Right now, I am sitting at home thinking about how the world is being held together by the Internet. So far, the Internet has stood up to our new reality amazingly well. This is despite redistributed traffic loads, and an explosive growth in interactive, high-bandwidth applications. For a brief time at least, even casual users are recognizing and appreciating the network’s robustness and availability.
We shouldn’t bask in this success yet. Failures will happen. And some of these failures might result in application impacts which could have been avoided. If you are an Enterprise Operator, now is the perfect time to examine your design assumptions against the new reality of your network. What weaknesses have become exposed based on the shift to Telework? What needs upgrading considering the shift in application mix and resulting performance requirements?
One way or another, your end users will adapt to what you are providing. And it is best if your network is flexible and robust enough to meet new expectations. Nobody wants end-users to acclimate themselves to a degraded Enterprise network experience.
Key to supporting today’s needs is understanding the flexibility–or lack thereof—of the end-to-end network architecture. For your architecture you need to understand:
◉ the behavior of deployed technologies/protocols,
◉ the strengths and weakness of embedded platforms, and
◉ how your topology can handle application demands while remaining resilient to failures.
Each of these impacts the resulting end-user experience, especially during failures.
But where do you start this architectural analysis? You need to first establish a quantitative basis that measures end-user application availability and performance under various failure scenarios. It is possible to do this as there is a direct relationship between the probability of failure and the end user’s perception of network availability. Such a quantitative basis is essential as availability with acceptable performance is ultimately how a network is judged.
Getting to Five Nines
The best-known metric of network availability is known as “five
nines”. What five nines means is that the end-user perceives that their application is available 99.999% of the time. This permits only 5.26 minutes of downtime a year. Depending on the application and network topology, this can be a very stringent standard.
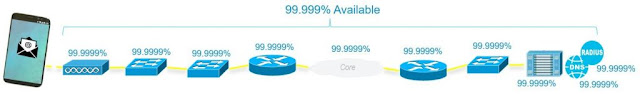
Consider Figure 1 below which shows serially connected routers, switches, access points, servers, and transited clouds. When these ten elements are connected without any redundancy, each of these elements must be up and available 99.9999% (or six nines) of the time for the end-user to perceive five nines of availability. As six nines allows only 32 seconds of downtime, having a single reboot a year could prove problematic.
Figure 1: Serial Transport Availability
The good news is that with the proper network, application, and services architecture, the individual devices making up the Internet do not need to support six nines of availability. All we need to do is add some redundancy. The following network design includes such a well-architected redundancy-based design. For this network design, if each element is fully independent, and if each element is available just 99.9% of the time, then the end-user will experience 99.999% availability.
Figure 2: Parallel Transport Availability
Despite the user’s experience being identical, the difference between the two figures above is huge. We have reduced the availability requirements of all component parts by three orders of magnitude. And we have made something highly reliable from less reliable parts. This really shouldn’t be surprising however. From its very beginnings, the Internet was designed to be available even when devices were lost to nuclear attacks.
In the decades since the Internet’s conception, Cisco has
documented many technologies and approaches to achieving a very high degree of availability. A small subset of these includes quickly converging routing and switching protocols, device and link redundancy, and boot time reduction. But such technologies and approaches are only part of the availability equation. Network operators have the ultimate say in deploying these technologies to maximize network availability. Strategies include the distribution of application servers across geographically and organizationally diverse datacenters, as well as redundancy of access and core networks all the way to ensuring that fiber-optic cables from different service providers don’t run in the same fiber conduit. These strategies are proven to be effective at providing high availability.
The result of all this good network design and planning is that the majority of application availability failures don’t come from equipment failures. Instead they come from equipment misconfiguration. Protecting the consistency of the network configuration is non-trivial and becomes more difficult as you add new technologies to the network. In fact, protecting network consistency is a key reason network operators are choosing to deploy controllers to manage device configuration based on higher level expressions of intent. One of the main goals of network controllers is to automatically ensure correct and consistent configuration of all of the equipment in the network.
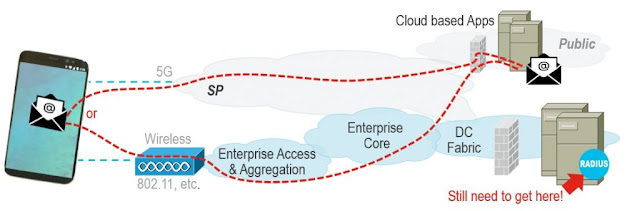
Intent, while very useful in this role, might not address every dimension of application availability. Consider the picture below of an Enterprise network integrated with a Public-Cloud topology.
