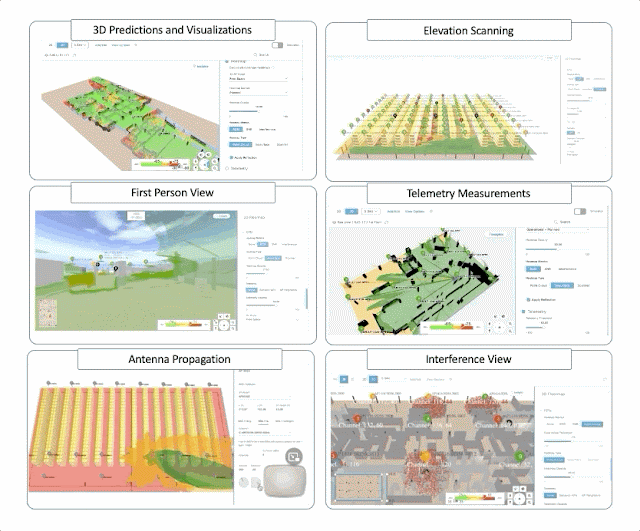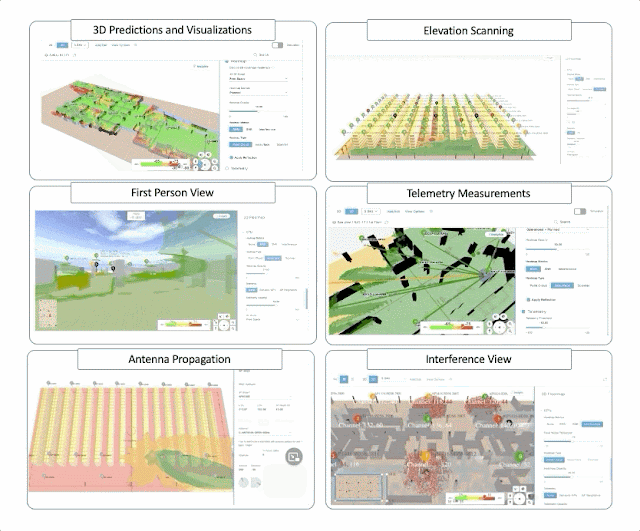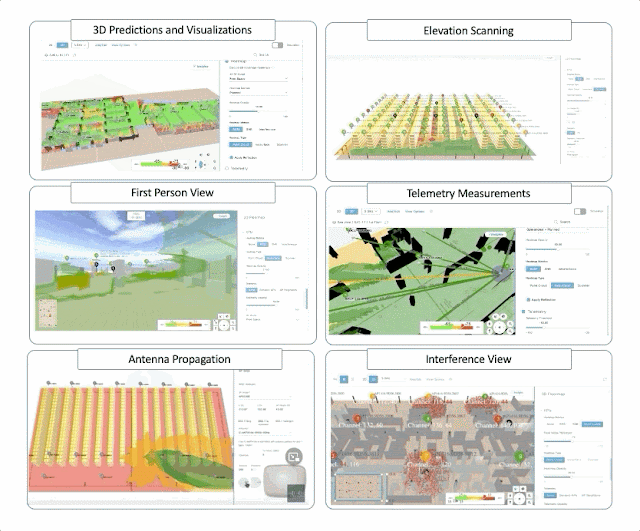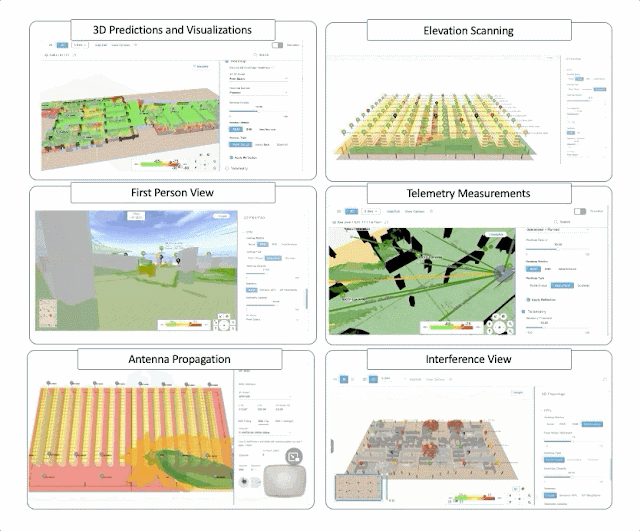
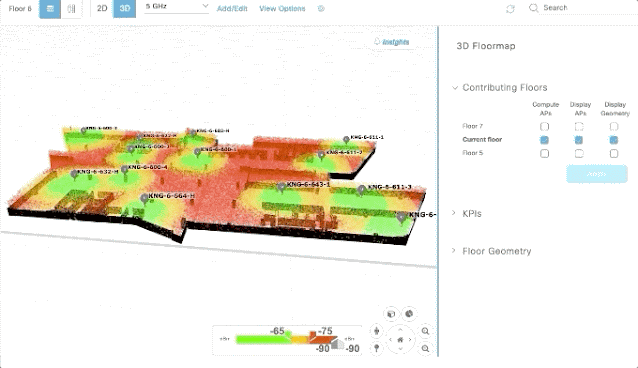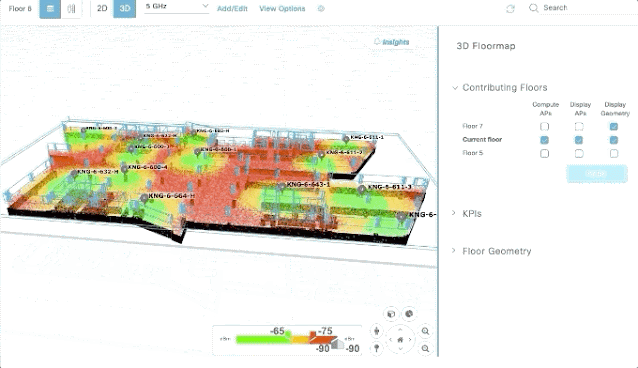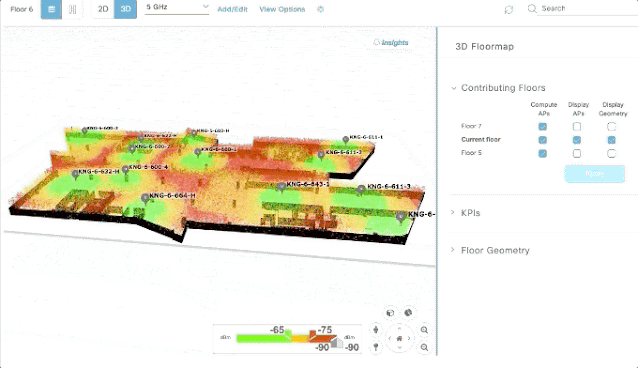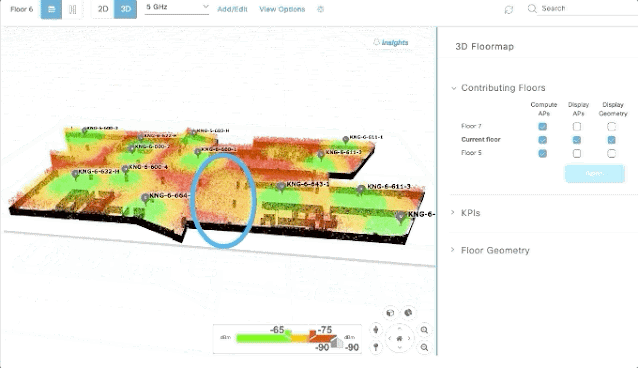
As part of our digital transformation, my Cisco colleagues and I were getting trained on business agility in our ONEx organization. Any transformation needs an effective way to measure the success at the end and throughout, and as part of our initiative, I could see there was enough awareness and emphasis given to metrics and measurements.
The training also addressed some points from the book “Measure What Matters,” which peaked my curiosity and inspired me to start reading it. It is a fantastic book with the origin of the Objectives and Key Results (OKR) concept and how companies have leveraged the framework. I wanted to share a bit here about how Cisco also embraces this framework – and more – in our organization, in a slightly customized and enhanced way, and how it can be extended further.
Finding Middle Ground between Vision, Strategy, and Execution
Although the OKR framework has generated more interest in recent decades, goals and metrics themselves have long been the foundation to any company to identify, set and succeed. As with technology, our approach to goals and metrics has also evolved over the time, namely to include a couple key concepts: MBO or Management by Objectives, and VSE or Vision, Strategy & Execution, extension of this, VSEM, to include Metrics.
Vision
The Vision has represented the true north-star of what the company wants to achieve. If we time box it, perhaps, 3 to 5 years or beyond, Vision does not change often unless the company goes through a major transformation or change of business. However, at an organization level or function level, it could change a bit but still align to the overall company vision. And, as you can imagine, there is still a healthy internal debate about whether one should have ONE single vision for all or a vision at each lower of functional levels – and different companies handle it in different ways.
Strategy
While Vision is a starting point, we need other elements to take it further. Strategy is the next level of Vision – how you plan to accomplish the vision. This could be multiple levers (or initiatives or methods or ways) to achieve the vision: A strategy, approach, or means to plan for the execution of it and, finally, deliver the desired outcome or results.
