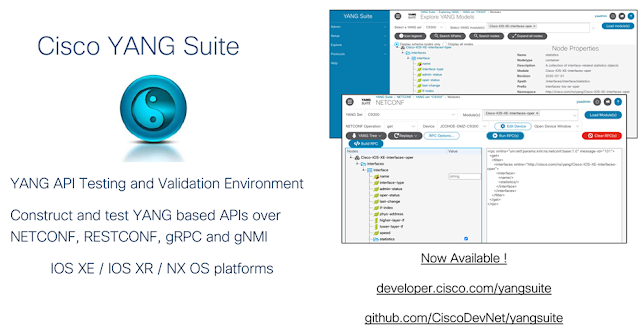
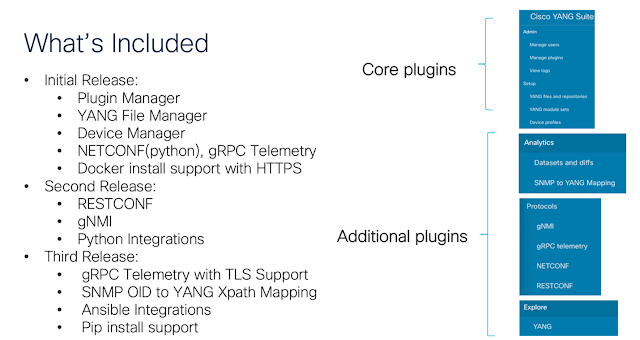
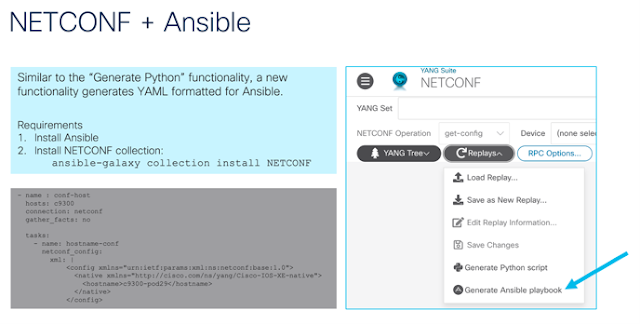
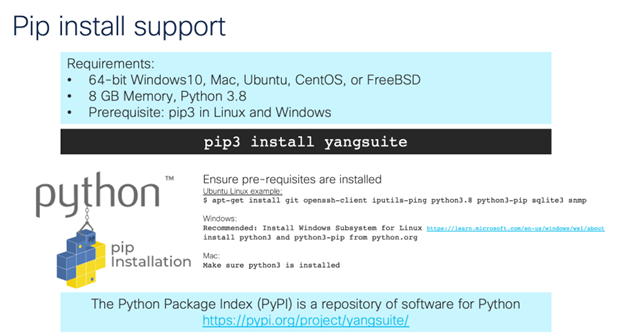
It’s Halloween — a time for too much candy, scary movies, kids in fun costumes, and lots of tricks and treats. As I thought about what to write for my blog this month, I quickly went to one of the scariest things for every network engineer: SPANNING TREE!!!! That’s right… can anything else bring the same level of dread and cold sweats as the potential for a bridging loop?!
Fear not. With a bit of good practical design and configuration practices, spanning tree doesn’t have to be scary. However, even the best engineers (or moderately decent ones like myself) can forget a best practice or two. Let me set the spooky scene for you…
It was a dark and stormy night…
The following anecdote took place about three or four years ago when I was part of the DevNet Sandbox team. We had recently stood up a new data center for hosting labs, and I had returned home from California after spending several weeks onsite, standing up the network and systems at the data center. I was feeling quite good about how well things had gone. Particularly, the speed and efficiency we were able to bring things online, thanks to a heavy amount of automation and programmability. In retrospect, I should have known something was going to go wrong…
I think the first sign there might be a problem in the network was when I noticed my remote connection into the new location started to get really laggy. I even got disconnected from some servers. It would clear up fairly quickly. But when the issues repeated several times, I started to wonder what might be the cause.
I checked other monitoring systems. Intermittent network issues had recently started showing up; slow response from systems, occasional disconnects that would clear up fairly quickly, that sort of thing. Nothing overly drastic, but they certainly were symptoms that indicated something might not be perfectly healthy in the network. I began to poke around a bit more. Eventually, I stumbled across a few things that pointed to a possible issue somewhere in the layer 2 parts of the network.
