi-floor coverage 3D visualization
High Ceiling Environment Analysis
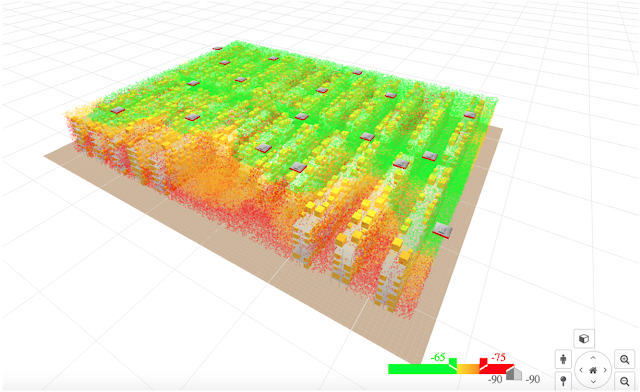
High ceiling environments, such as a warehouse, constitute challenging use cases, often mis-treated in design practice. Increasingly, it is not enough to only provide good coverage at the floor level. With automation and operations taking users to all levels within the physical environment, it has become increasingly important to understand the effectiveness of coverage from the floor to the ceiling. A 2D map can show the RF at an assumed user level but visualizing the coverage at every level in between can become a chore. The 3D visualization not only displays this but will allow the visualization to show as a scan with 6-inch resolution in elevation slices. The resulting visualization allows the user to visualize different configurations and effective solutions based on the modeled environments data in terms of shelves, racks, boxes, and capacity levels.
Figure 7 – Warehouse view
The coverage predictions consider all these obstacles, together with the actual antenna data to provide holistic floor views. Optimal efficiency is not an accident, it is planned. Through the lifecycle of the network, plans can and do change. The 3D analyzer can help watch it for you.
Figure 8 – Warehouse point cloud view
Figure 9 – Automatic Elevation Scanner
The picture above shows an elevation scanning playback. It allows users to get insights about coverage at each elevation from floor to ceiling.
First Person View
Invoking the first-person view allows the administrator to step into the modeled environment and view it from the user plane. The constant telemetry readouts while moving through the environment and mousing over the deployed assets all lead to an unprecedented ability to understand the physical environment. All this without even getting in the car.
Figure 10 – First Person View
Antenna Propagation
Challenging high ceilings, or high-density environments often require specific antennas to achieve desired results. It can be difficult for many people to visualize how a particular antenna type will fit into the coverage environment. With the Cisco Wireless 3D Analyzer this becomes easy. The administrator can visualize the coverage patterns at all RSSI values and see how an angle could be optimized. Moreover, the administrator can check how a different antenna can provide the optimal solution to the challenge.
Figure 11 – Antenna propagation view
Being able to visualize changes to existing or new solutions within a known environment not only allows for quick assessments for fluid change management, but also provides a safe environment to build confidence and skills in the management staff. Wireless is much more fun when you can see it. By the way, you get all of this “before” ever setting a foot on the site.
Source: cisco.com