Deploying sustainable manufacturing practices is tremendously important to most manufacturers in response to a variety of drivers, including stakeholder demands, regulatory mandates, climate concerns, and cost reduction. To make progress, action must take place on the factory floor to address concerns like these:
◉ Is a piece of heavy equipment running inefficiently because it has been run past its recommended hours and needs servicing?
◉ Has a piece of equipment been left running while unattended or not in use?
◉ What is the energy consumption across various industrial control systems, HVAC, and lighting on the plant floor?
Identifying potential areas of energy waste on the factory floor in a timely manner requires access to the underlying data, data analytics that derive insights from that data, and a dashboard that provides a single view of notifications and status on KPIs. After all, as the saying goes, “You can’t manage what you can’t measure.”
In response, Cisco — a leader in industrial, IOT networking — and HCLTech (HCL) — a leader in energy management solutions — have joined forces to develop an end-to-end digital sustainability solution leveraging existing products, including HCL’s Net-Zero Intelligent Operations platform (NIO), Cisco IOT gateways powered by the Cisco IOx application hosting environment, and IOx-enabled Cisco network devices. That solution won the 2022 Cisco Global Digital Sustainability Award.
HCL Net Zero Intelligent Operations (NIO) Platform
NIO is a Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emission management solution that helps companies become more sustainable and cost and energy efficient to reduce their carbon emissions and contribute to their net zero goals. NIO presents real-time energy consumption insights and analytics using baselined parameters from all critical energy consumption points originating, for example, in workspaces and on factory floors. This includes calculating, reporting, and identifying emission optimization potential for devices drawing power in a factory or building.
Of course, to provide these insights requires real time access to data from various sources. NIO is a vendor agnostic platform that tightly integrates with the edge data management layer through APIs.
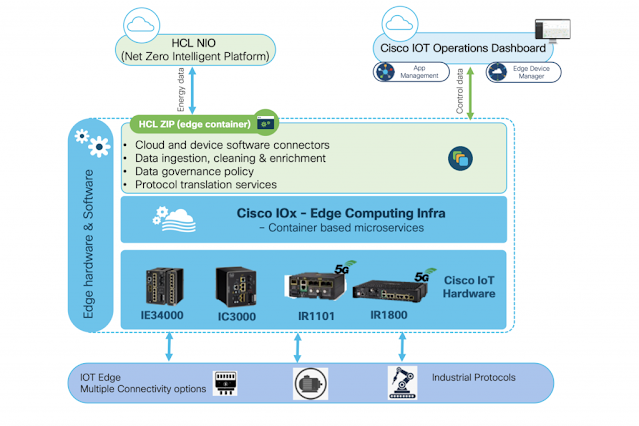
Figure 1: Data Management Layer
Data management layer with the HCL ZIP application and Cisco IoT gateways
As shown in Figure 1, the edge data management portion of the Cisco and HCL solution includes the HCL ZIP application hosting environment–running on Cisco IOT gateways that run the Cisco IOx application hosting environment–which communicates with the NIO platform running either in the cloud or on-premises servers.
The HCL ZIP application collects data from different power meters and directly from energy consuming devices like robots and various Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines such as lathes, routers, grinders and laser cutters or PLC’s. That data is pushed to the NIO platform, which applies analytics and provides insight to the business to help it achieve its sustainability goals.
The HCL ZIP application gains access to this data by running in the Cisco IOx application environment, which combines Cisco IOS and the Linux OS for highly secure networking. IoT applications such as HCL ZIP gain secure connectivity and reliable integration with third-party devices and sensors. In turn, the IOx application environment runs on Cisco all-in-one IoT gateways that provide simple, essential connectivity to various third-party edge devices.
The IoT Gateways are managed centrally through a simple, easy-to-use cloud management tool–the Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard. Using this dashboard, customers can remotely deploy, monitor, and troubleshoot the gateways and applications running on them. The dashboard provides customer insights into network usage and carries out updates remotely without sending anyone onsite. For example, customers can receive automatic alerts when a device on the network goes down so that immediate action can be taken. All of this is done remotely and at scale.
Example use cases
Condition-based maintenance
Many factories have energy meters installed but no power budget management or real time view of how the machines and robots are consuming power. As a simple example, feed motor load can be identified from current monitoring, which can tell if a machine is malfunctioning in either of the following ways:
◉ Consuming power but not producing product (underloading)
◉ Consuming more power than required (overloading)
This information can help inform sustainability goals around energy wasting and carbon emissions.
Improved operational efficiency
In another example, a manufacturer can compare energy consumption across multiple assembly lines or machine usage over a period of time. This practice can help identify optimal working conditions by regulating environmental conditions in systems like HVAC, air ventilators, furnaces, and chillers. This use case can improve plant operational efficiency and save on energy and carbon emission, once again helping a business inform and meet its sustainability goals.
Source: cisco.com





0 comments:
Post a Comment