Optimize your Workspace Through Control Hub
As announced at Cisco Live, we have introduced a new range of intelligent features in Control Hub under the new Workspaces tab. This will revolutionize the way IT, facilities, and HR work together, making the transition back to the office as seamless and safe as possible.
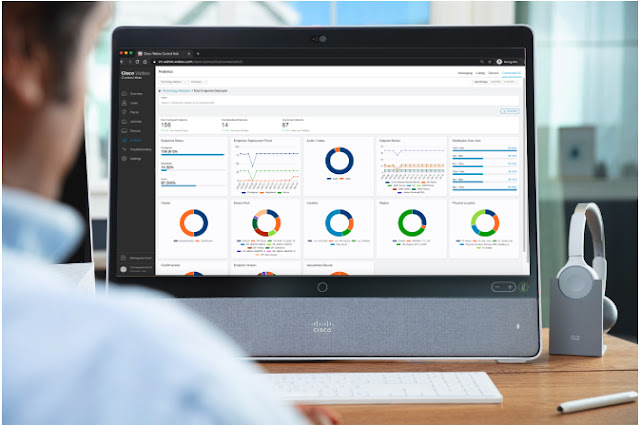
Control Hub is the single pane of glass management platform that provides administrators a view into their Devices, Meetings, Calling and Messaging environments, all without transitioning to different tools. Administrators have the ability to deep dive into analytical trends or troubleshoot reported issues directly in the platform. On the devices side, Control Hub has mostly focused on technical issues, such as packet loss and jitter. Now, we are expanding that to include what is happening in the physical workspace! By giving visibility into what is happening in the workspace, you will gain deeper insights into emerging and existing trends within the four walls of your workspace. Knowledge is power, and with these new insights, you can make better strategic decisions.
How to Navigate the Workspaces Tab
The first part of this new Workspaces section is the ability to set a “Workspace Type.” You can choose between a plethora of room types, such as “Meeting Room”, “Huddle”, or even “Desk.” This allows for effortless filtering and reporting on different workspace types to easily find trends. For example, if a certain style of workspace is not being adopted, or it is all the rave being spoken about around the coffee machine!
The other new attribute you can add to a workspace is capacity. Now administrators can easily find out their capacity in certain locations or find out if their workspaces are being utilized correctly. If the capacity is exceeded, you will be notified with visual indicators. This makes it easy to ensure you are staying in line with the recommended people counts in different rooms.
Real-Time Utilization and Environmental Data
That leads me to the next new change in Workspaces, and that is the ability to see real time usage of utilization and occupancy directly in Control Hub – no need to refresh! This data is not just limited to showing whether the room is being occupied or by how many people, but it also has environmental data like ambient noise level and sound levels. This data is vital to ensure the workspace is the set up for collaborative success. A workspace with ambient noise above a certain dBA level will impact the quality of the meeting experience, both for in-office and remote participants. No one wants to work in a noisy environment. It is simply distracting!
Let’s say you need to install some acoustic treatment based on the recommendations of our advanced troubleshooting tools to test the reverb of the meeting space. Then it is useful to know whether the workspace is booked for later, so that you can schedule the best time to intervene. We got you covered! You don’t even need to leave Control Hub to view the calendar in a different application – booking information for the next 24 hours is right at your fingertips. For privacy reasons the meeting title won’t be exposed, so no worries there.
These are just some of the changes, all designed to give administrators a better experience and help manage their workspaces and devices more efficiently. With the ability to see data directly on one page, it really is like a virtual cockpit for your workspace!
This is just the start of a journey. We are investing in bringing more tools and metrics of the workspace to the fingertips of administrators, the next thing on our roadmap is bringing historical metrics and APIs to connect to existing workflows.