Wednesday, 31 August 2022
Showcasing Cisco’s Commitment to Openness: VXLAN BGP EVPN with OpenConfig
Monday, 29 August 2022
How to Prepare for Cisco 700-680 CSaaS Certification?
Cisco 700-680 CSaaS Exam Description:
Cisco 700-680 Exam Overview:
- Exam Name- Cisco Collaboration SaaS Authorization Exam
- Exam Number - 700-680 CSaaS
- Exam Price- $80 USD
- Duration- 30 minutes
- Number of Questions- 35-45
- Passing Score- Variable (750-850 / 1000 Approx.)
- Recommended Training- Cisco SaaS Authorization Training
- Exam Registration- PEARSON VUE
- Sample Questions- Cisco 700-680 Sample Questions
- Practice Exam- Cisco Collaboration SaaS Practice Test
Cisco 700-680 Exam Topics:
- Webex Market Overview- 5%
- Webex Meetings, Webex Teams, Webex Devices, and Webex Edge- 30%
- Webex Calling- 5%
- Webex Control Hub, Webex security, compliance and Webex for developers- 30%
- Collaboration Flex Plan- 20%
- Overview of Ordering, Smart accounts and Webex Try and Buy- 10%
Related Article:-
Sunday, 28 August 2022
New Learning Labs for NSO Service Development
Getting started with network automation can be tough. It is worth the effort though, when a product like Cisco Network Services Orchestrator (NSO) can to turn your network services into a powerful orchestration engine. Over the past year, we have released a series of learning labs that cover the foundational skills needed to develop with NSO:
◉ Learn NSO the Easy Way
◉ Yang for NSO
◉ XML for NSO
Now we are proud to announce the final piece of the puzzle. We’re bringing it all together with the new service development labs for NSO. If this is your first time hearing about Cisco NSO and service development, let’s review some of the context.
Why change is the only constant
Network programmability has been enhancing our networking builds, changes, and deployments for several years now. For the most part, this was inspired by Software Defined Networks – i.e., networks based on scripting methods, using standard programming languages to control and monitor your network device infrastructure.
Software-defined networking principles can deliver abstractions of existing network infrastructure. This enables faster service development and deployment. Standards such as NETCONF and YANG are currently the driving force behind these abstractions, and are enabling a significant improvement in network management. Scripting can take out a lot of laborious and repetitive tasks. However, it may still have shortfalls, as it can focus on single devices, one vendor, or one platform.
Service orchestration simplifies network operations
Service orchestration simplifies network operations and management of network services. Instead of focusing on a particular device and system configuration that builds a network service, only the important inputs are collected. The rest of the steps and processes for delivery are automated. The actual details, such as vendor-specific configurations on network devices and the correct ordering of steps, are abstracted from the user of the service. This results in consistent configurations, prevention of errors and outages, and overall cost reduction of managing a network.
Remove the complexity
With NSO services, service application maps input parameters to create, modify, and delete a service instance into the resulting native commands to devices in the network. The input parameters are given from a northbound system such as a self-service portal via an API (Application Programming Interface). This calls to NSO or a network engineer using any of the NSO User Interfaces such as the NSO CLI.
NSO Service Development Module
Try it yourself now
Friday, 26 August 2022
Service Chaining VNFs with Cloud-Native Containers Using Cisco Kubernetes
To support edge use cases such as distributed IoT ecosystems and data-intensive applications, IT needs to deploy processing closer to where data is generated instead of backhauling data to a cloud or to the campus data center. A hybrid workforce and cloud-native applications are also pushing applications from centralized data centers to the edges of the enterprise. These new generations of application workloads are being distributed across containers and across multiple clouds.
Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) focuses on decoupling individual services—such as Routing, Security, and WAN Acceleration—from the underlying hardware platform. Enabling these Network Functions to run inside virtual machines increases deployment flexibility in the network. NFV enables automation and rapid service deployment of networking functions through service-chaining, providing significant reductions in network OpEx. The capabilities described in this post extend service-chaining of Virtual Network Functions in Cisco Enterprise Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVIS) to cloud-native applications and containers.
Cisco NFVIS provides software interfaces through built-in Local Portal, Cisco vManage, REST, Netconf APIs, and CLIs. You can learn more about NFVIS at the following resources:
◉ Virtual Network Functions lifecycle management
◉ Secure Tunnel and Sharing of IP with VNFs
◉ Route-Distribution through BGP NFVIS system enables learning routes announced from the remote BGP neighbor and applying the routes to the NFVIS system; as well as announcing or withdrawing NFVIS local routes from the remote BGP neighbor.
◉ Security is embedded from installation through all software layers such as credential management, integrity and tamper protection, session management, and secure device access.
◉ Clustering combines nodes into a single cluster definition.
