Defenders have a lot of work to do, and many challenges to overcome. While conducting the Cisco 2018 Security Capabilities Benchmark Study, where we touched more than 3600 customers across 26 countries, these assumptions were confirmed. We have seen that defenders are struggling with the orchestration of a mix of security products and that, by itself, may obfuscate rather than clarify the security landscape.
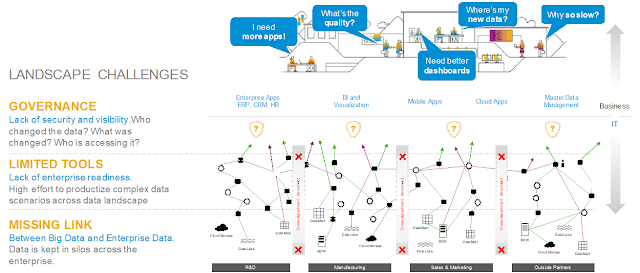
Let’s take a moment to imagine a security team and the tasks it performs daily. Reviewing increasing numbers of alerts, attempting to correlate information from various sources to build a complete picture of each potential threat, triaging and assigning priorities, are all complex tasks performed under time pressures. The goal is to quickly come up with an adequate response strategy based on the clear understanding of the threat, its scope of compromise, and the potential damage it could cause. This process is often error-prone and time-consuming when it is manual. At the same time when understanding the alerts becomes a challenge, high severity threats can slip through the defenses.
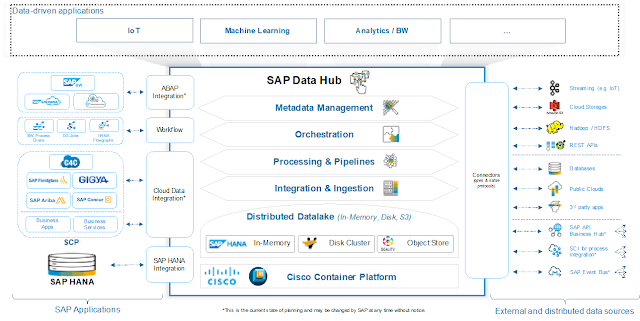
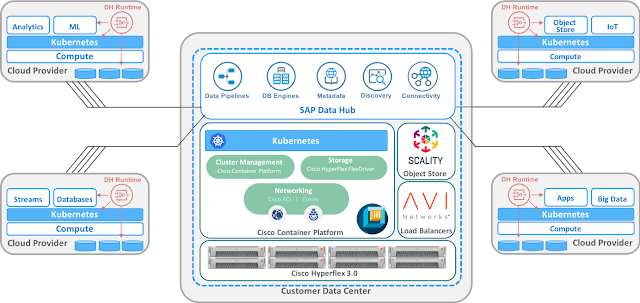
We have heard from the majority of customers that an integrated approach is easier to implement and is more cost effective. Listening to and understanding the needs of our customers has always been a priority for us. Therefore, to empower security analysts with effective weapons to defend their organizations, Cisco has built a security architecture that helps streamline security operations. Most recently we have developed two offerings: one a platform and the other a capability: Cisco Threat Response and AMP Unity. Both are exciting developments and while they are different, they serve the same strategic goal.
AMP Unity
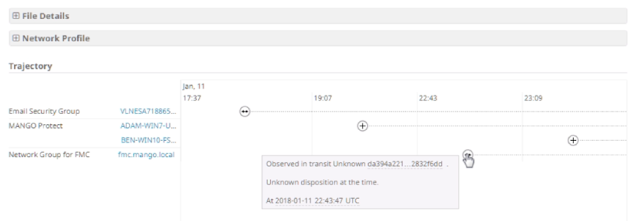
AMP Unity is a capability that allows organizations to register their AMP-enabled devices (Cisco NGFW, NGIPS, ESA, CES, WSA with a Malware/AMP subscription) in the AMP for Endpoints Console. In this way, those devices can be seen and queried (for sample observations) the same way the AMP for Endpoints Console already provides for endpoints. This integration allows correlating file propagation data across all of the threat vectors in a single User Interface (Global File Trajectory view).
