In April 2020, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) allocated 1,200 megahertz of spectrum for unlicensed use in the 6GHz band. That was the largest fleet of spectrum approved for WiFi since 1989. This Opening of the 6 GHz band more than doubles the amount of spectrum available for Wi-Fi, allowing for less congested airwaves, broader channels, and higher-speed connections and enabling a range of innovations across industries. Since the FCC decision to open the 6 GHz band, 70 countries with 3.4B people have approved or have 6 GHz regulations under consideration (Source- WiFi-Alliance)
Saturday, 24 July 2021
WiFi-6E 6GHz- WiFi Spectrum Unleashed
Thursday, 22 July 2021
Miercom validates deployment simplicity of Cisco’s SASE solution
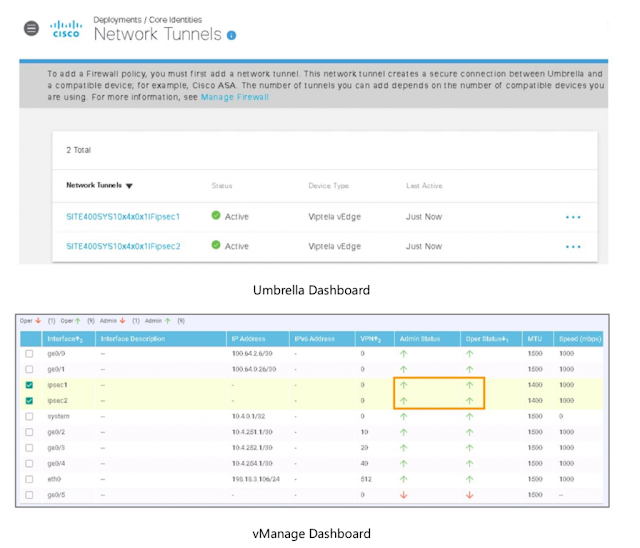
With the digital transformation of businesses, security is moving to the cloud. This is driving a need for converged services to reduce complexity, improve speed and agility, enable multicloud networking and secure the new SD-WAN-enabled architecture. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is the convergence of networking and security that is transforming the way organizations are delivering these services from the cloud. One of the key functions in SASE is SD-WAN that enables customers to connect users securely to applications and data regardless of location. Miercom recently did an independent study validating the setup simplicity of Cisco SD-WAN powered by Viptela with Cisco Umbrella integration, offering customers a foolproof, intelligible and complete Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) solution.
Read More: 350-901: Developing Applications Using Cisco Core Platforms and APIs (DEVCOR)
In today’s fast paced technology driven world, customers want a simplistic and seamless experience and expect the solution to be easy to deploy right from day 0 to day N setup. Cisco’s solution is simple to setup, intuitive and includes a true zero-touch SD-WAN solution that is faster to deploy and configure. Conversely, Competition setups are complex with multiple touchpoints which require manual intervention with no automated process, lacks template-based guided workflows and is more confusing to navigate. Cisco offers a cloud-hosting subscription where customers can self-provision SD-WAN controllers after order submission through a simple workflow on Cisco SD-WAN self-service portal (SSP) which incorporates vManage, vSmart and vBond in public cloud with secondary vBond and vSmart for high availability on desired region. The customers can sit back and relax while control plane/management plane setup is done via the cloud infrastructure automation tool and without any support intervention. Cisco’s SD-WAN integration with Cisco Umbrella via Cisco Smart Account licensing allows for template-based configuration workflows and automated secure tunnel deployment between SD- WAN routers and the nearest Cisco Umbrella data center. As validated by Miercom, Cisco proved more efficient in unified management mostly from a single platform (vManage), making it simple for even lean IT teams to manage via preloaded templates and troubleshooting features.
Wednesday, 21 July 2021
Trust Analytics and Anti-Spoofing Protection: It’s Already in Your Network
Nearly every day we can read about “ransomware” holding another organization’s data hostage, shutting their operations down, or disrupting their supply chain. Commercial enterprises. Major utilities. Large healthcare providers. Processing facilities. Even small businesses aren’t safe from being the target of these attacks.
The key to preventing your organization from falling prey to ransomware is to keep several steps ahead of hackers. In many cases, the tools you need to protect your data are already available in your network. With the recent introduction of Continuous Trusted Access and the new Cisco Trust Analytics you can now secure your network from several potential attack vectors.
Trust Analytics is part of Cisco SD-Access, Cisco’s best-of-breed Zero Trust solution for the workplace. Trust Analytics detects traffic from endpoints that are exhibiting unusual behavior by pretending to be trusted endpoints using MAC Spoofing, Probe Spoofing, or Man-in-the-Middle techniques.
