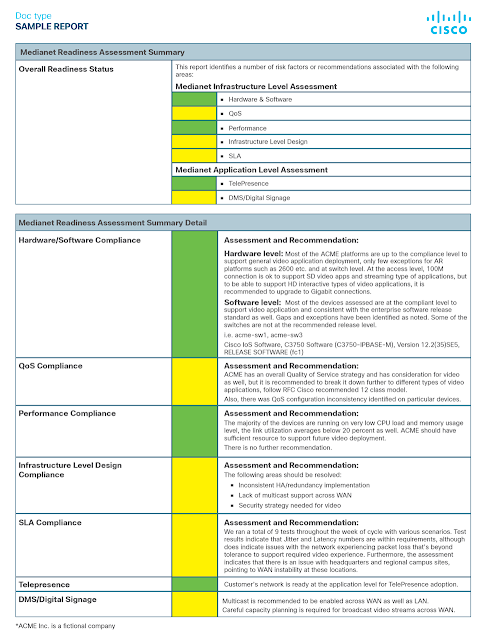
The issue with that 1995 playbooks is in its results. Eighty percent of businesses think they deliver superior customer service. Only 8% of customers think businesses deliver superior customer service.
It’s time for this to change. Here are four customer service trends that must impact how you interact with your customers from this point forward.
Proactive Customer Experience
While responding to customers online is less expensive than legacy customer service mechanisms like phone or email, the costs are real and the public nature of those pose risk. Perhaps the best way to invest your resources is to legitimately improve your customer experience so fewer people have any reason to be upset with your business in the first place.
If you’re paying attention to customer feedback, you’re probably aware of the weak parts of your business. You know where and when customer satisfaction is likely to dip. Instead of waiting for your customers to experience those dips, proactively head them off at the pass. The best way to handle unhappy or unsatisfied customers is to eliminate the forces that make them unhappy or unsatisfied.
The best customer problems are the ones that don’t have to happen in the first place.
Self-Service Solutions
If customers can easily and thoroughly address problems on their own, they will. Self-service is an efficient path to issue resolution because customers don’t have to wait on your business to respond.
Self-service makes a lot of sense — on both the customer experience and cost efficiency fronts. According to Forrester, self-service increases customer satisfaction and lowers costs for businesses.
Forrester also found that 72 percent of consumers prefer using a company’s website to answer their questions. Unfortunately, businesses are not universally adept at this approach. Only half of customers can find the information they need online.
The best self-service programs are living organisms. They expand and morph and change to fit customer questions and complaints. To do this, managers must meet often with personnel interacting with customers to discuss what questions and issues are emerging. Many of the questions will be repeats. In fact, one-third of customer questions are common or repeat issues. The objective with self-service is to determine all of those likely questions, and then provide answers to customers in (ideally) multiple online formats.
Community-Based Service
If the most efficient way to get answers to consumers is to give them access to that information in a self-service capacity, the next best approach is to enable support from a customer community.
One of the reasons community-based customer service tools are so powerful is that collectively, the community knows more than any one customer service representative possibly could. These programs also have financial implications. Research from Gartner suggests businesses that implement community-based support can reduce costs by 10 – 50 percent. There’s another business benefit to these programs: Online communities can also breed deep insights that allows businesses and organizations to change their offerings, communicate more effectively, and enhance customer service when it does not need to be provided on a one-to-one basis.
Mobile Messaging Apps
Messaging has fundamentally changed the way we communicate with each another, and it’s making this transformation with gusto. According to Statista, Facebook Messenger has more than 1.3 billion active monthly users. WhatsApp (owned by Facebook) has more than 1.6 billion active monthly users, and WeChat is nearing 1.1 billion.
Messaging apps are the biggest force in communication today, and their functionality for one-to-one messaging has everything you need for customer service. They’re private, which companies love. They’re persistent, which customers love. They’re real-time, and they’re asynchronous. Asynchronicity is one of the key factors that make messaging apps so convenient and powerful. A consumer can start a conversation with a business, do something more important, and pick up the same conversation where she left off 10 or 20 minutes later. Gone are the days of being on hold and gone are the expectations that being on hold is normal.
Not to mention the fact that messaging apps often get better satisfaction ratings than any other CX channel, including phone calls.
If you haven’t already, archive the playbook from 1995 and adjust how your business delivers customer service to meet the expectations of today’s customer.