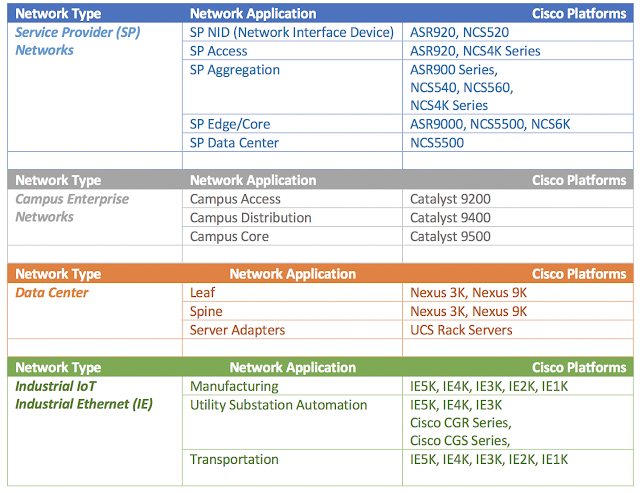
In industries like utilities, manufacturing, and transportation, the operations side of the business is revenue generating. As a result, uptime is critical. While uptime is important in IT, interdependencies in the OT environment make it challenging to maintain uptime while addressing security threats. For example, you can’t simply isolate an endpoint that’s sending anomalous traffic. Because of the interdependencies of that endpoint, isolating it can have a cascading effect that brings a critical business process to a grinding halt. Or, worse, human lives may be put at risk. It’s important to understand the context of security events so that they can be addressed while maintaining uptime.
With uptime requirements in mind, securing the industrial network can feel like an insurmountable challenge. Many industrial organizations don’t have visibility into all of the devices that are on their OT networks, let alone the dependencies among them. Devices have been added over time, often by third-party contractors, and an asset inventory is either non-existent or grossly outdated. Bottom line: organizations lack visibility into the operational technology environment.
To help industrial organizations address these challenges and effectively secure the OT environment, we’ve put together a four-step journey to securing the industrial network. It’s important to note that while we call it a journey, there is no defined beginning or end. It’s an iterative process that requires continual adjustments. The most important thing is to start wherever you happen to be today.
There are many places from which to begin, and what makes a logical first step for one organization will not necessarily be the same for another. One approach is to start with gaining visibility through asset discovery. By analyzing network traffic, deep packet inspection (DPI) can identify the industrial assets connected to your network. With this visibility, you can make an informed decision on the best way to segment the network to limit the spread of an attack.
In addition to identifying assets, DPI identifies which assets are communicating, with whom or what they are communicating, and what they are communicating. With this baseline established, you can detect anomalous behavior and potential threats that may threaten process integrity. This information can then be fed into a unified security operations center (SOC), providing complete visibility to the security team.
How you deploy DPI is important. Embedding a DPI-enabled sensor on switches saves hardware costs and physical space, which can be at a premium, depending on the industry. DPI-enabled sensors allow you to inspect traffic without encountering deployment, scalability, bandwidth, or maintenance hurdles. Because switches see all network traffic, embedded sensors can provide the visibility you need to segment the network and detect threats early on. The solution can also integrate with the IT SOC while providing analytical insights into every component of the industrial control system. With DPI-enabled network switches, industrial organizations can more easily move through the four-step journey to securing the industrial network.