When anomalies in the network are detected (see Figure 1), Trust Analytics lowers the Trust Score for the endpoint to limit or completely deny access to the network through integration with Cisco Identify Services Engine (ISE). In this blog, we will describe how Trust Analytics can help to secure your network.
Device Spoofing
Zero Trust
Already in Your Network
Tuesday, 20 July 2021
Preventing Network Loops! A Feature You Need to be Aware of
No matter how secured or precise the configurations are, there are some problems you can’t almost avoid, particularly L2 loops. The looped frames have no TTL to decrement and nothing else to lose. It unleashes at a perfect time, a critical production hour or perhaps Friday nights!
A common approach is to tighten STP configuration and enable BPDU guard, root guard, loop guard, Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD), storm-control or disable unused ports, where ever applicable.
Even with the right configurations in place, incorrect STP port transitions, hardware issues, misplaced root bridge etc., can still cause loops. And not to forget the mysterious unmanaged switches that occasionally show up on the network.
The STP loopguard will only react if a root or Alternate port stops receiving BPDUs. But nothing that explicitly detects and stops an ongoing loop.
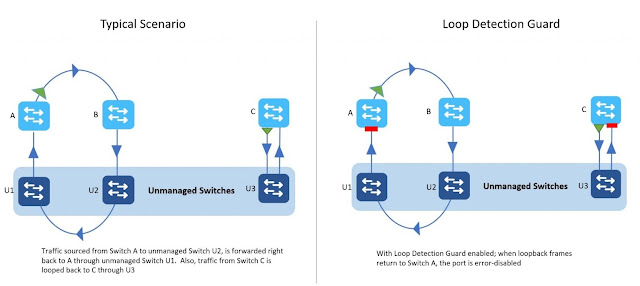
One such feature is the Loop Detection Guard on the catalyst 9000 switches. The function is simple, send a frame out of one port and see if it returns on another. The feature is introduced on 17.2.x & later releases and supported on all Catalyst 9000 platforms.
So how does the Loop Detection Guard work?
A port enabled with Loop Detection Guard sends out a loopback frame and checks if it returns to the switch. If it does, the switch error disables source port or destination port, whichever is the configured action. The loop detect frames are L2 frames with Ethertype loopback. The loopback frames have the source interface mac as the source mac and switch base mac address as the destination mac.
A recipient device typically drops these frames as the destination MAC address is different. If the frame is forwarded back to the originating switch, the loop detect guard will kick in.
The loopback frames are untagged, it doesn’t matter what VLAN the frame is sent on, it just shouldn’t return to the originating switch.
Configuration & Implementation Flexibility
STP Loopguard vs Loop Detection Guard
Monday, 19 July 2021
Practical Study Tips for CCNA 200-301 Exam Prep That Includes Practice Tests
When you own a certification like CCNA in front of you to pass, you must possess great knowledge of the subject. Be it CCNA tutorial, PDFs, Official books, or certified trainer’s guidance; you need all of them to pass the certification exam on the first shot.
Why Get CCNA 200-301 Certified?
Professionals today actively engaged in the networking domains go for Cisco certifications to prove their knowledge and boost the possibilities of getting hired. As,
- A substantial percentage of organizations globally use Cisco products and services and so demand professionals with CCNA certification and distinct skills to execute, install, monitor, and manage them.
- Cisco CCNA certification delivers you the skills you require to launch your career in the networking domain and grants you the appreciation you need.
- CCNA exam syllabus is consistently updated corresponding to the most recent in networking; passing the exam is an amazing way to hold your importance.
- CCNA certified professionals get a better salary than non-certified professionals. Also, they are proposed exciting job opportunities consisting of mentorship and leadership positions at the workplace.
Here are some tips which will assuredly work for CCNA 200-301 Exam with a proper approach:
1. Trust Yourself
Entitle yourself with a frame of mind for excellence to pass the Cisco CCNA 200-301 qualifying exam and thus pass them with excellent scores.
2. Learn from Valid Resources
Cisco Self-learning resources will enhance your learning with profound knowledge and equip you with so-craved confidence. Though these resources can’t be contemplated as a developed learning set, they shall work as a sturdy learning portal. Engage in the Cisco study group to boost your study with peers.
- E-learning. There are many online resources readily available for Cisco exam preparation. You can find online training courses, Ebooks, study guides, and much more. According to your learning preference, choose the study resources wisely.
- Hands-On Practice. Try to pass your CCNA exam through the actual certification path or benefit from Cisco learning labs for the 200-301 exam.
