Security is critical when transmitting information over any untrusted medium, particularly with the internet. Cryptography is typically used to protect information over a public channel between two entities. However, there is an imminent threat to existing cryptography with the advent of quantum computers. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), “When quantum computers are a reality, our current public key cryptography won’t work anymore… So, we need to start designing now what those replacements will be.”
Quantum computing threat
A quantum computer works with qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously, based on the quantum mechanical principle of superposition. Thus, a quantum computer could explore many possible permutations and combinations for a computational task, simultaneously and swiftly, transcending the limits of classical computing.
While a sufficiently large and commercially feasible quantum computer has yet to be built, there have been massive investments in quantum computing from many corporations, governments, and universities. Quantum computers will empower compelling innovations in areas such as AI/ML and financial and climate modeling. Quantum computers, however, will also give bad actors the ability to break current cryptography.
Public-key cryptography is ubiquitous in modern information security applications such as IPsec, MACsec, and digital signatures. The current public-key cryptography algorithms are based on mathematical problems, such as the factorization of large numbers, which are daunting for classical computers to solve. Shor’s algorithm provides a way for quantum computers to solve these mathematical problems much faster than classical computers. Once a sufficiently large quantum computer is built, existing public-key cryptography (such as RSA, Diffie-Hellman, ECC, and others) will no longer be secure, which will render most current uses of cryptography vulnerable to attacks.
Store now, break later
Why worry now? Most of the transport security protocols like IPsec and MACsec use public-key cryptography during the authentication/key establishment phase to derive the session key. This shared session key is then used for symmetric encryption and decryption of the actual traffic.
Bad actors can use the “harvest now, decrypt later” approach to capture encrypted data right now and decrypt it later, when a capable quantum computer materializes. It is an unacceptable risk to leave sensitive encrypted data susceptible to impending quantum threats. In particular, if there is a need to maintain forward secrecy of the communication beyond a decade, we must act now to make these transport security protocols quantum-safe.
The long-term solution is to adopt post-quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms to replace the current algorithms that are susceptible to quantum computers. NIST has identified some candidate algorithms for standardization. Once the algorithms are finalized, they must be implemented by the vendors to start the migration. While actively working to provide PQC-based solutions, Cisco already has quantum-safe cryptography solutions that can be deployed now to safeguard the transport security protocols.
Cisco’s solution
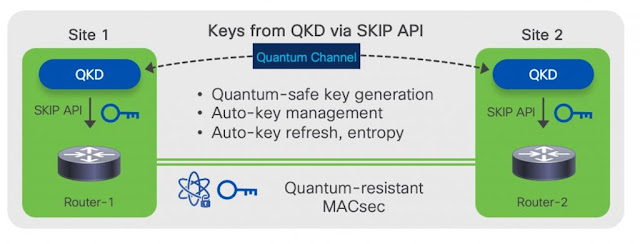
Cisco has introduced the Cisco session key import protocol (SKIP), which enables a Cisco router to securely import a post-quantum pre-shared key (PPK) from an external key source such as a quantum key distribution (QKD) device or other source of key material.
Figure 1. External QKD as key source using Cisco SKIP
For deployments that can use an external hardware-based key source, SKIP can be used to derive the session keys on both the routers establishing the MACsec connection (see Figure 1).
With this solution, Cisco offers many benefits to customers, including:
- Secure, lightweight protocol that is part of the network operating system (NOS) and does not require customers to run any additional applications
- Support for “bring your own key” (BYOK) model, enabling customers to integrate their key sources with Cisco routers
- The channel between the router and key source used by SKIP is also quantum-safe, as it uses TLS 1.2 with DHE-PSK cipher suite
- Validated with several key-provider partners and end customers
Figure 2. Cisco SKS engine as the key source
In addition to SKIP, Cisco has introduced the session key device (SKS), which is a unique solution that enables routers to derive session keys without having to use an external key source.
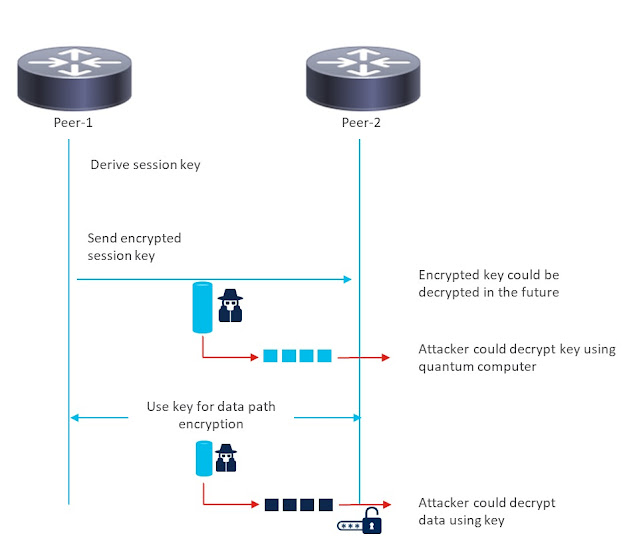
Figure 3. Traditional session key distribution
The SKS engine is part of the Cisco IOS XR operating system (see Figure 2). Routers establishing a secure connection like MACsec will derive the session keys directly from their respective SKS engines. The engines are seeded with a one-time, out-of-band operation to make sure they derive the same session keys.
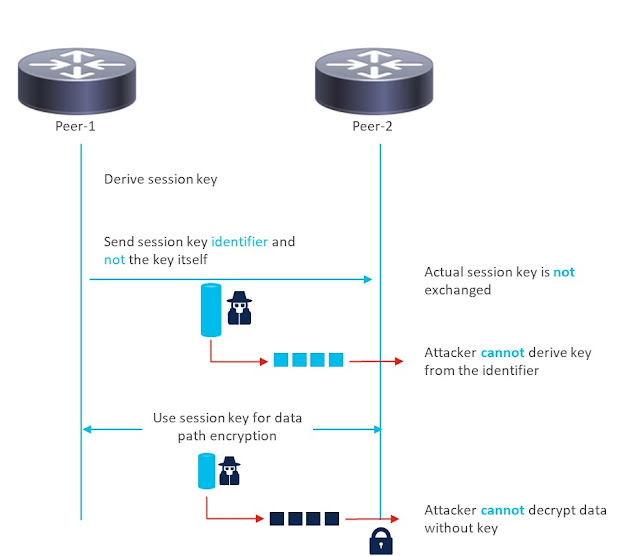
Unlike the traditional method (see Figure 3), where the session keys are exchanged on the wire, only the key identifiers are sent on the wire with quantum key distribution. So, any attacker tapping the links will not be able to derive the session keys, as having just the key identifier is not sufficient (see Figure 4).
Figure 4. Quantum session key distribution
Cisco is leading the way with comprehensive and innovative quantum-safe cryptography solutions that are ready to deploy today.
Source: cisco.com