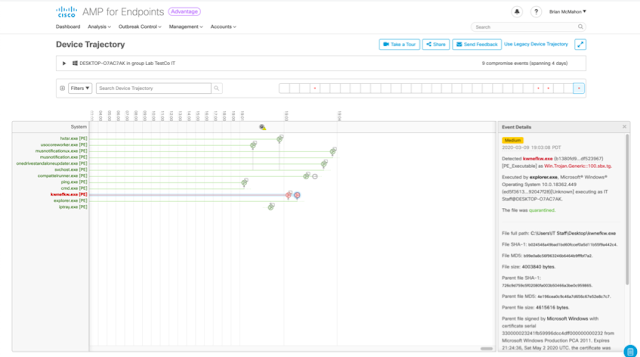
Digital transformation is essential for all businesses, from the smallest to the largest of enterprises. These businesses are striving to become more agile, innovate quickly, and respond to change faster – and they’re turning to modern applications to fuel that change. One of the first steps businesses need to take when commencing on a digital journey is to answer two critical questions: “What business outcomes do you want to achieve?” and “How will you overcome new demands digital transformation places on your IT teams?
There is a saying, “If you are not moving forward, you are falling behind.” This statement could not be any truer than it is in today’s complex and application centric environments.
The History of Digital Transformation
If we look back at Netflix’s journey to reshape markets through digital transformation, it’s easy to see how embracing digital transformation helped the company move forward. As most of us know, Netflix led the way for digital content when it started in 1997 by offering DVD rentals and sales via its website. Customers quickly saw the value in its data insights, called the “Personalized Recommendation System,” which used member ratings to accurately predict a user’s next movie choice. A decade later, in 2007, the company began offering streaming content for personal computers. Another decade passed and in 2017 Netflix won its first academy award for best documentary.
In its first 20 years, Netflix transformed its business model from mailing digital content to streaming digital content, and finally, creating digital content. Why did Netflix succeed when so many others didn’t? Because of its rapid adoption of digital transformation tools and apps. There were many companies that entered the space with Netflix, but those that didn’t embrace digital transformation not only couldn’t keep up, most are no longer in business.
In today’s application centric world, innovations need to happen in days or weeks, not decades. Is your company ensuring its application tools, operations, networking, and security features are working together to transform your business?
Application Challenges Landscape
All industries are making the shift to become more application centric, putting them into a place where they compete on application experience. But to compete effectively, they need to iterate quickly, learn with real-time telemetry, and get that feedback incorporated back into the business application. Changing the way companies monitor and maintain application availability, performance, and security means it’s imperative that they shift their operational model from siloed to collaborative teams. These collaborative teams then need to understand what’s going on from the business perspective to the user experience to the applications performance, the infrastructure, the network, and the security domain.
Enhance your day-to-day tools with a digital upgrade
Customers use many tools to monitor and alert when issues surface. Application Performance Monitoring (APM) and network performance monitoring tools give detailed insights within their silos. While those individual parts are important, what really matters is how those tools work together, as well as how they impact application performance and the end user experience.
Cisco is uniquely positioned with its broad product portfolio to provide the tools, insights, automations, and integrations that give users visibility across the entire stack, otherwise known as “full stack visibility.” This delivers insights into application-to-application dependencies, application-to-infrastructure dependencies, infrastructure performance and availability, infrastructure resources utilization (compute, storage, and memory), end-to-end visibility, and business outcomes. To improve performance and availabilty, protect the workload wherever it’s located, reach a faster MTTR, and maintain exceptional customer experience requires giving day-to-day tools a digital upgrade.
In order to ensure your company has the best digital journey possible, the following products offer additional insights and automation:
Data Insight Tools
◉ AppDynamics (AppD). An application performance management (APM) tool that manages performance and availability of applications across cloud and DC. Appd baselines, monitors, and reports on the performance of all transactions that flow through your app.
◉ Cisco Workload Optimization Manager(CWOM). Software that continuously analyzes workload consumption, costs, and compliance constraints, while automatically allocating resources in real-time. It assures workload performance by giving workloads the resources they need, when they need them.
◉ Tetration. Hybrid-Cloud workload protection platform to secure workloads. Using machine learning, behavior analysis, and algorithmic approaches to offer holistic workload-protection strategy. This approach allows the implementation of true micro-segmentation, proactive identification of security incidents, and reduction of attack surface by identifying software vulnerabilities.
Automation Tools
◉ ACI anywhere. Technology that supports integrating virtual and physical workloads in a programmable, multi-hypervisor fabric to build a multiservice or cloud data center. The ACI fabric consists of discrete components that operate as routers and switches, but it is provisioned and monitored as a single entity.
◉ Intersight. A unified management platform that delivers intuitive management across data centers and remote locations from a single management platform. This platform offers an intelligent level of management that enables IT organizations to analyze, simplify, and automate their environments in ways that were not possible with prior generations of tools.
◉ Networks Assurance Engine (NAE). A comprehensive, intent-assurance solution that mathematically verifies the entire data center network for correctness, providing users with the confidence that the network is operating as intended.
◉ CloudCenter (CC). Multi-cloud management software that helps enterprises work with disparate environments. CC delivers workflow automation, ALM, cost optimization, and governance across multiple clouds.
It’s much easier to identify the root cause of an issue quickly and accurately with a tight integration of the above-mentioned products, third party applications, such as ServiceNow, InforBlox, Moogosoft, and more, along with end-to-end dependencies and the specific details of each layer. By doing this, your IT teams will work collaboratively and not in solitude.
A subset of the integrations and how the products collaborate to bring exceptional application experience
The diagram above shows how Cisco ACI, with AppD integration, identifies problems faster by correlating applications and network data. Cisco then provides the dynamic correlation between application and network constructs, and notes the problems with application services on a network fabric that can then be investigated by the application and networking teams, each with their own separate tools.
NAE will inform CWOM of any network anomalies so those issues are part of the recomendation process CWOM uses in its decision engine. NAE effectively makes CWOM “Network Aware,” and CloudCenter will model an application and apply an AppD agent as part of that profile. Deploying the AppD enabled profile using CC will allow the AppD controller to trigger action for CC based on metrics from AppD. Tetration and CWOM team up by using Tetration’s analytics. CWOM can take Tetration’s application dependency mapping between endpoints by localizing chatty workloads that were across clusters, datacenters, and cloud to reduce latency.
Application Needs Rule the Day
It’s no longer adequate – or sustainable – to take a legacy approach to ensuring application experience, availability, and security are working properly in today’s technology environment. These modern day applications demand superior experience be delivered, whether they are executed on-prem, hybrid, or in cloud datacenters. Using a combination of tools from Cisco enables the scale, performance, visibility, and operational excellence needed for efficient deployment of all next-generation applications, helping companies overcome their greatest digital transformation challenges.