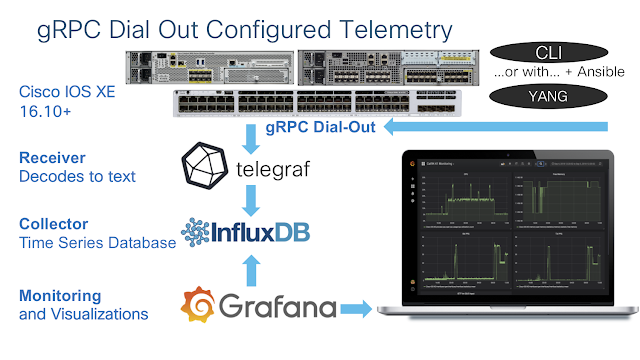
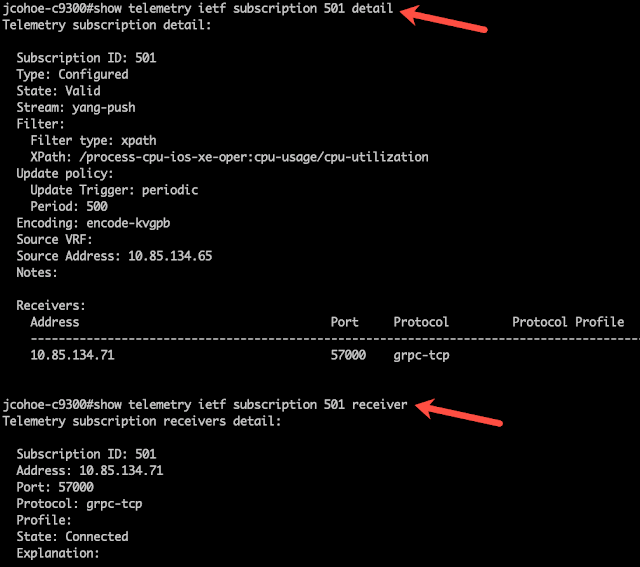
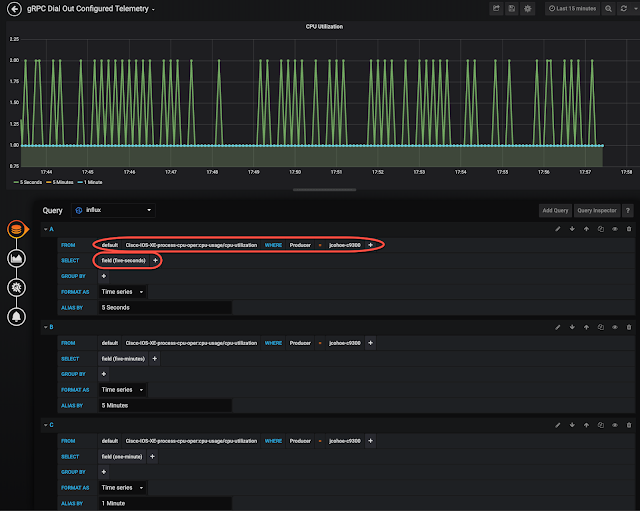
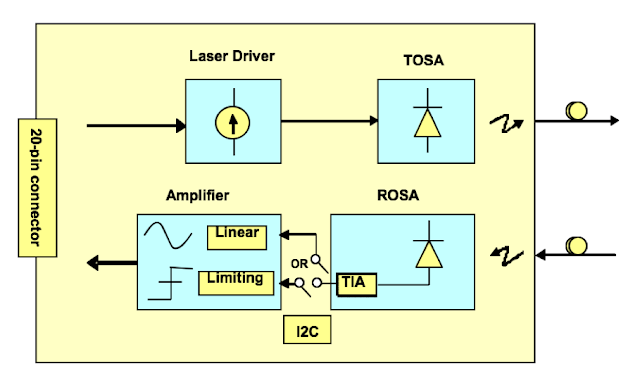
We looked at how Cisco can help service providers (SPs) deliver high-quality 5G solutions to their enterprise customers.
We now continue the story by focusing on two important 5G-network enablers: automation and orchestration.
In the light of today’s changing market trends, this blog briefly reviews some key Cisco orchestration solutions, illustrating their benefits via case studies.
Preparing for an accelerating world
If the 4G network was all about smartphones and consumer data, 5G is more about addressing the strict demands of vertical markets with the expectation of improved quality of experience (QoE) and application performance resulting in rapidly changing business models and customer behaviour.