- CCNA 200-301 Practice tests. Practice tests are the best means when evaluating your knowledge gaps because answering the questions can help you interpret your weak areas. You can get the best and updated practice tests from the trusted platforms. Practice tests are created to feel the absolute exam presence and thus test themselves in an actual environment.
3. Study the CCNA 200-301 Exam Structure and Summarize the Information
This is one of the most critical steps you should consider in your preparation process. Having a picture of the exam is a perfect technique of getting prepared to answer the CCNA exam questions correctly.
Final Takeaway
Cisco certifications are universally acknowledged when it comes to networking technology. Passing the CCNA 200-301 certification is an ideal step in penetrating the world of technology. The skills you gain with passing Cisco 200-301 are all you need to solve real-world problems.
Make your career discovery by obtaining the CCNA certification and get prepared with practice tests and other valid study resources available on reliable platforms!
Friday, 16 July 2021
Nanosecond Buffer Visibility with Hardware-Based Microburst Detection
What Are Microbursts and Why Do They Matter?
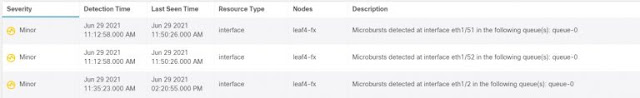
Ever wondered why a switch interface shows an average utilization of well below wire rate, and yet egress discards are incrementing? Most likely, that interface is experiencing microbursts. Often, when multiple input interfaces simultaneously receive traffic destined to a single egress interface – a so-called “incast” traffic pattern – no problem arises because the instantaneous receive rate is low enough that the output interface can handle the load.
The term “microburst” refers to the same situation, but where the receive rate of those interfaces in aggregate exceeds the wire rate of the output interface for some time. In this case, the excess traffic must be buffered. If enough such traffic arrives simultaneously, the buffer on the output interface can fill and potentially overflow, resulting in discards. Figure 1 illustrates the microburst concept.
What Is Hardware-Based Microburst Detection and How Does It Work?
Consuming Microburst Data for Analysis
Key Takeaways
Thursday, 15 July 2021
Reinventing Small to Medium Wi-Fi 6 Deployments
As many organizations are looking at wireless refreshes that include both expansion and upgrades to Wi-Fi 6, those with small, medium or branch locations have some cool (and very useful) new options to consider and should seriously rethink the deployment model.
Historically, small, medium and branch wireless deployments have been an operational challenge for many organizations. Some of those challenges include:
◉ Solution cost including procurement, deployment, and maintenance,
◉ Management complexity
◉ Lack of visibility into the user experience
◉ Limited feature sets, including security limitations, that force a compromise on features in smaller sites to uphold cost effectiveness
◉ Approaching smaller sites as home Wi-Fi setups for lack of better solutions
I wanted to emphasize that size does not matter, meaning that the deployments representing smaller locations can easily represent significant cash flow where user experience is key. I have personally struggled in the past with the need to purchase multiple wireless controllers for sites with 10 to 20 access points.
Today, things are looking a little different for smaller enterprise grade deployments. Cisco’s latest enhancements of the Cisco Embedded Wireless Controller (EWC) licensing model means its easy and cost effective to deploy these smaller networks without the need for a physical or even a cloud-based controller. Some might say it’s a game changer, and for those with small to medium wireless deployments up to 100 access points, it really is.
It is important to note that 100 access points is a large site. In my opinion, most deployments will consist of a handful of access points but it’s good to know the EWC can scale up to 100 APs if needed. Add in Cisco’s recent announcement that AireOS is going into sunset mode and you can see why EWC is a much-needed solution to support smaller sites. It also provides an exit strategy for some of the smaller site controllers like the 2504.
Full featured wireless controller integrated into the AP
As stated earlier, I think it is time to reinvent how we think and deploy these smaller wireless networks. With EWC we have the full enterprise features and management capabilities of a standalone (HA capable) controller(s), integrated into the Cisco Catalyst 9100 series access points. Previous embedded solutions were somewhat cumbersome to use and suffered feature parities, I know this because I’ve used them. With the latest EWC capabilities, Cisco really scored a home run thats worthy of taking a closer look at.
The EWC leverages the same IOS-XE software that runs on the Cisco Catalyst 9800 wireless controllers, so what you get is essentially controller without the appliance or licenses. And beyond supporting Catalyst APs, the EWC also supports many of Cisco’s existing AC Wave 2 access points including the 18xx, 28xx, 38xx, 48xx. While these Aironet APs can be part of the EWC network serving clients, they cannot function as the EWC controllers, that privilege is reserved for the Catalyst 91oo series access points.