More and more customers are deploying workloads and applications in Amazon Web Service (AWS). AWS provides a flexible, reliable, secure, easy to use, scalable and high-performance environment for workloads and applications.
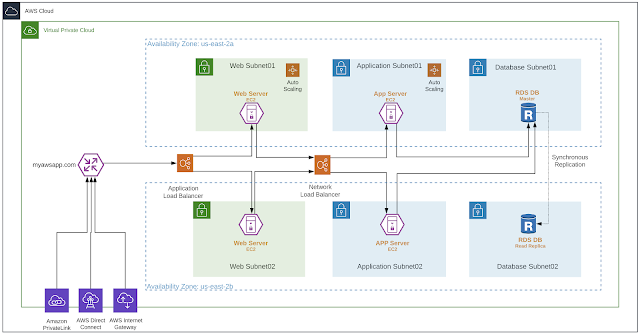
AWS recommends three-tier architecture for web applications. These tiers are separated to perform various functions independently. Multilayer architecture for web applications has a presentation layer (web tier), an application layer (app tier), and a database layer (database tier). There is the flexibility to make changes to each tier independent of another tier. The application requires scalability and availability; the three-tier architecture makes scalability and availability for each tier independent.
AWS recommends three-tier architecture for web applications. These tiers are separated to perform various functions independently. Multilayer architecture for web applications has a presentation layer (web tier), an application layer (app tier), and a database layer (database tier). There is the flexibility to make changes to each tier independent of another tier. The application requires scalability and availability; the three-tier architecture makes scalability and availability for each tier independent.
Figure 1: AWS three-tier architecture
AWS has a shared security model i.e., the customers are still responsible for protecting workloads, applications, and data. The above three-tiered architecture offers scalable and highly available design. Each tier can scale-in or scale-out independently, but Cisco recommends using proper security controls for visibility, segmentation, and threat protection.
Figure 2: Key pillars of a successful security architecture
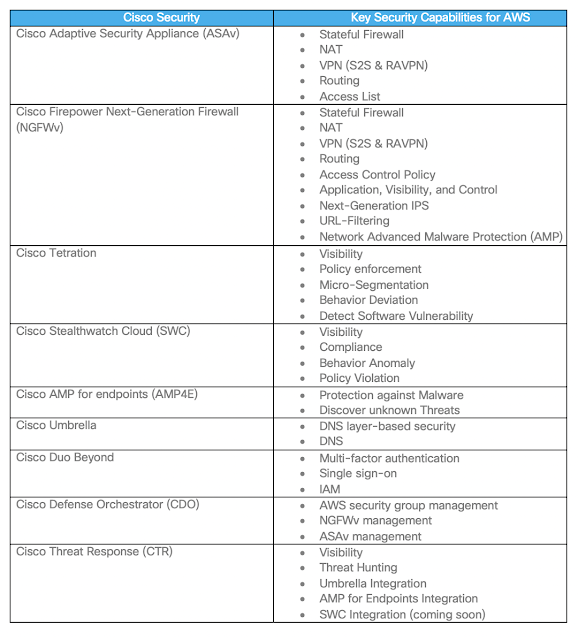
Cisco recommends protecting workload and application in AWS using a Cisco Validated Design (CVD) shown in Figure 3. All the components mentioned in this design have been verified and tested in the AWS cloud. This design brings together Cisco and AWS security controls to provide visibility, segmentation, and threat protection.
Visibility: Cisco Tetration, Cisco Stealthwatch Cloud, Cisco AMP for Endpoint, Cisco Threat Response, and AWS VPC flow logs.
Segmentation: Cisco Next-Generation Firewall, Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance, Cisco Tetration, Cisco Defense Orchestrator, AWS security group, AWS gateway, AWS VPC, and AWS subnets.
Threat Protection: Cisco Next-Generation Firewall (NGFWv), Cisco Tetration, Cisco AMP for Endpoints, Cisco Umbrella, Cisco Threat Response, AWS WAF, AWS Shield (DDoS – Basic or Advance), and Radware WAF/DDoS.
Another key pillar is Identity and Access Management (IAM): Cisco Duo and AWS IAM
Figure 3: Cisco Validated Design for AWS three-tier architecture
Cisco security controls used in the validated design (Figure 3):
◉ Cisco Defense Orchestrator (CDO) – CDO can now manage the AWS security group. CDO provides micro-segmentation capability by managing firewall hosts on the workload.
◉ Cisco Tetration (SaaS) – Cisco Tetration agent on AWS instances forwards “network flow and process information” this information essential for getting visibility and policy enforcement.
◉ Cisco Stealthwatch Cloud (SWC) – SWC consumes VPC flow logs, cloud trail, AWS Inspector, AWS IAM, and many more. SWC includes compliance-related observations and it provides visibility into your AWS cloud infrastructure
◉ Cisco Duo – Cisco Duo provides MFA service for AWS console and applications running on the workloads
◉ Cisco Umbrella – Cisco Umbrella virtual appliance is available for AWS, using DHCP options administrator can configure Cisco Umbrella as a primary DNS. Cisco Umbrella cloud provides a way to configure and enforce DNS layer security to workloads in the cloud.
◉ Cisco Adaptative Security Appliance Virtual (ASAv): Cisco ASAv provides a stateful firewall, network segmentation, and VPN capabilities in AWS VPC.
◉ Cisco Next-Generation Firewall Virtual (NGFWv): Cisco NGFWv provides capabilities like stateful firewall, “application visibility and control”, next-generation IPS, URL-filtering, and network AMP in AWS.
◉ Cisco Threat Response (CTR): Cisco Threat Response has API driven integration with Umbrella, AMP for Endpoints, and SWC (coming soon). Using this integration security ops team can get visibility and perform threat hunting.
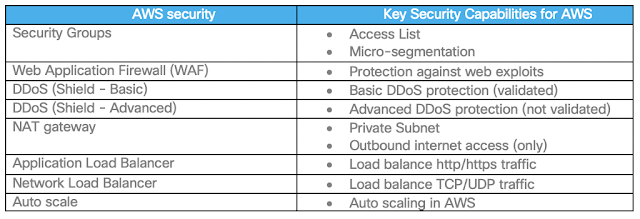
AWS controls used in the Cisco Validated Design (Figure 3):
◉ AWS Security Groups (SG) – AWS security groups provide micro-segmentation capability by adding firewalls rules directly on the instance virtual interface (elastic network interface – eni).
◉ AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) – AWS WAF protects against web exploits.
◉ AWS Shield (DDoS) – AWS Shield protects against DDoS.
◉ AWS Application Load Balancer (ALB) and Network Load Balancer (NLB) – AWS ALB and NLB provides load balancing for incoming traffic.
◉ AWS route 53 – AWS Route53 provides DNS based load balancing and used for load balancing RAVPN (SSL) across multiple firewalls in a VPC.
Radware controls used in the Cisco Validated Design (Figure 3):
◉ Radware (WAF and DDoS): Radware provides WAF and DDoS capabilities as a service.
Cisco recommends enabling the following key capabilities on Cisco security controls. These controls not only provide unmatched visibility, segmentation and threat protection, but they also help in adhering to security compliance.
In addition to the above Cisco security control, Cisco recommends using the following native AWS security components to protect workloads and applications.






0 comments:
Post a Comment