It was quite a while ago, so the details are a little fuzzy. I think I was on one of the top of rack Nexus 9000 switches in a hardware hosting rack when syslog messages hit the terminal about MAC flapping occurring. Now, MACs will move around a network occasionally. However, a flapping MAC address happens when a switch sees it changing back and forth between two ports. This is not normal. It often points to a network loop — something spanning tree is supposed to prevent from occurring.
Here is an example syslog message related to MAC Flapping:
*Apr 5 18:17:43.242 GMT: %SW_MATM-4-MACFLAP_NOTIF: Host d8e6.a5cd.3f41 in vlan 61 is flapping between port Ethernet1/23 and port Ethernet1/24
After a bit more troubleshooting, I also noticed that the network was reconverging spanning tree, changing the root bridge over and over again. This was definitely a problem. Even “rapid” spanning tree convergence is noticeable to network users who find themselves waiting for a port to transition to forwarding after ports change state.
Enough of the trick already, Hank… where’s the treat?
Long story short, the root of the problem (pun TOTALLY intended) was a new physical switch that was being added to the network for one of the hardware labs we were setting up.
The new switch hadn’t been fully configured for its new role yet, and the upstream switches it was connected to already had the ports enabled in preparation for the new lab gear being added. The lab topology had multiple ports connected between this new switch and the data center fabric for different purposes and networks, but none of the final configuration had been applied yet. There were actually some remnants of old configuration applied to the switch, which resulted in the bridging loop and MACFLAP log messages.
Furthermore, this switch had previously served as the spanning tree root in a previous network and had a lower (i.e., better) priority than the actual spanning-tree root in our data center. Between connections being made/removed, ports getting errdisabled for different reasons, and other instabilities, the root was bouncing between this new switch and the main distribution switches in the data center every couple of minutes.
I was able to quickly stop the problems from occurring by shutting down the ports connected to this new switch until it was correctly configured and ready to be made an active part of the network. So, problem solved… kinda.
The bigger problem was that I had overlooked the critical spanning tree design and best practices for the configuration step in bringing the new data center network up and online. Had I remembered my fundamentals, this problem wouldn’t have happened: The network would have automatically blocked ports that were behaving in unexpected ways.
You are NOT root: Preventing unexpected root bridges with root guard
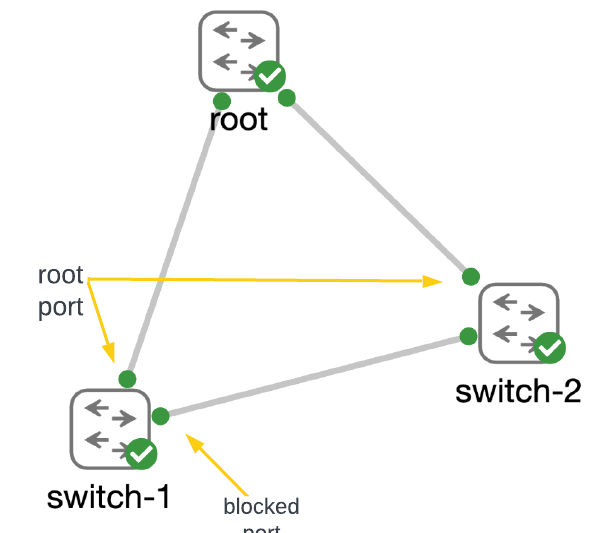
Consider this very simple triangle of switches as a quick review of the importance of the root bridge in a spanning-tree network.
Switches connected together with layer 2 links use BPDUs (bridge protocol data units) to learn about each other and determine where the “root” of the spanning tree will be placed. The switch that has the best (i.e., lowest) priority becomes root. With the root bridge identified, switches begin the process of breaking loops in the network by blocking ports that spanning tree identifies as having the worst priority on redundant links.
A full discussion on the spanning-tree process for building the tree is out of scope for this blog post. It is a very important topic for network engineers to understand, so I might return to spanning tree in future blog posts. If you’d like to dive deeper into the topic now, check out our CCNA and ENCOR courses.
