As we move into the exciting era of 5G and witness an ever-growing number of new devices coming online, the transport network is finding its overall capacity tested in ways we’ve never seen before. Millions of mobile voice, data, and video users and millions more Internet of Things (IoT) devices connecting 24 hours per day means handling this traffic load will present a real challenge in the future.
Cisco predicts* there will be 50 billion devices connected to the Internet by 2020. Advancements in 5G make it more possible to connect industrial IoT, cars, virtual education, smart communities, industrial machinery, and robotics around the world, all piped through the same ultra-fast network.
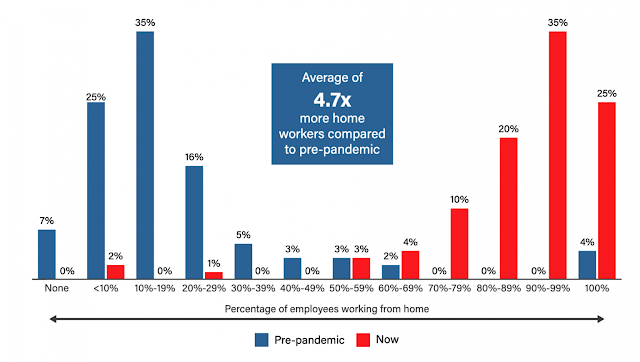
There is a new perspective on the modern workplace. The first half of 2020 will go down in history as one of the most tumultuous times in living memory. The number of people working from home worldwide has doubled during the corona virus crisis. The pandemic is likely to cause a permanent increase in remote working even after the crisis. With little notice, this culminated in many businesses having to shift a large proportion of their workforce to a home working model – Leading to humongous reliability on technology to communicate and collaborate within an enterprise and between businesses.
Where Service Providers stand nowadays?
We’re living in a world where application loyalty has become a real measure of brand loyalty. Service Providers are striving to make the application capable of reaching the end-user quickly enough to prevent the degradation of the experience. Network slicing and segment routing provide intelligent routing and traffic differentiation required to efficiently support this distributed architecture.
Service Providers end to end network starts with a fabric relying on the Cisco Nexus 9000 Switches, which provide the foundation for data centers, data centers interconnection with the core and segment routing traffic engineering SR-TE for network slicing.
Segment Routing Operation
Segment routing divides the network into “segments” where each node and link could be assigned a segment identifier, or a SID, which gets advertised by each node using standard routing protocol extensions (ISIS/OSPF or BGP), eliminating the need to run additional label distribution protocols.
As service providers architect the 5G transport domains, leveraging segment routing with traffic engineering is the next generation network design direction.
Nowadays, many Service Providers are moving to Segment Routing because it allows the network to differentiate the way it delivers applications with unmatched simplicity and scalability.
We have engineered segment routing to the NX-OS software code on Nexus 9000 series switches. The unprecedented growth requires Service Providers to transform their networks, and Segment Routing is becoming one of the keys to successfully paving the way to that transformation.
Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE)
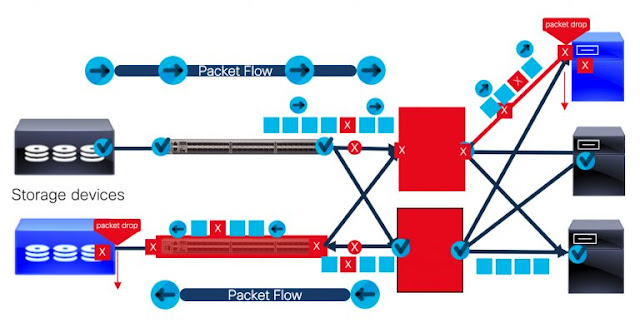
Segment Routing Traffic Engineering (SR-TE) provides a simple, automated, and scalable architecture to engineer traffic flows in a network. SR-TE takes place through a tunnel between a source and destination pair where it uses the concept of source routing, where the source calculates the path and encodes it in the packet header as a segment.
TE is a discipline that assigns traffic flows to network paths in order to satisfy Service Level Agreements (SLAs). For example, assume that a service provider maintains an SLA with a customer. The SLA guarantees low loss but does not guarantee low latency. Therefore, the service provider might apply a TE policy to that customer’s traffic, which forces it to take low loss paths.
