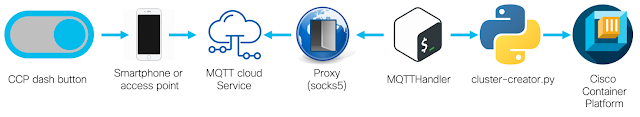
However, aggregating access to multi-cloud applications from multiple branches to regional CoLocation facilities may be a better solution for:
◈ Multi-national organizations that prohibit using direct internet connections to cloud and SaaS platforms at the branch level due to data security restrictions and international privacy regulations for cross-border sharing of personal information.
◈ Global organizations, such as financial institutions, that often have thousands of branch offices spread over multiple geographic regions, each one requiring high application QoE with granular security over traffic segmentation and application access; providing each site with an edge router may not be the most cost-effective implementation.
◈ Partners and vendors, who are not using SD-WAN, still need connectivity to their customers’ enterprise resources and applications but do not want to install a customer’s SD-WAN routing appliance in each of their sites to provide secure access.
◈ Remote workers—at home offices or mobile—need secure VPN connections to enterprise resources over inexpensive direct internet links without backhauling traffic to a VPN firewall at a central data center and incurring additional latency that affects application performance and voice/video quality.
In these cases, it can be more efficient and economical to regionalize SD-WAN services in colocation facilities that are physically closer to the branches and often may even host the cloud resources they need to access. Creating a software-defined virtualized multi-cloud onRamp for CoLocation facilities to serve groups of regional branch offices, partners, and a remote workforce, provides consolidation, control, and security for large distributed organizations and those with regulatory compliance challenges.
Consolidation, Control, and Security
To simplify the deployment and management of SD-WAN for multiple branches distributed over several regions, Cisco is introducing the Cisco SD-WAN Cloud onRamp for CoLocation. This new capability expands Cisco SD-WAN onRamp features that make it easy to optimize IaaS and SaaS performance. The platform of virtualized network functions (VNFs) and trusted hardware runs in a colocation facility to provide connectivity to multi-cloud applications, along with an integrated security stack and cloud orchestration for remote management.
A typical use case for implementing a Cloud onRamp for CoLocation is an enterprise that has dozens of distributed branch offices, clustered around major cities, spread over several countries. The goal is to tie each branch to enterprise data center databases, SaaS applications, and multi-cloud services while meeting SLAs and application QoE expectations. Each region encompassing the target cities uses a colocation IaaS provider that hosts the Cisco Cloud onRamp for CoLocation, which consists of physical and virtual components:
◈ Cisco SD-WAN vManage for centralized management of the SD-WAN Fabric, the Cloud onRamp for CoLocation feature makes it easy to manage policy and deploy VNFs in a colocation facility.
◈ Cisco Cloud Services Platform (CSP) 5444 for hosting the VNFs.
◈ Cisco Catalyst 9500-40 Switches provide multi-gigabit backplane switching to VNFs, redundancy, inbound/outbound WAN connectivity, and access to colocation management tools.
With Cisco SD-WAN Cloud onRamp for CoLocation operating regionally, connections from colocation facilities to branches are set up and configured according to traffic loads (video vs web browsing vs email), SLAs (requirements for low latency/jitter), and Quality of Experience for optimizing cloud application performance. Each branch or private data center is equipped with a network interface that provides a secure tunnel to the regional colocation facility. In turn, the Cloud onRamp for CoLocation establishes secure tunnels to SaaS application platforms, multi-cloud platform services, and enterprise data centers. All traffic is securely routed through the Cloud onRamp for CoLocation stack which includes security features such as application-aware firewalls, URL-filtering, intrusion detection/prevention, DNS-layer security, and Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) Threat Grid, as well as other network services such as load-balancing and Wide Area Application Services.
Multi-Cloud, Multi-SaaS Connectivity with Security and Trust
With virtualized Cisco SD-WAN running on regional colocation centers, the branch workforce has access to applications and data residing in AWS, Azure, and Google cloud platforms as well as SaaS providers such as Microsoft 365 and Salesforce—transparently and securely. Distributing SD-WAN functionality over a regional architecture also brings processing power closer to where data is being generated—at the Cloud Edge. It’s at this intersection of the network, cloud, and security where businesses face greater risks, inconsistent application performance, and increasing complexity. The Cisco Cloud OnRamp for CoLocation applies consistent security policies across branches, devices, and people depending on authorized access requirements, even when multiple service providers are routing traffic.
With the SD-WAN functionality hosted in a colocation facility, ensuring that router appliances and software are original Cisco products and have not been tampered with at any stage of installation and operation is a critical consideration. That’s why Cisco embeds an encrypted Secure Unique Device Identifier (SUDI) in tamper-resistant silicon in SD-WAN router appliances. This foundational level of trust is complimented with VNF image signing, secure boot, and the Cisco Secure Development Lifecycle to ensure software and hardware are tamper-proof. With this built-in level of trust established, IT can remotely configure and manage Cisco Cloud onRamp for CoLocation installations from the other side of the world with confidence that the target Cisco hardware and software are original and uncorrupted.
Open Architecture Integrates Third-Party Functionality
Recognizing that enterprises with distributed workforces and regional offices often rely on a variety of networking products, the Cisco Cloud onRamp for CoLocation has an open architecture, enabling third-party VNFs to integrate with the SD-WAN fabric. For example, even though Cisco SD-WAN comes with an integrated security stack, an organization may already have trained and programmed a third-party security firewall or Intrusion Protection solution and wish to integrate those services in each Cloud onRamp for CoLocation. Other VNFs such as Load Balancers and Web Application Security can be added as needed to conform to an enterprise’s existing configurations and security policies. The Cisco Cloud onRamp for CoLocation fully supports custom applications as well, using a custom packaging tool to bundle the specialized apps and integrate them into a service chain.
Secure Multi-Cloud Connectivity—Everywhere You Need It
Whether deploying SD-WAN at the cloud edge to serve an individual branch office or via colocation facilities to serve multiple regional sites, Cisco provides simplified orchestration and automation of enterprise WAN service chains. Our software-defined architecture ties together a distributed workforce with multi-cloud applications using VNFs that can be rapidly provisioned and expanded on flexible colocation platforms to meet evolving business needs and regulatory requirements. Keeping regional offices connected and productive is more cost effective and easier to manage than ever.