Execution
If Vision is the desired outcome, and Strategy is the big plan, then Execution is the detailed plan. The key to Execution is measurement, and thus it is often broken into smaller chunks – goals or objectives – which are easier to accomplish and show progress.
Finding Meaningful Measurements
In the process of transforming our operations I’ve found several things to be true, and helpful, during this endeavor:
1. As Peter Drucker said, “What cannot be measured, cannot be improved“, but even before improving upon a thing, identifying and establishing the right set of metrics is key for any goal. Drucker also observed, “A manager should be able to measure the performance and results against a goal.” However, truly effective organizations must not limit measurements to the management level, but instead, equip employees at every level to identify and track meaningful metrics. These metrics could be milestones or KPIs and can be annual, quarterly, or even monthly. Some of these metrics could be in multiple systems (say ERP or CRM or ITSM) or Project Portfolio Management tools. The goals and objectives can be (and in some cases should be) inherited either vertically or across the organization or cross-functionally beyond the organization for shared goals.
2. When employing new measurement metrics within a company, the ideal scenario would be to integrate, automate, and bring all of these metrics into one single dashboard. A one-stop shop for metrics viewing simplifies the process, ensuring that there is minimal manual work involved in updating these metrics periodically. Several of the SaaS solutions provide APIs that can be used to easily integrate and get the needed metric and based on a set threshold, can even provide indicators about whether metrics have been achieved, and communicate that critical information in real-time to impacted teams.
3. Although Goals & Results could be separately reviewed from employee performance review discussions, the ideal would be to review them together.
4. WHAT was achieved should be equally evaluated with HOW it was achieved. Equally important to the Vision are the types of behaviors that were exhibited to accomplish these results, and they should be reviewed to ensure that we understand and agree with the methods and the values represented in the achievement.
5. It’s critical that metrics and measurements are looked at holistically and together. Operationalization of the entire framework, process, or activity makes it efficient for the organization, but defining and setting meaningful metrics cannot be a one-time activity. Putting a structure and defining these annually is a good start but this is just the beginning – goals need to be measured, reviewed, revisited, and adjusted as needed.
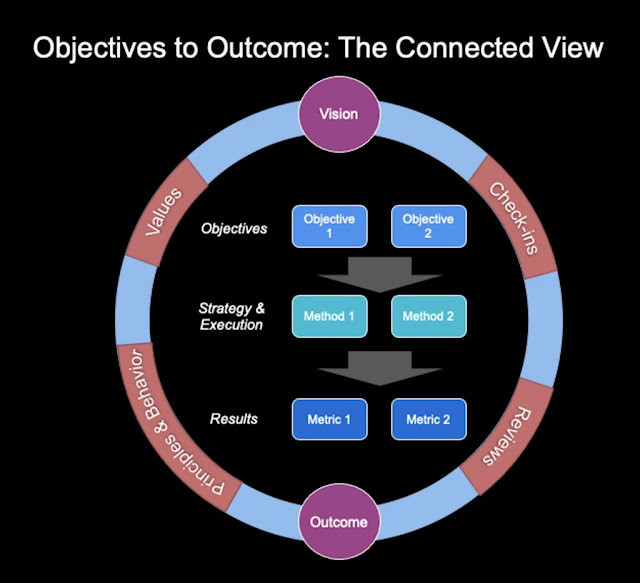
Operationalization of the OKR framework can include various elements:
1. Conducting reviews at Initiative, Program, and Project level – leveraging metrics from the Portfolio Management and other IT Systems/Tools
2. Organizational health metrics from various sources
3. Ongoing operational reviews (RtB or Run your Business) – both IT (ideal to do weekly, monthly, and quarterly) and Business Reviews (ideal is Quarterly)
Among all of these observations I’ve made through this process, one of the most critical ones is that the information about meaningful metrics cannot be created and kept safe somewhere secretly. Instead, it needs to be published centrally, so that anyone can check on the goals of their colleagues and leaders at any point in time. This not only brings transparency and trust but also avoids duplication when found.
We are still in the process of creating a more mature, sophisticated practice around our internal OKRs, and in parallel, my colleagues across Cisco are also applying metrics to inform smarter, more efficient operations within our customer organizations.
For those who want to dig into the topic even more deeply,
click here to learn more about how Cisco’s IoT practice is using metrics as a powerful tool in our customers’ digital transformation.
On that note, how is your team doing it? What can you share about what it takes to set and achieve measurable goals in your organization’s digital transformation?
Source: cisco.com