Product cycles and new, more agile companies are disrupting markets. Savvy customers expect services to be available on demand, from anywhere, at the touch of a button. And technologies such as cloud services, virtualisation/containerisation and intent based networking (IBN) are enabling new commercial opportunities.
All of these developments demand more powerful and flexible network orchestration and automation solutions. But what are the business benefits for SPs?
To give just some examples, Cisco orchestration can reduce configuration and support costs, enable SPs to offer more innovative services quicker with shorter TTM (Time-to-Market), and help them build new revenue streams.
Managing tomorrow’s 5G network traffic
Let’s take a look at two Cisco automation solutions that SPs can use to manage next-generation networks.
Cisco Network Services Orchestrator (NSO) seamlessly configures, automates and provisions end-to-end services across traditional and virtualised networks with Cisco and 3rd Party products. It can add, change and delete services without disrupting the overall service, and help ensure that services are delivered in real time.
NSO 5 is the latest release. It’s a key part of Cisco’s Evolved Services Platform (ESP), which benefits from being:
• Open – multi-vendor and based on open standards and API.
• Extensible – its modules span the full SP architecture (cloud, video, mobile and fixed).
• Elastic – it seamlessly scales services and resources, whenever and wherever needed.
This industry-leading software offers a significant five-year ROI of 383 per cent.1
Cisco Crosswork is the newer suite of automation and orchestration solutions that can enable SPs to proactively manage end-to-end networks. This includes:
• Cisco Crosswork SON Suite – an automation solution concerning the self organising of the radio access network (RAN) that enables companies to reduce operating costs while improving the end-user experience.
• Cisco Crosswork Network Insights – a cloud service that analyses routing and network data to reduce the time taken to fix issues.
• Cisco WAN Automation Engine (WAE) – a solution that offers precise network modelling and optimisation of network traffic across the Wide Area Network (WAN).
Cisco Crosswork is a truly scalable orchestration solution for the new era of 5G networks.
Cisco orchestration and automation in action
Many companies are partnering with Cisco on 5G projects to reap the benefits of automation and orchestration solutions. Here are three examples.
Netherlands operator, VodafoneZiggo, wanted to automate its radio access network (RAN) for the 5G era, so it deployed a Cisco Crosswork SONFlex solution. The solution works in a multi-vendor environment, enabling the company to reduce the cost-per-bit while improving its overall customer experience with superior voice quality.
This move marks a new milestone for VodafoneZiggo. The company’s automation strategy has now shifted from traditional network-focused optimisation to customer-centric, self-organising network (SON)-based automation solutions.
As Matthias Sauder, VodafoneZiggo’s Director, Mobile Networks commented: ‘With Cisco SONFlex, we are now in a position to manage increasing network complexity with 5G on the horizon, improve operational efficiency, and gain greater autonomy to develop a unique automation strategy.’
Another mobile network operator, Rakuten Mobile Network (RMN), plan to launch its services in Japan, late 2019, with a 5G architecture that will disrupt the telecom industry globally.
This will be the world’s first cloud-based network that’s fully virtualised the RAN and Core components, with end-to-end automation for both the network and services. RMN will deliver services from consumer mobile, narrowband IoT and rich media, to low-latency services that include augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR).
Cisco NSO enables full end-to-end automation along with the element management system (EMS) and operations support systems (OSS). It helps reduce OpEx and, compared to traditional operators, greatly reduces the need for people to deploy and operate the network. It also minimises human error.
As Tareq Amin, CTO of Rakuten Mobile Network Inc., commented: ‘Our services will benefit from a unique computing infrastructure that enables the best possible user experience.’
Innovative service provider, Orange, is also planning to deploy the Cisco NSO software platform to its network. The company wants to be able to programme its infrastructure while automating its method-of-procedure operations and customer-facing services.
This will enable Orange to cut service activation times from days to hours, automate its service lifecycles and remove the risk of human error.
Christian Gacon, VP of Wireline Networks and Infrastructure at Orange, said: ‘Cisco’s model-driven approach to network automation and service orchestration is enabling Orange to drastically speed up delivery of services across our entire lifecycles.’
The solution will also enable Orange to continue delivering superior customer services without disruption.
Cisco trusted solutions are ready to orchestrate today’s increasingly complex networks, simplifying management, cutting costs and, above all, offering outstanding services to end-users.
In the light of today’s changing market trends, this blog briefly reviews some key Cisco orchestration solutions, illustrating their benefits via case studies.
