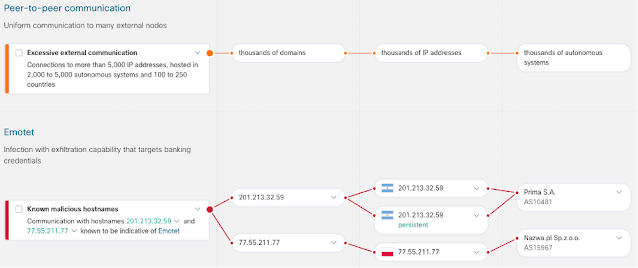
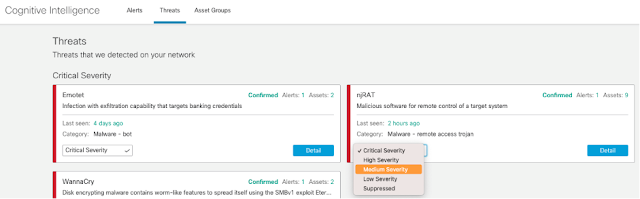
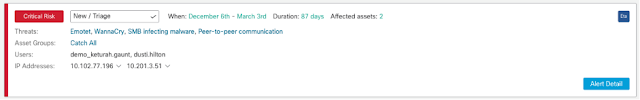
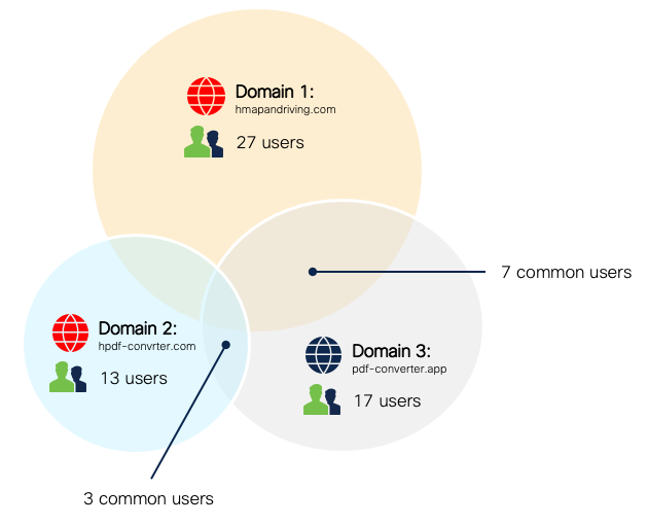
Complexity is one of the top challenges our customers face today. CISOs not only want to enable their teams to detect and respond to threats faster, they want to simplify workflows and streamline operations at the same time. In our annual CISO surveys, we’ve been seeing a trend toward vendor consolidation, which tells us CISOs are looking for ways to make their solutions simpler.
Vendors typically work in siloes to solve these kinds of challenges. But at Cisco, we believe we can achieve more through collaboration. That’s why we’ve been working in partnership with IBM Security to provide joint customers an in-depth, end-to-end defense strategy while simplifying their vendor relationships.
The average organization juggles 45 different security vendors. Leveraging the breadth of Cisco and IBM’s security portfolios allows our customers to drastically reduce that number of vendors while still using best-in-class products. The reduction in vendor surface creates more than just technical efficiencies. By consolidating vendor relationships, customers can maximize their buying power through vehicles like Enterprise Agreements, as well as simplify contract management and support cases.
Leveraging Cisco and IBM strengths
At Cisco, we believe we have excellent technologies to help customers prevent threats to their businesses, and with products like Cisco Threat Response, we even speed up various elements of the technical response. With IBM, we have focused our initial integrations on QRadar and Resilient product lines to help customers further prioritize threats and better assist with their response both at a technical and business level.
Let’s say you had an insider attack. The Cisco/IBM integrated solutions enable faster investigations of suspicious behaviors that could compromise credentials or systems. For example:
◉ Cisco Stealthwatch looks for behavioral indicators of compromise in activity traversing the network, including encrypted traffic without the need to decrypt the data. IBM QRadar builds on that detection, as well as other Cisco solutions like Firepower Threat Defense, to correlate events from network traffic and logs to help security teams quickly prioritize threats.
◉ Cisco Identity Services Engine helps you associate malicious activity with specific user credentials, and you can quarantine the user and lock down network access right from QRadar.
Responding to the attack is not just about gathering the information. You also need to understand how the business responds to the threat — is this something that needs public release of information, do you need to involve law enforcement, will this result in employee termination, and so on. To help operationalize incident response, you can use investigation results from all the integrated solutions to create a report in Resilient.
Innovative solutions to address customer needs
Many of the Cisco/IBM collaborative solutions are unique for the industry, and they’re based on lessons Cisco and IBM have learned from our extensive customer bases and our threat intelligence teams, Cisco Talos and IBM X-Force.
To make breach response more efficient, earlier this year we integrated Cisco Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) for Endpoints with QRadar and IBM Resilient SOAR. These integrations enable security teams to do things like:
◉ Receive AMP for Endpoints telemetry directly in QRadar for a consolidated view of events across endpoints and ability to search, analyze, and correlate them.
◉ Pull AMP for Endpoints data into Resilient to investigate events, automatically bring the results into an incident, and get more details on detected threats, then quarantine detected malicious files.
Since threats evolve quickly, defenses can’t rely on one mechanism alone. We work together in various other ways to help you detect unknown threats like ransomware or speed up response time. For instance:
◉ Resilient customers can submit suspicious malware samples to Cisco Threat Grid to get detonated, with the hashes sent back to Resilient. This can stop malware or ransomware before it ever reaches the end user.
◉ IBM Resilient users can query Cisco Umbrella for a list of blocked domains, save them to a data table, and delete or add new ones — preventing end users from accessing risky internet connections.
We’re listening to your feedback
Because we’re invested in the results that this collaboration can produce for our customers, we’re continuously expanding and improving our integrated solutions based on your feedback. The latest examples are enhancements made to the Firepower Threat Defense and QRadar SIEM integration, which accelerate threat investigation and remediation by correlating events across network, applications, and users.
Our customers wanted to dig deeper than the top-level summaries previously available. We listened — and the new, enhanced Firepower app that we’re releasing provides a higher level of detail in the integrated dashboard.
With Firepower Threat Defense and QRadar, you can answer questions like:
◉ Which hosts in my network are potentially compromised?
◉ Which hosts are known to be compromised?
◉ What malware is most often observed in my network?
◉ Which hosts have sent the most malware?
This is just one of the new enhancements and expansions we’ve been making as part of our alliance, and more are on the roadmap. By reducing complexities, increasing visibility, and improving threat defenses, our collaboration is improving outcomes in areas that are top of mind for our customers.