◉ Third-party VNFs are supported through the Cisco VNF Certification Program.
Integrate Cloud-Native Applications with Cisco Kubernetes
Collaborative Tools to Simplify Cloud Native Container Applications
Thursday, 25 August 2022
Rise of the Open NOS
Open networking Innovations are largely driven by an industry need to protect network platform investments, maximize supply chain diversification, reduce operating costs, and build a homogenous operational and management framework that can be consistently applied across platforms running standardized software. By virtue of its adoption by cloud scale operators and its most recent inclusion in the Linux Foundation, SONiC has gained tremendous momentum across different market segments. This blog outlines key factors relevant to SONiC adoption, its evolution in the open network operating system (NOS) ecosystem, and Cisco’s value proposition with the SONiC platform validation and support.
Why use an open NOS?
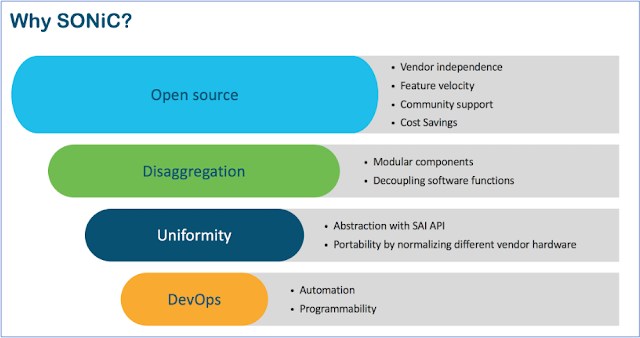
Disaggregation enables decoupling hardware and software, giving customers the ability to fully exercise plug-and-play. An open-source NOS like SONiC can provide a consistent software interface across different hardware platforms, allowing for supply chain diversity and avoiding vendor lock in, further leveraged by in-house custom automation frameworks that don’t have to be modified on a per-vendor basis. A DevOps-centric model can accelerate feature development and critical bug fixes, which in turn reduces dependency on vendor software release cycles. The open-source ecosystem can provide the necessary support and thought leadership to enable snowflake use cases prevalent in many network deployments. The freedom to choose can protect investment across both hardware and software, thus leading to significant cost savings that further reduce total cost of ownership (TCO), operating expenditures (OpEx), and capital expenditures (CapEx).
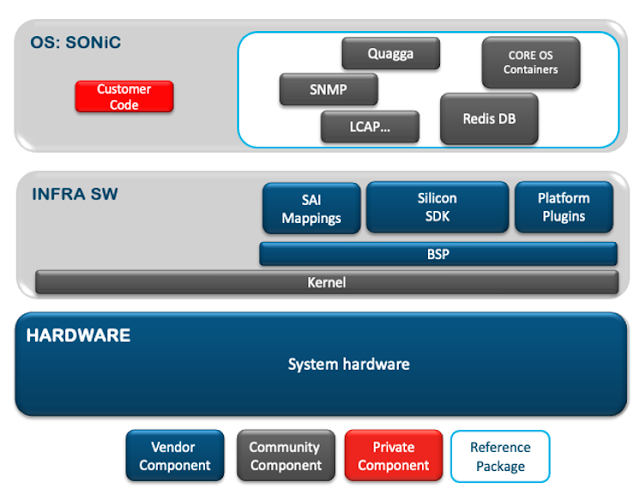
What is SONiC?
SONiC (Software for Open Networking in the Cloud) was created by Microsoft in 2016 to power their Azure cloud infrastructure connectivity. SONiC is Debian based and has a microservice based containerized architecture where all major applications are hosted within independent Docker containers. In order to abstract the underlying hardware and ASIC, SONiC is built on SAI (Switch Abstraction Interface)which is a standardized vendor neutral hardware abstraction API. The NOS provides north bound interfaces (NBIs) to manage the device and these NBIs are based on gNMI, ReST, SNMP, CLI, and Openconfig Yang models so it’s easily integrated with automation frameworks.
Why SONiC?
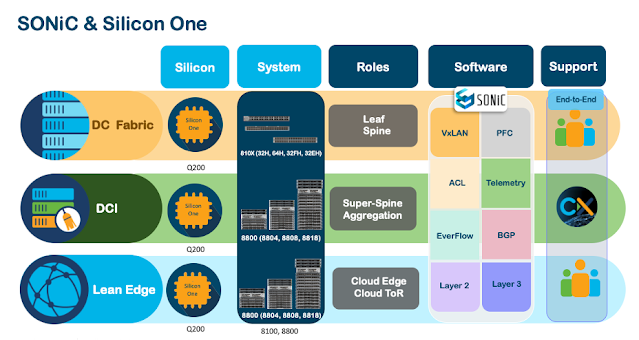
Where does SONiC fit in various use cases?