Preparing for an accelerating world
If the 4G network was all about smartphones and consumer data, 5G is more about addressing the strict demands of vertical markets with the expectation of improved quality of experience (QoE) and application performance resulting in rapidly changing business models and customer behaviour.
Product cycles and new, more agile companies are disrupting markets. Savvy customers expect services to be available on demand, from anywhere, at the touch of a button. And technologies such as cloud services, virtualisation/containerisation and intent based networking (IBN) are enabling new commercial opportunities.
All of these developments demand more powerful and flexible network orchestration and automation solutions. But what are the business benefits for SPs?
To give just some examples, Cisco orchestration can reduce configuration and support costs, enable SPs to offer more innovative services quicker with shorter TTM (Time-to-Market), and help them build new revenue streams.
Managing tomorrow’s 5G network traffic
Let’s take a look at two Cisco automation solutions that SPs can use to manage next-generation networks.
Cisco Network Services Orchestrator (NSO) seamlessly configures, automates and provisions end-to-end services across traditional and virtualised networks with Cisco and 3rd Party products. It can add, change and delete services without disrupting the overall service, and help ensure that services are delivered in real time.
NSO 5 is the latest release. It’s a key part of Cisco’s Evolved Services Platform (ESP), which benefits from being:
• Open – multi-vendor and based on open standards and API.
• Extensible – its modules span the full SP architecture (cloud, video, mobile and fixed).
• Elastic – it seamlessly scales services and resources, whenever and wherever needed.
This industry-leading software offers a significant five-year ROI of 383 per cent.1
Cisco Crosswork is the newer suite of automation and orchestration solutions that can enable SPs to proactively manage end-to-end networks. This includes:
• Cisco Crosswork SON Suite – an automation solution concerning the self organising of the radio access network (RAN) that enables companies to reduce operating costs while improving the end-user experience.
• Cisco Crosswork Network Insights – a cloud service that analyses routing and network data to reduce the time taken to fix issues.
• Cisco WAN Automation Engine (WAE) – a solution that offers precise network modelling and optimisation of network traffic across the Wide Area Network (WAN).
Cisco Crosswork is a truly scalable orchestration solution for the new era of 5G networks.
Cisco orchestration and automation in action
Many companies are partnering with Cisco on 5G projects to reap the benefits of automation and orchestration solutions. Here are three examples.
VodafoneZiggo runs with RAN automation
Netherlands operator, VodafoneZiggo, wanted to automate its radio access network (RAN) for the 5G era, so it deployed a Cisco Crosswork SONFlex solution. The solution works in a multi-vendor environment, enabling the company to reduce the cost-per-bit while improving its overall customer experience with superior voice quality.
As Matthias Sauder, VodafoneZiggo’s Director, Mobile Networks commented: ‘With Cisco SONFlex, we are now in a position to manage increasing network complexity with 5G on the horizon, improve operational efficiency, and gain greater autonomy to develop a unique automation strategy.’
Rakuten Mobile Network launches the first fully virtualised network
Another mobile network operator, Rakuten Mobile Network (RMN), plan to launch its services in Japan, late 2019, with a 5G architecture that will disrupt the telecom industry globally.
This will be the world’s first cloud-based network that’s fully virtualised the RAN and Core components, with end-to-end automation for both the network and services. RMN will deliver services from consumer mobile, narrowband IoT and rich media, to low-latency services that include augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR).
Cisco NSO enables full end-to-end automation along with the element management system (EMS) and operations support systems (OSS). It helps reduce OpEx and, compared to traditional operators, greatly reduces the need for people to deploy and operate the network. It also minimises human error.
As Tareq Amin, CTO of Rakuten Mobile Network Inc., commented: ‘Our services will benefit from a unique computing infrastructure that enables the best possible user experience.’
Orange invests in Cisco automation
Innovative service provider, Orange, is also planning to deploy the Cisco NSO software platform to its network. The company wants to be able to programme its infrastructure while automating its method-of-procedure operations and customer-facing services.
This will enable Orange to cut service activation times from days to hours, automate its service lifecycles and remove the risk of human error.
Christian Gacon, VP of Wireline Networks and Infrastructure at Orange, said: ‘Cisco’s model-driven approach to network automation and service orchestration is enabling Orange to drastically speed up delivery of services across our entire lifecycles.’
The solution will also enable Orange to continue delivering superior customer services without disruption.
Cisco trusted solutions are ready to orchestrate today’s increasingly complex networks, simplifying management, cutting costs and, above all, offering outstanding services to end-users.