In this blog, we look at the campus network, where IT professionals have traditionally required intricate, expert knowledge and extensive configuration expertise to manage a wide range of technologies and devices arranged in multi-tier switched or routed-access networks, complemented by wireless-overlay networks.
Access networks are at the heart of many IT teams’ operations, yet it can be no easy task for IT teams to authenticate, authorize, segment, monitor, and allocate the appropriate resources in a campus network. However, recent innovations in intent-based networking can bring relief throughout all phases of its operational lifecycle. Let’s explore how.
Campus networking can be hard! But help is at hand…
Access networks are at the heart of many IT teams’ operations, yet it can be no easy task for IT teams to authenticate, authorize, segment, monitor, and allocate the appropriate resources in a campus network. However, recent innovations in intent-based networking can bring relief throughout all phases of its operational lifecycle. Let’s explore how.
Simplify Provisioning for Campus Networks
With a Cisco intent-based network, administrators can start by automating software-defined-access (SD-Access) network configurations. Switches are added to the network using Digital Network Architecture LAN Automation, leveraging Cisco plug-and-play functionality. The DNA Center then pushes the correct configuration (consistent with the role of the device). The result? Automated provisioning of an entire campus network within minutes.
Manage by Identity, Not IP Address: Group-Based Policies for Endpoints
Before intent-based networking IT had to plan Internet Protocol (IP) addressing and virtual-local-area-network (VLAN) structure to separate users and devices into confined segments. IT teams have also had to take care of the associated Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) policies. These policies may have:
◈ varied by device type (think IoT) or user-group
◈ treated wired and wireless access differently.
Each device needs to be configured to represent the application policies that IT teams wish to implement for users or end-devices throughout the access network, in order to achieve the desired transport treatment.
In an intent-based network, endpoints are referenced by a natural expression of their identity, as opposed to classification by IP addresses.
Endpoints can then be grouped together based on their natural attributes, and a group-based policy (GBP) can then be applied. A large number of endpoints can then be treated as one – in a single group – which reduces the scale and complexity of the network (from the operator’s perspective). Overall, these natural and highly powerful abstractions can dramatically improve the human understandability and ease of operating a network.
Segmentation policies are abstracted by means of overlay networks.
Users and devices in a group-based policy can then be placed into their own virtual networks that are constructed independently of virtual local-area network (VLAN) tags or internet-protocol (IP) prefixes.
No more mental acrobatics!
In an intent-based-network application, policies – such as quality of service (QoS) – are also applied through the abstracted expression of intent. For example:
◈ applications can be marked (including: “business critical”, “default” or “irrelevant”)
◈ a Cisco DNA controller can then derive the desired configurations to support the intended application policy, taking the controller’s holistic knowledge of devices and state into account.
Automation then drives the desired capabilities into the network. No more mental acrobatics for network managers to determine command-line interface (CLI) commands! And no manual steps to configure each switch (and its operating system) in the network, individually via command-line interface (CLI)!
Express your segmentation policy by first associating devices or users with groups, and then groups to network segments – it’s that simple!
Since segmentation policies are anchored by a group tag in the virtual extensible LAN (VXLAN) frame headers, both wired- and wireless-connected devices can be treated consistently and in a unified manner.
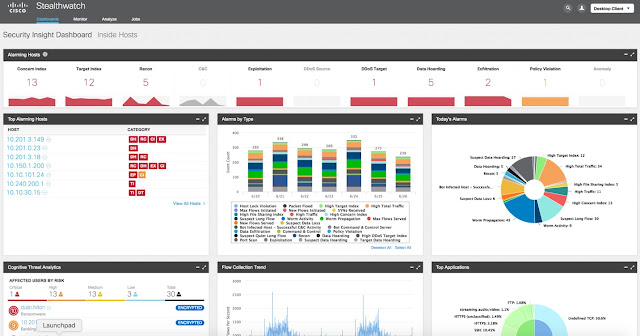
Know What’s Going on in Your Campus Network
Comprehensive assurance functions provide a Cisco intent-based access network with major advantages over a traditional switched campus.
Historically network administrators have had limited visibility across a network, and limited tools to confirm that the network is operating as desired. Often, problems were only realized after the fact, when something in the network went wrong.
The assurance functionality of an intent-based network now provides ongoing visibility into network operations. Various forms of network data are gathered, recorded and analyzed continuously using sophisticated algorithms and machine learning to determine if the campus network is behaving as intended.
In case of discrepancies between the desired intent and actual operation, the assurance capabilities can even suggest remedies to take corrective actions.