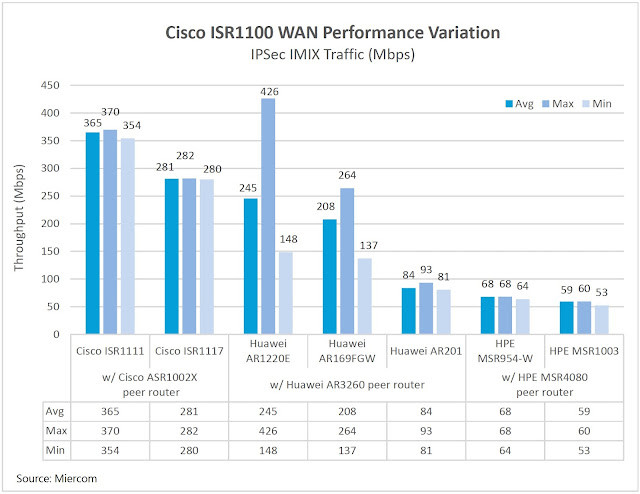
Security is a topic that is a top-of-mind for every CIO out there. It is interesting to know that according to a study performed by Research 451, 64% of enterprises report information security is not a separate line in terms of budget, instead, it is part of their IT infrastructure one.
In other words, most of us take security for granted until something bad happens. Pete Johnson (“Cloud Unfiltered”) even referred to it as “insurance” and I believe that it is the appropriate term for it.
We all know we need insurance, but what is the right-coverage for me? Well, it really depends on what are the type of assets you are trying to protect and how your business would be impacted if something happened.
If we think about our daily lives, imagine having 20 doors/windows wide open and then just locking or adding video-surveillance to the one in the backyard (because your neighbor just told you he had been robbed the night before and that the thief broke into his house through the backyard door). Well, that’s a good start, however there are still more than 19 doors & windows still wide open and vulnerable for anybody to access right?
Well, that’s pretty much what happens in IT and only securing a few “doors” is called “black-listing”. Let me explain: every server has 65535 ports open (for TCP and the same amount for UDP). If we consider the black-listing approach, we may just close a few ports based on common vulnerabilities knowledge. Most of the times, we don’t know which ports our apps need to work on, therefore we need to follow this approach and just block a few ports while permitting the rest of them.
In today’s Multicloud world, constant and more sophisticated threats are a fact and black-listing security is definitely not enough.
All we must do is install a Tetration software sensor on top of Operating Systems like Windows, Linux, Solaris, AIX among others, it does not matter if they are running bare-metal, virtualized, container-based or even on any Public Cloud or non-Cisco hardware. Once installed, the sensors will continuously feed every flow going in and out of that host to the Tetration Engine, which will show us the Application Dependency Mappings.
Think of the sensors as continuous-feed cameras while the Tetration Engine performs as that person in the SoC watching 24×7, reporting any process-level/network anomalies and having all the recordings from the past available for you to analyze when needed. Before, we would only rely on “video-samples” from specific places and at specific times (using things like Netflow or SPAN sessions).
This provides us with great value, since now we know what specific ports our apps really need and we can close the rest, which is called “white-listing” or “zero-trust policies”. We can now use that information and execute our Zero-Trust Policies either manually or even automatically as shown in the video below.
Tetration supports enforcing those policies at the sensor level, turning the software sensor into an enforcement agent and executing segmentation at the OS level. We could also automate the configuration of those policies on ACI or on your own firewall using tools like Tuffin.
Tetration software sensors log every flow at the process level, therefore, they may help us to identify any anomalies or deviation from the standard (like privilege escalation, change in binary files, failed logons and many more).
There are many other types of coverage we may need for IT and our apps and a comprehensive solution may be needed. This is where Stealthwatch & Stealthwatch Cloud (which effectively report potential attacks), ACI (that can execute and complement our security strategy at the multicloud network level while encrypting VXLAN communications) and an effective Next-Generation Firewall like the Firepower Family among others, can further reduce blind-spots and help us react faster to potential threats.
Having multiple homes (in this case Clouds) where our applications may live, would normally force us into having multiple insurance policies. With solutions like these, we can have a single, continuous and consistent one, which should help us getting some extra hours of quality sleep at night!
We all know we need insurance, but what is the right-coverage for me? Well, it really depends on what are the type of assets you are trying to protect and how your business would be impacted if something happened.
If we think about our daily lives, imagine having 20 doors/windows wide open and then just locking or adding video-surveillance to the one in the backyard (because your neighbor just told you he had been robbed the night before and that the thief broke into his house through the backyard door). Well, that’s a good start, however there are still more than 19 doors & windows still wide open and vulnerable for anybody to access right?
Well, that’s pretty much what happens in IT and only securing a few “doors” is called “black-listing”. Let me explain: every server has 65535 ports open (for TCP and the same amount for UDP). If we consider the black-listing approach, we may just close a few ports based on common vulnerabilities knowledge. Most of the times, we don’t know which ports our apps need to work on, therefore we need to follow this approach and just block a few ports while permitting the rest of them.
In today’s Multicloud world, constant and more sophisticated threats are a fact and black-listing security is definitely not enough.
All we must do is install a Tetration software sensor on top of Operating Systems like Windows, Linux, Solaris, AIX among others, it does not matter if they are running bare-metal, virtualized, container-based or even on any Public Cloud or non-Cisco hardware. Once installed, the sensors will continuously feed every flow going in and out of that host to the Tetration Engine, which will show us the Application Dependency Mappings.
Think of the sensors as continuous-feed cameras while the Tetration Engine performs as that person in the SoC watching 24×7, reporting any process-level/network anomalies and having all the recordings from the past available for you to analyze when needed. Before, we would only rely on “video-samples” from specific places and at specific times (using things like Netflow or SPAN sessions).
This provides us with great value, since now we know what specific ports our apps really need and we can close the rest, which is called “white-listing” or “zero-trust policies”. We can now use that information and execute our Zero-Trust Policies either manually or even automatically as shown in the video below.
Tetration supports enforcing those policies at the sensor level, turning the software sensor into an enforcement agent and executing segmentation at the OS level. We could also automate the configuration of those policies on ACI or on your own firewall using tools like Tuffin.
Tetration software sensors log every flow at the process level, therefore, they may help us to identify any anomalies or deviation from the standard (like privilege escalation, change in binary files, failed logons and many more).
There are many other types of coverage we may need for IT and our apps and a comprehensive solution may be needed. This is where Stealthwatch & Stealthwatch Cloud (which effectively report potential attacks), ACI (that can execute and complement our security strategy at the multicloud network level while encrypting VXLAN communications) and an effective Next-Generation Firewall like the Firepower Family among others, can further reduce blind-spots and help us react faster to potential threats.
Having multiple homes (in this case Clouds) where our applications may live, would normally force us into having multiple insurance policies. With solutions like these, we can have a single, continuous and consistent one, which should help us getting some extra hours of quality sleep at night!