SONiC in the real world
The Cisco 8000 Series advantage
Support
Tuesday, 23 August 2022
Cisco Project, “An-API-For-An-API,” Wins Security Award
Enterprise software developers are increasingly using a variety of APIs in their day-to-day work. With this increase in use, however, it is becoming more difficult for organizations to have a full understanding of those APIs. Are the APIs secure? Do they adhere to the organization’s policies and standards? It would be incredibly helpful to have a suite of solutions that provides insights to these questions and more. Fortunately, Cisco has introduced our An-API-For-An-API project to address these concerns.
Introducing
An-API-For-An-API (AAFAA) is a project that controls the end-to-end cycle for enterprise API services and helps developers, from code creation to deployment into a cloud, provisioning of API gateways, and live tracking of API use while the application is in production. Leveraging APIx Manager, an open-source project from Cisco, it combines CI/CD pipelines where API interfaces are tested to enterprise (security) policies, automatic deployment of applications behind an API gateway in a cloud system, and dynamic assessment of the API service through.
Figure 1. provides an overview of how the various pieces of the AAFAA solution fit and work together. Let’s look at the pieces and what insights they each provide the developer.
AAFAA in Practice
What Else?
Saturday, 20 August 2022
Optimize and secure transit fleet management with visibility to connected devices and secure remote access
Children have been singing “The wheels on the bus go round and round” since 1939. What’s new today is the tech that keeps those wheels rolling safely and on schedule.
Transit fleet operators work towards achieving on-time performance and vehicle reliability in order to attain safety, cost, and ridership goals. That requires deploying new technologies to improve operational efficiency and predictability. Who doesn’t like a bus service that’s on-time, reliable, safe to ride and has other perks such as free WiFi?
Some ways transit fleet operators are increasing operational efficiency include leveraging vehicle telematics, remotely connected devices in the vehicle, real-time vehicle location, and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors. Together these devices and information provide critical data to the operations center via the Cisco Catalyst IR1800 Rugged Series cellular and Wi-Fi router.
Some of the connected devices on buses today include:
➣ Computer-aided dispatch and automatic vehicle location (CAD/AVL). These transmit route and real-time location information so dispatchers can see if the bus is on time, ahead or behind schedule.
➣ Vehicle telematics to monitor engine temperature, oil pressure, emissions, fuel economy, etc. in support of predictive maintenance.
➣ Fare collection systems for plastic card or mobile payment.
➣ Passenger counting, which is useful for route capacity planning and complying with pandemic-related occupancy restrictions.
➣ IP security cameras that capture video triggered by events like doors opening and closing or the driver pressing a distress button in the event of a disturbance.
➣ Voice communications between the driver and dispatch center.
Operational efficiency takes a hit whenever one of these connected devices, IoT sensors or the vehicle telematics system stops working because buses are often simply taken out of service when issues like these are reported. If the CAD/AVL system goes offline, for example, the fleet operator can’t provide accurate ETAs to passengers on digital signs and online schedules. Loss of the fare collection system results in revenue loss for the transit agency as passengers ride for free. Loss of a video camera feed might prevent the counting of passengers or visibility of a potential safety threat as passengers enter and exit the bus. And an outage on a vehicle telematics system might result in a breakdown that could have been detected and prevented—inconveniencing passengers and requiring the operator to assign an on-call driver and replacement vehicle to take over the route. That’s costly and inconvenient. As fleet operators grow and the number of vehicles that need to be supported increases, these issues are further magnified.
Visibility and secure equipment access boost operational efficiency
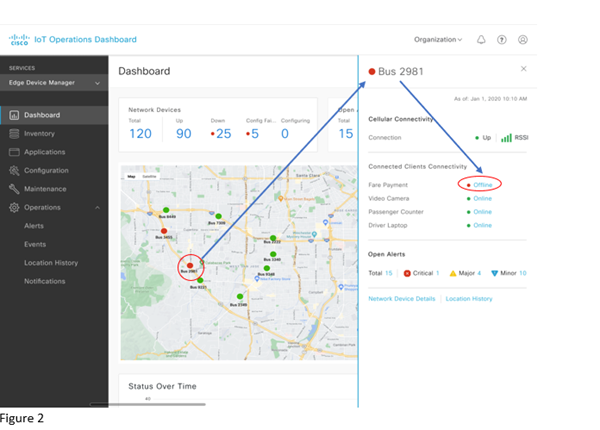
Now, fleet operators can quickly detect, assess, and fix problems with connected equipment using the Cisco IoT Operations Dashboard. It’s a modular cloud service with a simple user interface to help operations teams view important data about the health and operational status of connected equipment and sensors, using the IR1800 cellular Wi-Fi router (see Figure 1).