The process of electing the root bridge and converging on a loop-free network can take tens of seconds to even a minute (or more) in large networks, depending on which version of spanning tree is used and how well the network is designed. During the process of convergence, the network prevents bridging loops by defaulting to blocking traffic on ports. This will result in significant disruption to any users and applications that are actively using the network. Remember in my example above, how my network access had gotten “laggy” and my connections had even become disconnected? As long as the root bridge remains stable and does NOT change, adding a new switch to a network is a non-disruptive activity.
So, how does a network engineer prevent the root bridge from changing in the network? I’m glad you asked.
Identifying the root bridge for the network
The first step is to look at the network design and identify which switch makes the most logical sense to be the root, explicitly configuring it to have the best (i.e., lowest) priority. Here, I configure my root switch to run rapid per-vlan spanning tree (rapid-pvst) and set the priority to 16384.
root#show run | sec spanning
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
spanning-tree vlan 1-4094 priority 16384
root#show span
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 16385
Address 5254.000e.dde8
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 16385 (priority 16384 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 5254.000e.dde8
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi0/1 Desg FWD 4 128.2 P2p
Gi0/2 Desg FWD 4 128.3 P2p
Gi0/3 Desg FWD 4 128.4 P2p
Note: With “per-vlan spanning-tree” every VLAN will have its own spanning-tree constructed. The priority of each bridge is the configured priority plus the VLAN number. So for VLAN 1, the priority is 16384+1 or 16385.
If we look at the spanning-tree state on one of the other switches in the network, we can confirm the root bridge and the creation of a loop-free network.
switch-1#show span
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 16385
Address 5254.000e.dde8
Cost 4
Port 2 (GigabitEthernet0/1)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 5254.0017.ae37
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi0/1 Root FWD 4 128.2 P2p
Gi0/2 Desg FWD 4 128.3 P2p
Gi0/3 Altn BLK 4 128.4 P2p
switch-1#show cdp neighbors gigabitEthernet 0/1
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
root Gig 0/1 146 R S I Gig 0/1
If you compare the address of the root bridge shown on switch-1 to the output above from root, you will see that the Address and Priority for the root bridge match. Also, notice that interface G0/1 has the role of “Root” — this is the interface on the switch that has the best path back to the root bridge. And as the output from CDP shows, it is actually directly connected to the root.
Stopping a new root on the block… err, network
Identifying an intended root bridge for your network is great, but it doesn’t prevent a newly added switch from causing trouble.
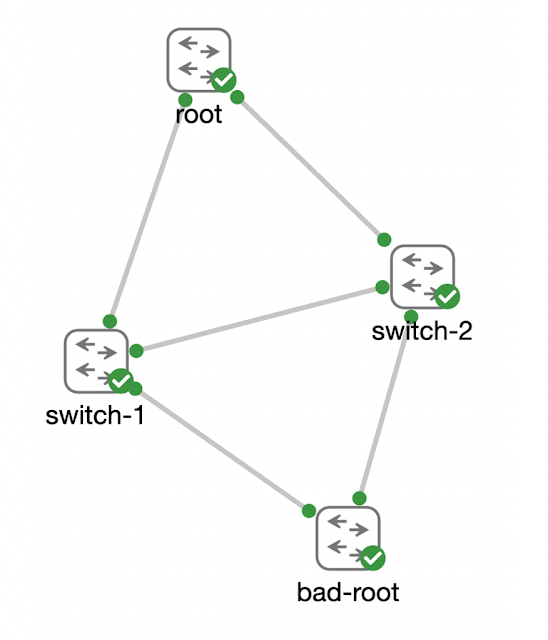
Consider back to my example from my anecdote where a new switch was being added to the network that had previously been configured as the root in another network. While it could be argued that it is best practice and important to clear old configuration from a switch before adding it to the network, the reality is… things like this happen. It is important to engineer a network to handle events like this.
First, let’s see what happens to the spanning-tree network when bad-root is cabled into the network without any extra configuration protecting the spanning-tree network.
switch-1#show span
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 4097
Address 5254.001e.82a2
Cost 4
Port 1 (GigabitEthernet0/0)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 5254.0017.ae37
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi0/0 Root FWD 4 128.1 P2p
Gi0/1 Desg FWD 4 128.2 P2p
Gi0/2 Desg FWD 4 128.3 P2p
Gi0/3 Altn BLK 4 128.4 P2p
switch-1#show cdp neighbors gigabitEthernet 0/0
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
bad-root Gig 0/0 154 R S I Gig 0/1
Total cdp entries displayed : 1
Notice how the address and priority for the root bridge have changed, and that port Gi0/0 is now the “Root” port for switch-1. This is definitely not what we would want to happen if a bad-root were connected to the network.
