Cisco DNA Center has seen several releases with significant innovation and the evolution of the product platform. With DNA Center capabilities aligned to Gartner’s four IT personas (AIOps, NetOps, SecOps, and DevOps), it is important to take a step back and look at the platform or networks-put the “underlay.”
With changes in the IT landscape, several megatrends are shaping what the network platform needs to deliver. With the new landscape where both applications and users are on the move, the face of the campus network has changed and expanded.
Figure 1. Megatrends shaping digital transformation
Cisco DNA Center Virtual Appliance, deployment flexibility
With applications moving to the cloud, it is no surprise that management platforms are moving to the cloud. Cisco DNA center is no exception. DNA Center is now able to run on AWS, and the deployment of the AWS VA takes under an hour from start to finish. A lot of flexibility is also provided to the end user through the support of a launchpad to automate the installation or through a manual mode for users who already have a custom AWS environment. DNAC install is completely programmatic in both cases (no login to shell required!)
At this point, users can get on the Cisco DNA Center UI and begin configuration, discovery, and more.
Figure 2. Virtual Appliance Diagram
Following AWS, a VMWare version of the appliance will be released, allowing customers to use their existing VMWare infrastructure to run Cisco DNA Center instead of a physical appliance. As part of Cisco’s commitment to the platform, no matter how you deploy Cisco DNA Center, users will see feature parity it is the same Cisco DNA Center code and capabilities.
Hardened Security Features
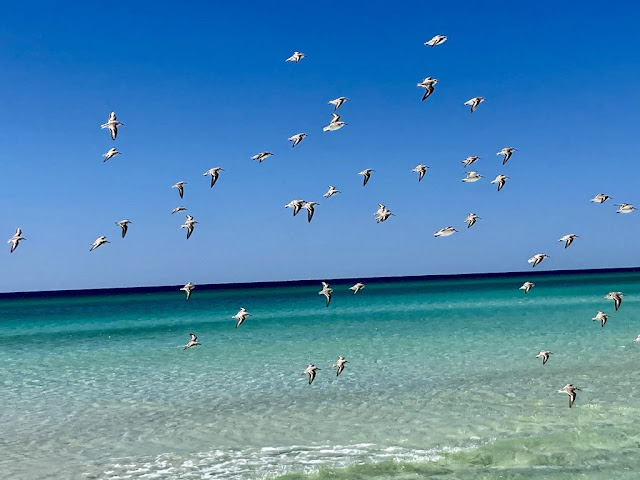
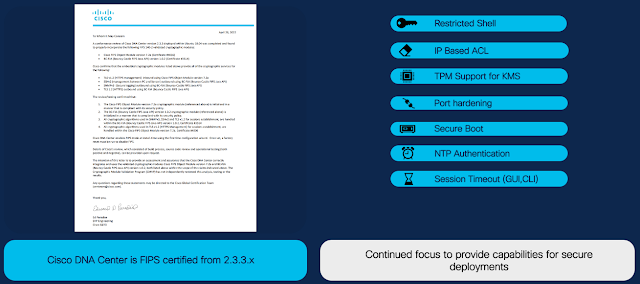
Some verticals, industries, and organizations have specific security requirements mandated, such as FIPS.
Activation of FIPS compliance at Cisco DNA Center install time enables security features such as secure boot, TPM, session timeouts, and password expiration. When data is shared using weak or deprecated ciphers, that data is at risk of being decrypted by malicious actors. Cisco DNA Center now supports FIPS 140-2-compliant cryptography modules, ensuring that only strong NIST-approved ciphers are used and enabling deployment in security-conscious verticals such as the public sector, finance, and healthcare.
Figure 3. FIPS compliance letter
ACL to management access for Cisco DNA Center appliance
By popular demand – many customers utilize ACL’s to control access to the network devices for management. As Cisco DNA Center is now the centralized monitoring and management point for network estate, customers can now create ACL’s to control what networks or IPs can access the Cisco DNA Center UI
Restricted shell support
Again by popular demand customers have requested to provide an enable shell for DNA Center so that sensitive CLI commands can be protected at all times. DNAC now comes with a restricted shell as standard and only non-invasive CLI is allowed to be run on the console. For any CLI which requires root level / Sudo permissions, the shell will default deny it. A special token needs to be acquired to remove the restriction.
Scale – the agility to keep up with your business
Scale is a constant growth factor with post-pandemic life coming back to normal, with the proliferation of IoT and OT devices on the network on the rise. There is a constant need to ensure that the network management and orchestration platform can continue to scale with the network and business needs. With each release, Cisco DNA Center team has been making continuous strides with an increased platform scale. Recent scale updates for version 2.3.3 include up to 6,000 sites and 24,000 devices (Access Points and Network Devices for both Fabric and non-fabric networks).
Figure 4. DNA Scale
Remote support
As part of improving the support engagement between customers and TAC, at times providing TAC easy access to the equipment has contributed to extending the MTTR (Mean time to repair). To ease the process, customers are now able to allow TAC access to network equipment via Cisco DNA Center. This solution enables the customer to provide TAC-specific access to equipment and the ability to revoke access at any time.
Figure 5. Remote Support Activation
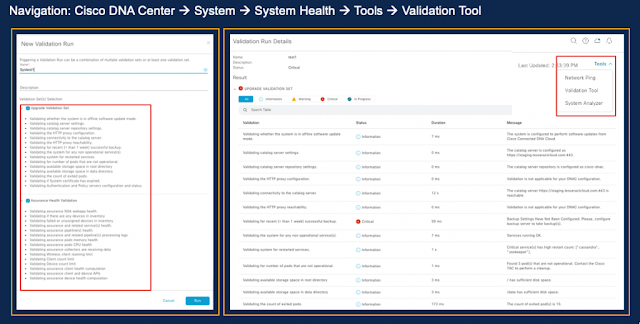
Aura (Audit & Upgrade Readiness Analyzer)
AURA stands for Audit & Upgrade Readiness Analyzer and performs various health, scale, and upgrade readiness checks for the Cisco DNA Center and the rest of the Fabric network. The tool is extremely simple to run and is executed on the Cisco DNA Center.
Figure 6. AURA screen image
The tool uses API calls, DB reads and CLI show commands (read-only operations) and hence, doesn’t affect performance or cause impact the Cisco DNA Center or the networking devices. This functionality was built in collaboration with Cisco DNA Center Escalation Engineering, Sales, and CX Centers TAC Engines team to ensure an efficient upgrade experience. AURA Tool Check Areas:
◉ DNA Center Scale Test
◉ DNA Center Infra Health
◉ DNA Center Assurance Health
◉ WLC/eWLC Assurance Health
◉ SDA Device CLI Capture
◉ SDA Control & Security Audit
◉ Software Bugs Causing Upgrade Failures
◉ Upgrade Readiness Checks
◉ SDA Compatibility Check (Switches, Wireless Controllers & ISE for 2.2.2.x)
◉ DNAC-ISE Integration Checks
◉ Fabric Devices Configurations Capture and Compare using inbuilt diff tool
Figure 7. System Analyzer screen image
Source: cisco.com