The threat landscape evolves constantly, with new and increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks launching with growing frequency across network, cloud, and software-as-a-service environments.
As threats continue to stack up against organizations, IT teams face the challenge of managing heterogeneous end-user device environments composed of various network-connected devices, operating systems, and applications. They must ensure that consistent, organizationally-sanctioned controls are applied across these environments.
While this is achievable with the right security expertise, there is also a global cybersecurity skills shortage. In fact, 3.5 million cybersecurity positions are expected to remain unfulfilled by 2021.
These challenges are not insurmountable. They can be conquered with the security operations and incident response approach called SOAR.
What is SOAR?
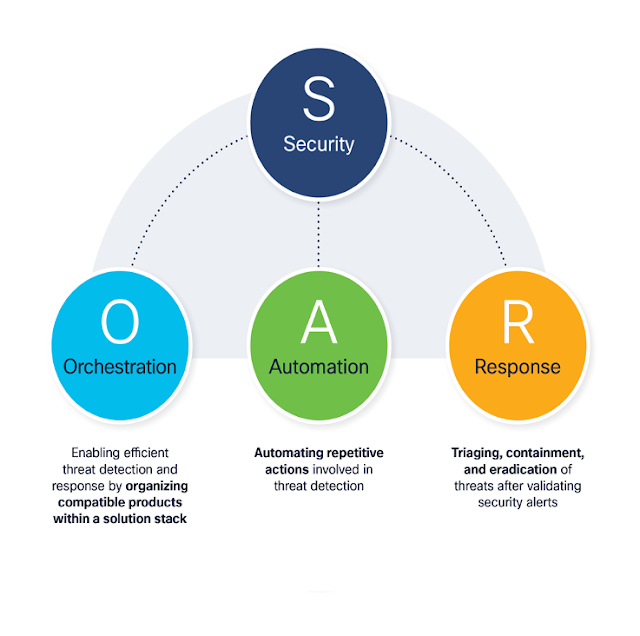
SOAR refers to a solution stack of compatible software that allows organizations to orchestrate and automate different parts of security management and operations to improve the accuracy, consistency, and efficiency of security processes and workflows with automated responses to threats.
How does SOAR work?
Security orchestration
The first component of SOAR, security orchestration, involves leveraging the different, compatible products for use within a solution stack to orchestrate the management and operations activities through standardized workflows. These security solutions automatically aggregate data from multiple sources, add context to that data to identify potential weaknesses, and use risk modeling scenarios to enable automated threat detection. Recognizing this, more and more organizations are prioritizing the need for effective integration between security technologies to enable rapid threat detection and response.
Security automation
The second component is security automation, which involves automating many of the repetitive actions involved in the threat detection process.
Traditionally, security analysts within an organization would handle threat alerts manually, usually multi-tasking to size up alerts from numerous point solutions. This increases the likelihood of human error, inconsistent threat response, and high severity threats being overlooked.
SOAR, on the other hand, automates gathering enrichment and intelligence data on an event, can perform common investigative steps on behalf of the analyst to help triage events, and consistently delivers on the orchestration and response of the incident response lifecycle.
Security response
The third component, security response, involves triage, containment, and eradication of threats.
Response methods depend on the type and scope of the threat. Some threat responses can be automated for faster results, such as quarantining files, blocking file hashes across the organization, isolating a host or disabling access to compromised accounts.
However, sophisticated cyber-attacks require sophisticated responses. This is where security playbooks come in.
With Cisco Managed Detection and Response (MDR), automation is supported by defined investigation and response playbooks, containing overviews of known threat scenarios and best practices for responding to different types of threats. The role of automation is to rapidly execute these playbooks.





0 comments:
Post a Comment