Bringing out the Guard… root guard, that is
We can leverage root guard to prevent this from happening. Root guard is one of the “optional spanning-tree features” that really shouldn’t be considered “optional” in most network designs.
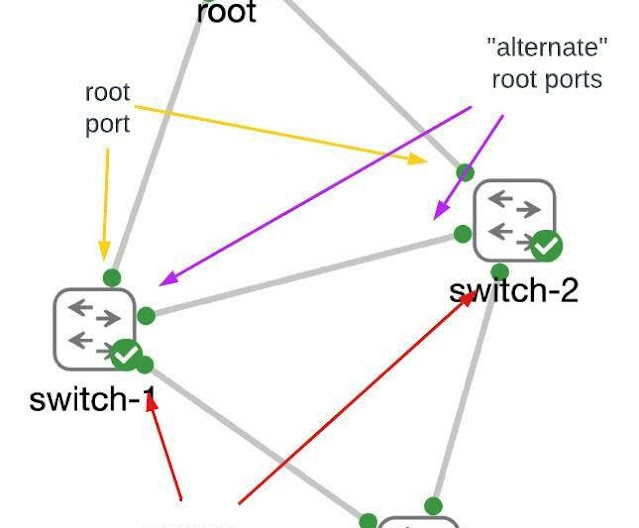
As a network engineer, you should be able to look at your network and know which ports “should be” the root port on each switch. Then consider the redundancy that you’ve built into the network and identify which port should become the root port if the primary port were to have problems. Every other port on each switch should never become the root port. Those are the ports that should be configured with root guard.
Note: The root bridge in a network has NO root ports as it is the root of the tree. Therefore ALL PORTS of the root bridge should have root guard enabled.
Now we’ll go ahead and enable root guard on interface Gig0/0 on both switch-1 and switch-2.
switch-1(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
switch-1(config-if)#spanning-tree guard root
*Oct 13 15:06:28.893: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARD_CONFIG_CHANGE: Root guard enabled on port GigabitEthernet0/0.
*Oct 13 15:06:28.909: %SPANTREE-2-ROOTGUARD_BLOCK: Root guard blocking port GigabitEthernet0/0 on VLAN0001.
And look at that. As soon as it is enabled, we see syslog messages indicating that root guard has begun blocking the port. If we check the status of spanning tree on switch-1 we can verify that the root of the spanning tree has returned to the correct root switch.
switch-1#show span
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp
Root ID Priority 16385
Address 5254.000e.dde8
Cost 4
Port 2 (GigabitEthernet0/1)
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 5254.0017.ae37
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 300 sec
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
------------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Gi0/0 Desg BKN*4 128.1 P2p *ROOT_Inc
Gi0/1 Root FWD 4 128.2 P2p
Gi0/2 Desg LRN 4 128.3 P2p
Gi0/3 Altn BLK 4 128.4 P2p
There’s one other command that is handy to know when troubleshooting spanning-tree ports that aren’t behaving as expected:
switch-1#show spanning-tree inconsistentports
Name Interface Inconsistency
-------------------- ------------------------ ------------------
VLAN0001 GigabitEthernet0/0 Root Inconsistent
Number of inconsistent ports (segments) in the system : 1
Take the scare out of spooky spanning tree with knowledge
Hopefully, this post helps to lower your heart rate a little the next time you think about making changes to the network that might impact your spanning-tree network. But I also hope it shows you, as a network engineer, the importance of recalling the fundamental skills and knowledge you have learned as you move onward to more specialized areas of networking. I was definitely kicking myself when I realized that I had completely overlooked ensuring that our spanning-tree network was well-designed and protected from unexpected or unintended changes.
While no one wants to have a network outage or even a minor disruption, they will happen. What is important, is that we learn from them. And we become better network engineers for them.
Do you have a spooky network ghost story from your own work as a network engineer? Ever had a scary encounter with a network outage or problem that helped you learn a lesson you’ll never forget? Share them in the comments. Trick or treat!
Source: cisco.com