Figure 3: Public Cloud Apps need Enterprise Authentication
In this network design, the Public cloud-based applications accessed solely through cellular data do not just depend on the cloud. They still depend on the accessibility of an Enterprise’s RADIUS Authentication infrastructure. In other words, at best a cloud-based application will only be as available as access to your Enterprise Data Center. This is a nuance which very few end-users will be able to recognize or troubleshoot as a cause of availability issues.
New Technologies Add Risks to Availability
It is not just the Enterprise’s Authentication infrastructure which we need to consider when thinking about the future of availability. There is a set of forces which are changing network design. Geoffrey Moore has done much work describing the continuous technology invention and deployment cycle. Based on this, it is best to think of the network as a continually changing entity.
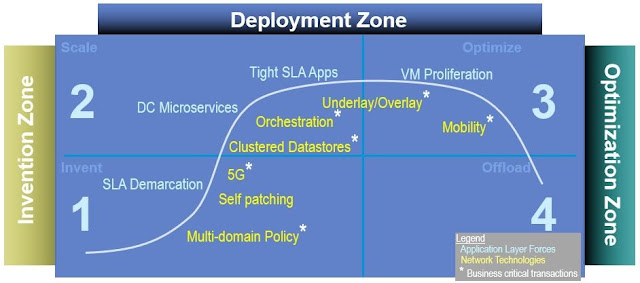
Figure 4 below shows a subset of the forces and technologies which are top-of-mind Enterprise network design. Each of these have the opportunity to improve or degrade application availability if they are not taken into consideration during the network design.
Figure 4: Emerging Technologies Use Controllers
With the advent of Software-Defined Networking (SDN), the emergence and growth of new types of controllers is a trend which broadly impacts network availability calculations. Above in Figure 4, you can see a number of starred* technologies. Each star represents a new controller involved in the establishment and maintenance of an application flow. And the result of each star is the addition of a transactional subsystem which impacts the calculation of network availability.
What are examples of these transactional subsystems? Historically we have depended on transactional subsystems as DNS, BGP, DHCP, and Wireless LAN Controllers. As networks evolve, we are seeing the proposal or introduction of new transactional subsystems such as OpenFlow servers. We are also seeing the evolution of existing transactional subsystems such as RADIUS/Identity. The RADIUS/Identity evolution is quite important here. The evolution of user and workload identification is becoming more complex as cloud systems are integrated into the Enterprise. It is worth considering the impacts to application availability as corporate access control gets more deeply integrated into the cloud via technologies like Azure AD, Google IAP, SPIFFE, and ADFS.
Calculating the Availability of a Component Subsystem
The emerging technologies listed above are changing established network availability profiles. As a result, now is a good time for you to revisit any previous calculations. And if you do not have previous calculations then this may be an excellent time to calculate your availability and determine if it is appropriate.
If you are looking to get started, an excellent primer is the Cisco Press book “High Availability Network Fundamentals“. Although it is from 2001, it is still excellent. Within the book the
free introduction chapter discusses two base concepts upon which system level availability calculations are ultimately constructed. The first concept is Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). MTBF is equal to the total time a component is in service divided by the number of failures. The second concept is Mean Time To Repair (MTTR). MTTR is equal to the total down time divided by the number of failures. You can also think about MTTR is the mean total time to detect a problem, diagnosis the problem, and resolve the problem. Using these two concepts, it becomes possible to calculate expected component availability via the equation:

In this equation, “A” stands for availability, which is expressed as a probability of 0% to 100%. Key in the equation are the words “component subsystem”. A component subsystem can be one device. A component subsystem can also be a network of devices. A component subsystem can even be infrastructure software running on a cloud of virtual hardware. What is critical for the equation is that the
failure modes of this component subsystem are understood and can be quantified.
While the equation itself is simple, quantifying MTBF and MTTR for any component subsystem does take some effort. To begin with you should acquire MTBF estimates for equipment provided by your vendor. You may then choose to adjust these vendor MTBF estimates by considering factors as diverse the age of the equipment and even your local weather. But equipment MTBF is only part of the picture. MTBF for transmission links should also be considered. When estimating these numbers, you need consider questions such as “how often do you see cable cuts or other failures in your environment” and “how well secured are your networking patch panels?”
Beyond MTBF is MTTR of your component subsystem. Getting a history of your MTTR is easy — as all you need to do is divide the total outage time by the total number of repairs during a given reporting interval. But your historical MTTR might not be an accurate predictor of your future MTTR. The longest (and most painful) outages are infrequent. The best way to predict future MTTR is to estimate the average time it takes to make a repair across the universe of all conceivable repairs. This helps you start quantifying infrequent issues. Especially if you are a small Enterprise, you really want to understand the hours or days it might take to diagnosis a new issue type and then a get a spare part installed or a cable fixed by a qualified local support.
If you are interested in quantified examples of MTBF and MTTR, again I recommend “High Availability Network Fundamentals“. This book explores specifics at a useful level of depth.