Global File Trajectory view (showcasing file transfer through an email gateway, down to the endpoint, across the network to another endpoint)
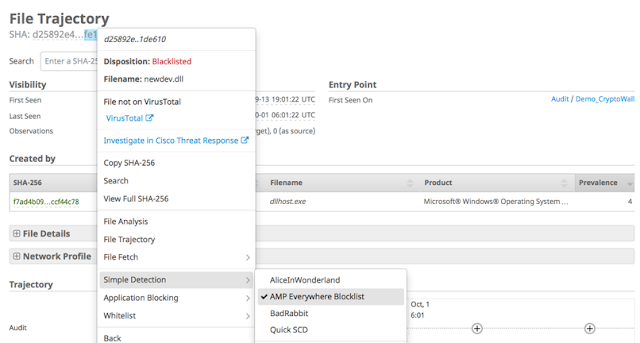
But it doesn’t stop there. AMP Unity also allows you to create common file whitelists and file blacklists (through the same AMP for Endpoints Console) and enforce them across all of the registered AMP-enabled devices in the organization alongside your AMP endpoints (Global Outbreak Control).
Global Outbreak Control (adding a file to a Simple Detection list which enforces a blocking action across all AMP-enabled devices and endpoints)
In an incident response scenario, being able to quickly understand the scope of compromise and the way threats propagate across the environment, is essential. Being able to enforce policy across the malware inspection gateways and endpoints consistently helps security teams save time and address threats that matter.
Keep in mind that AMP Unity is a capability. It doesn’t introduce new dashboards or policies – it’s all managed through the AMP for Endpoints Console. That helps you derive more value out of your existing AMP investments.
Cisco Threat Response
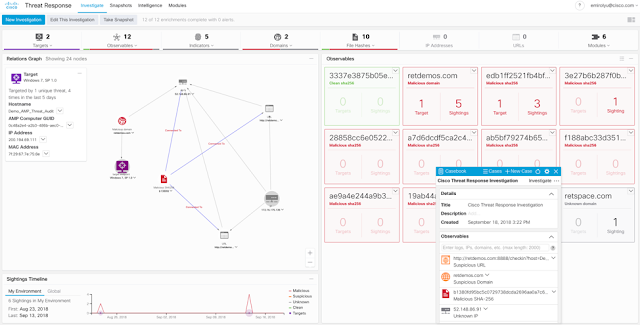
Cisco Threat Response is an innovative platform that brings together security-related information from Cisco and third-party sources into a single, intuitive investigation and response console. It does so through a modular design that serves as an integration framework for event logs and threat intelligence. Modules allow for the rapid correlation of data by building relationship graphs that in turn, enable security teams to obtain a clear view of the attack, as well as to quickly make effective response actions.
Cisco Threat Response Relationship Graph
As of the time of publishing this blog, Cisco Threat Response brings together event logs and threat intelligence from multiple Cisco and 3rd party modules. It’s likely that by the team you read this blog, the platform has added additional modules and capabilities.
Cisco Threat Response Modules
The obvious value here is automation and the reduction of incident response lag caused by shifting through multiple user interfaces and attempting to correlate available data manually. That’s precisely what Threat Response does for you. The daily workflow is also streamlined through the integrated case management tool named “Casebook”. That is a tiny UI component that allows you to gather and pivot on observables, assign names to your investigations, take notes and much more. Casebooks are built on a cloud API and data storage, and can be referenced by any product (with your credentials). Because of this, they can follow you from product to product, eventually across the entire Cisco Security portfolio.
Casebook
Cisco Threat Response is currently available to AMP for Endpoints and Threat Grid customers, who can take advantage of this powerful platform and the possibilities it provides today.
Tying AMP Unity and Cisco Threat Response Together
Considering both of these developments provide added value to security teams through tighter native integrations, how do they relate to each other? Simple – Cisco Threat Response queries correlated event telemetry from AMP for Endpoints and allows you to quickly take containment actions. It does so through the AMP for Endpoints API, via the AMP for Endpoints module enabled in Threat Response. Since AMP for Endpoints Console is a central place to correlate telemetry from AMP-enabled devices, this information can be used to enrich relationship graphs built by Threat Response. On top of that, Global Outbreak Control capabilities introduced by AMP Unity can be used through the Threat Response User Interface.
AMP Unity Events in Threat Response
AMP Unity brings your AMP-enabled device data to Threat Response via the AMP for Endpoints module, and in turn Threat Response allows you to quickly take action at both the endpoint and edge layers of your AMP deployment based on investigation results across all Threat Response data.
As Cisco continues to develop new modules for Threat Response, enabling AMP Unity will be an optional step to correlate event telemetry from AMP-enabled devices. Eventually Threat Response will be able to query these devices (WSA, ESA, CES, NGFW, NGIPS) directly without having to rely on the AMP for Endpoints module (which is especially important for customers who do not have AMP for Endpoints).