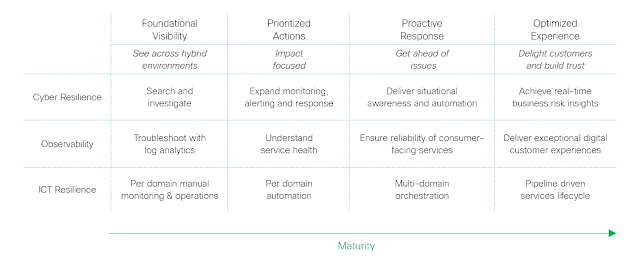
In today’s modern IT environment, most organizations leverage both the public cloud and private data center to house critical business applications. In many cases, these applications require communication with other applications to execute a particular need for the business. A common challenge among the customers I have spoken...