Looking back at the component subsystem availability equation, it is important to remember that the perception of what a failure is at the overall system level is unlikely to be the same as the definition of a failure in a component subsystem. For example in Figure 2, a failure of any single router component should be invisible at the overall system layer. I.e., MTBF is zero at the system level as there is no user perceived system failure.
However, if there are concurrent failures in redundant subsystems, there will be outages at the system level. We need to account for this in our availability calculations.
Luckily most network failures are independent events. And where networks do have cascading outages, this is often the result of underestimating the traffic needing support during failure events. As a result, simulating traffic during peak usage periods while a network is under load should result in the provisioning of adequate link capacity. And assuming link capacities are properly dimensioned, traditional system level availability equations, such as we describe in this article, can then be applied.
As a network designer, it is important to remember where there are failure domains which can span subsystems. For example, if a clustered database is shared between two nodes, then a failure here will potentially impact what you considered your redundant subsystem. When this is a possibility, it is necessary to dimension this failure type at the system level, being careful not to also double-count that outage type at the component subsystem level.
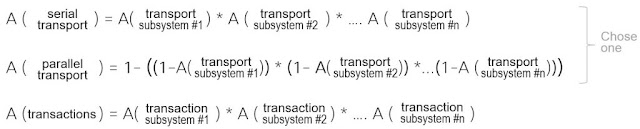
Once you have a handle on your subsystems, you can start assembling larger availability estimates using the three probability equations listed below:
Serial Transport Availability
The first of these probability equations is used to calculate availability when several transport systems exist in serial. Here each transport subsystem encompasses its own failure domain, with its own availability estimate. The availability of a serial transport subsystems is the product of all the subsystems, as the component subsystem failure domains are serialized. That is, if any subsystem in the chain fails the whole system fails. Below is an example of how such a network availability calculation might be made for a simple Enterprise topology where the user application is connected via WiFi to a server located in an Enterprise data center.
Parallel Transport Systems Availability
The second of these equations is where transport systems exist in parallel. In other words, one transport subsystem backs up another. These are, unsurprisingly, known as parallel transport subsystems. The availability of a parallel transport subsystem is 1 minus the chance the multiple subsystems are out at the same time. A good example of such a design would be your home Wi-Fi which is backed up by your service provider wireless data service.
In practice, parallel transport subsystems will eventually connect to some serial subsystem. This is because application servers will typically exist within a single administrative domain. A more complex example of parallel subsystems in practice is shown in the figure below. Here an SD-WAN service is used to back up an Enterprise core network, but the application servers exist in a single datacenter.
Business Critical Transactional System Availability
The third equation calculates business critical transactional availability. This calculation is much like that of the serial transport calculation in that the product of all subsystems is included. However, as a transactional subsystem might only be required at or before flow initiation, it is sometimes useful to separate out this calculation, as shown in the figure below. Here the application user is accessing the network via campus WiFi, the application is itself sitting in public cloud, and the Application Authentication Server (such as a RADIUS single sign-on server) is in the Enterprise datacenter.

Such a calculation shows that the availability of cloud service is dependent on the availability of the enterprise Application Authentication Server. It is interesting to note that perhaps only once a day a user might need to acquire authentication credentials needed to access a cloud service during the remainder of the day. Such caching of transactional information itself can improve availability and scale.
As you use these equations, remember that your results can be no better than the underlying assumptions. For example, each equation is most easily applied where there is a strict hierarchical topology consisting of uniformly deployed equipment types. Topologies with rings and irregular layering either need far more complex equations, or you need to make simplifying assumptions, such as users having slightly different experiences based on where they sit within your topology.
Results of Modeling
After you have constructed these system and component level equations, measure them! It is this measurement data which will enable you to prove or disprove the MTBF and MTTR assumptions which you have made. They might even enable you to make changes before a more serious outage adversely impacts your business.
When you have modeled and measured for a while, you will see that a well-designed, redundant network architecture plays a paramount role in achieving excellent and predictable availability. Additionally, you will internalize how good design results in networks which are capable of five nines to be constructed out of subsystems which individually are not nearly as available.
The results of such calculation efforts might even provide you the business justification needed to make fundamental changes in your network architecture allowing you to achieve five nines. This should not be surprising. This result has been borne out by decades of network operator experience across a variety of deployment environments.
What are your experiences?
As mentioned above, these methods of calculating availability are not new. However they can seem heavyweight, especially to network operators not used to such quantification. As a result, network operators sometimes make simplifying assumptions. For example, some Enterprise operators will assume that their Internet backbone providers are 100% available. Such assumptions can provide reasonable simplification as the backbone might not be part of that individual’s personal operational metrics.
So how do you measure the availability of your operational environment? It would be great to hear from you below on any rules of thumb you use, as well as any simplifying assumptions you make!