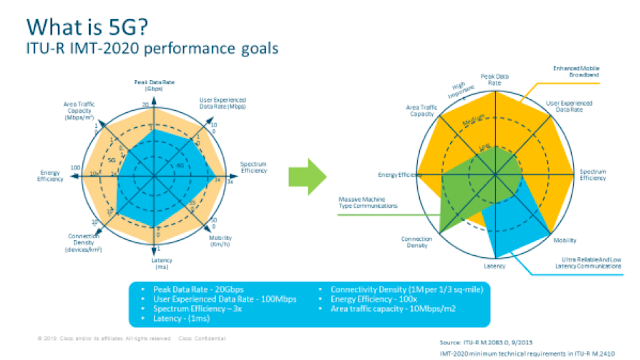
Today’s wireless technology is allowing organizations to improve productivity and worker safety. Organizations such as Caterpillar offer wireless technologies for unmanned vehicles, and mining operations such as Boliden in Garpenberg, Sweden are using wireless technology to remotely operate 23 ton loaders in a small space. If communications fail, it could result in the unit stopping and halting production, ultimately requiring human intervention. On the other hand, a loss in communications with a high-speed train or subway is unacceptable. While most wireless solutions work well for slow moving objects (<30km/h), Fluidmesh’s leading technology is designed to provide zero loss of data transfer at speeds in excess of 300 Km/h.
Beyond high speed rail, numerous industries from manufacturing, oil & gas and mining, to shipping ports, are all looking at how they can use wireless connectivity to automate operations in an effort to reduce operational costs. Today, customers are using Fluidmesh’s reliable wireless technologies in a range of industries to improve productivity, safety, and the customer experience.
Cisco will use Fluidmesh’s products to extend its industrial wireless leadership position to on-the-move applications and where reliable backhaul is mission critical, including:
◉ Rail and transportation: Provide high-speed and reliable connectivity between the trains and the trackside eliminating potential gaps in data transfer, all without the need to stop even when traveling at high speeds.
◉ Mining operations: Improving worker safety with ultra-reliable communication systems for remote operations of mining equipment, eliminating the need to send workers into a potentially hazardous environment.
◉ Manufacturing and industrial automation: Increased productivity with autonomous moving robots operating on a resilient and low-latency wireless network.
With organizations digitizing and interconnecting their systems, the speed of business is constantly being redefined. Fluidmesh’s leading technology will allow us to address these new and emerging use cases with a solution set that is quick to deploy and provides low operational costs and maintenance. We are excited to bring this unique technology to our customers!