Sunday, 27 November 2022
High Availability – Features in Cisco IOS XE Software Makes It Appear Seamless
Saturday, 26 November 2022
Kenna.VM Premier: Accelerate Vulnerability Management with Cisco Talos Intel and Remediation Analytics
Remediation scoring
Zero-day vulnerability intel—brought to you by Cisco Talos
Vulnerability intelligence—your way
Thursday, 24 November 2022
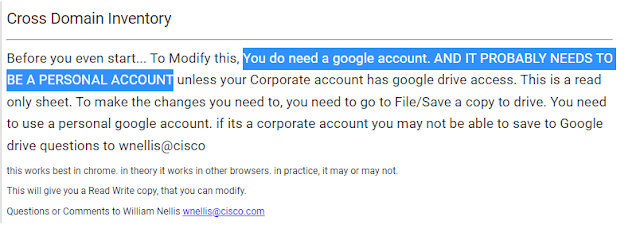
Using APIs to create a Multidomain Inventory for Asset Management
Tuesday, 22 November 2022
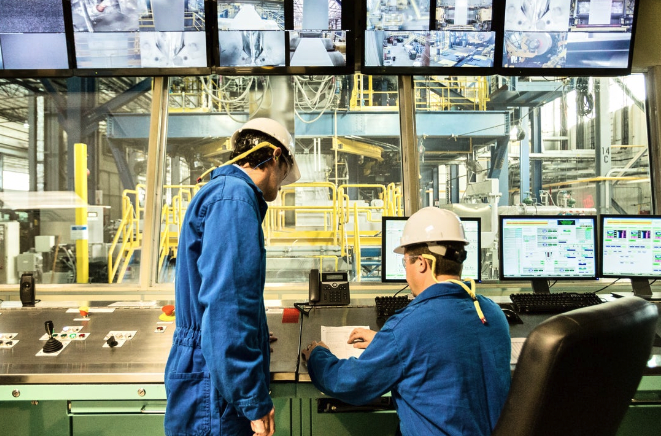
Secure the Industrial Edge with Cisco SD-WAN
The Expansion of Enterprise Networks
Challenges Surrounding IoT
Cisco SD-WAN Can Help
Sunday, 20 November 2022
Supercharge 5G with Converged CRAN Architecture
5G CRAN explained
Building efficient RAN transport
5G xHaul transport with NCS 540 and NCS 5700 series
Saturday, 19 November 2022
Cisco Intersight Gets a New Look
New User Interface Signals Milestone for Hybrid Cloud Operations Platform
Thursday, 17 November 2022
CCT Routing and Switching 100-490 RSTECH Exam: Get to Know How to Pass
Cisco CCT Routing & Switching certification emphasizes on the skills needed for onsite support and sustenance of Cisco routers, switches, and working environments. Technicians in this field must be able to recognize Cisco router and switch models, cabling, accessories, and interfaces; perceive the Cisco IOS Software operating modes and recognize ordinarily found software; and be able to utilize the Cisco Command Line Interface (CLI) to link and service products. One must pass the Cisco 100-490 RSTECH exam to obtain the CCT Routing & Switching certification.
CCT Routing & Switching 100-490 RSTECH Exam Information
The applicant is only said to be completely prepared once they understand and master the essential information for any exam. The CCT Routing and Switching (100-490 RSTECH) exam evaluates an applicant's understanding and expertise concerning the following objectives.
Cisco 100-490 RSTECH Exam Objectives
Basic Details of Cisco 100-490 Exam
Let us dive into the basic details of the Cisco 100-490 RSTECH exam. The exam comprises 55-65 multiple-choice questions. This Cisco exam is available in the English language. Also, the Cisco CCT Routing and Switching (100-490 RSTECH) certification is valid for three years.
Studying for CCT Routing and Switching 100-490 RSTECH Exam
If you want to obtain the CCT Routing and Switching certification, you need to pass Cisco 100-490 RSTECH exam. If you consider this exam as another task to accomplish, you will be able to carry it out with amazing results. Just concentrate on learning and mastering all the exam syllabus topics; the rest will be pretty easy whenever you are taking any exam; one of the initial things you will require to do is to obtain the right study resources.
The first platform from where you should begin is the Cisco official website. Cisco itself offers many learning materials for those who want to utilize official resources. You can come across many learning materials on the official website, like the Cisco community, 100-490 RSTECH study guide, training courses, practice tests, and much more. The Cisco community is the ideal place to join in to solve all the questions you have with other members of the community. All the details of these learning resources can be found on the certification's official webpage.
And to perform the CCT Routing and Switching practice exam, you can explore the nwexam website. This is the best website providing practice tests for the Cisco certification exam. They help you assess your preparation level for the exam topics as well as equip you with exam-taking skills. The practice tests will equip you with knowledge and skills but also helps you get familiar with an exam environment before facing the actual exam.
Additional Tips for CCT Routing and Switching Exam
During the preparation stage, not only study resources are important, but also the steps that you take. When you are studying for the CCT Routing and Switching 100-490 RSTECH certification exam, try to make a study plan so that you can learn the syllabus topic within time and assign enough time for each of them. Take into account all the resources available and give each of them an identical time during every week of your preparation. But don’t overlook counting your free time with your family, responsibilities, and other pleasing things you require.
If you want to pass this CCT Routing and Switching exam on the first shot, it is best to concentrate on studying the essential objectives. Thus, you should attempt as many practice tests as possible because they will make a huge difference. Once the exam day reaches, you should ensure that you sleep well the night before and don’t learn anything new on this day. If you start revising concepts instead of just giving yourself a break before the actual exam, there is a possibility that you might start to ignore important details. Have faith in your exam preparation and take your certification exam smoothly.
Pro Tip: Don’t be frightened to use multiple resources because this might be the thing that will help you pass the exam.
Conclusion
Passing the CCT Routing and Switching 100-490 RSTECH exam will demonstrate to organizations that you hold all the skills needed for onsite support and maintenance of Cisco routers, switches, and operating environments.
Cisco certifications are greatly appreciated in the professional world, and if you hold one, it will be a shining star on your CV. Obtaining the CCT Routing and Switching certification will smooth your career path, so why not grab this opportunity and put all your efforts into this milestone?