Nowadays, Cisco Nexus 9000 series switches enables customers with segment routing for traffic engineering (SR-TE), which enables Services Providers not needing to maintain a per-application and per-flow state. Instead, it simply obeys the forwarding instructions provided in the packet. This is the corner stone capability to have 5G networking slicing within a backhaul network.
SR-TE utilizes network bandwidth more effectively than traditional MPLS-TE networks by using ECMP at every segment level. It uses a single intelligent source and relieves remaining nodes from the task of calculating the required path through the network.
What is Network Slicing and what the Nexus Switching platform with NX-OS offers to Service Providers?
Network slicing is a flexible, scalable architecture that allows the multiplexing of virtualized, independent networks on the same physical infrastructure, taking advantage of concepts such as Software Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV). It enables the management of multiple logical networks as virtually independent business operations on a common physical infrastructure.
With end-to-end network slicing, Services Providers differentiated services can be offered on the same network infrastructure with guaranteed SLAs, creating a sizable opportunity. As the underlying virtualized 5G networks become more complex, automation is essential to operate at scale to contain costs. And an open environment is critical to enable new industry partners to develop new services and drive revenue.
It offers the ability to partition mobile networks into a set of virtual resources, and each “slice” can then be allocated for different purposes. It is a key concept in 5G and a way to utilize the network in a more intelligent and cost-effective way than ever before.
How Does Network Slicing Differ from Segment Routing?
Network slicing and segment routing are two separate functions that work together to improve the end-user experience.
Segment routing is gaining popularity as a means of simplifying Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) networks. We see segment routing changing the way MPLS networks function and facilitating the adoption of SDN. Because segment routing directs traffic on a stateless, flexibly defined path, it has the benefit of being programmed by an SDN controller or locally by the head-end source-based routing.
Introducing Service Provider 5G Networking with SR on NX-OS – SRTE – Flow-based Traffic Steering
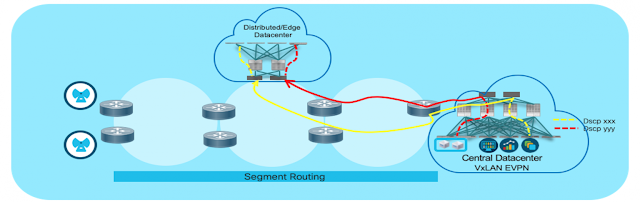
Cisco NX-OS provides a seamless protocol gateways functionality that merges the border leaf/spine and the MPLS provider edge router into a single device (WAN Edge) to provide Layer 3 external connectivity to data center fabric.
Seamless Protocol Gateways
Data Center deployments have adopted VxLAN EVPN for its benefits such as EVPN control-plane learning, multitenancy, seamless mobility, redundancy, simple expansions, and proportional multipath for VNF.
Within the data center fabric, VxLAN QoS enables Service Providers to provide Quality of Service (QoS) capabilities to traffic that is tunneled in VXLAN. This includes classifying traffic and assign different priorities, and queuing & scheduling process which allows to control the queue usage and the bandwidth that is allocated to traffic classes.
For large scale deployments involving several VRFs extending to the core transport, configuration and operations becomes cumbersome especially using VRF-Lite with large number of routing sessions. A single control plane session (MP-BGP EVPN) is used for all VRFs instead of having per-VRF session between VxLAN EVPN fabric node and core network.
Cisco Nexus functionality seamlessly interconnects VxLAN EVPN fabric with Segment Routing L3VPN by allocating a per VRF (tenant) label and advertises to the L3VPN peer(s) across the Telco core transport network providing an end-to-end traffic classes path control by matching the 5-tuples and/or DSCP values which is a key 5G network slicing concept.
This functionality seamlessly interconnects VxLAN EVPN fabric with Segment Routing L3VPN by allocating a per VRF (tenant) label and advertises to the L3VPN peer(s) across the Telco core transport network providing an end-to-end traffic classes path control by matching the 5-tuples and/or DSCP values which is a key 5G network slicing concept.