It’s such an odd time right now. Standing where we are, we know the world and the workforce is changing. While there’s universal consensus that nothing will be the same, no one is sure exactly what the new workforce environment will look like. Sure, there are hints. According to a recent IDC webinar—COVID 19 and Enterprise Networking—Assessing the Impact, Planning for the Future—the number of remote workers will surge from less than 7% to nearly 30%. And networks will need to change to support business continuity in this geographically dispersed workforce with application and collaboration experiences that mirror those in the office.
But what will that look like? VPN? Cloud?
One sure thing is that network automation will play an increasingly important role going forward. The same IDC report bears this out, indicating that, at 48%, the number one area of increased IT investment will be for network automation. Why? Because regardless of how IT pivots to support distributed workers, the infrastructure required to handle that load will be more complex and more demanding. The management task is simply too heavy a lift to perform manually. It must be handled through automation.
This distributed workforce requirement aligns with the core automation capabilities built into Cisco DNA Center. We have always touted the time and cost savings available using Cisco DNA Center automation capabilities. Those benefits still remain. However, the emphasis moving forward will be on business resilience and continuity.
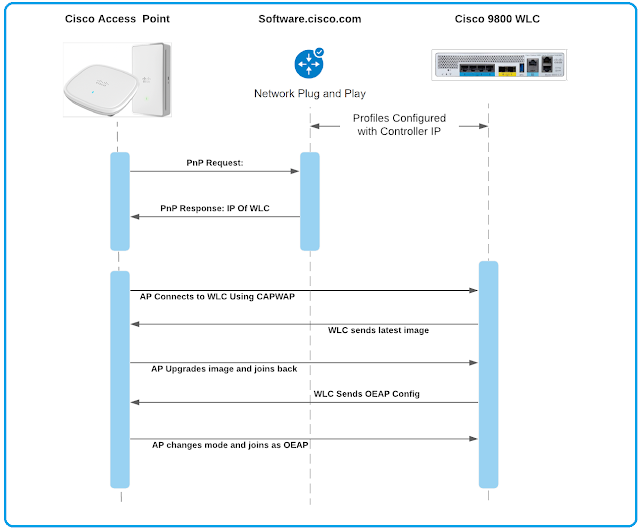
Cisco DNA Center automation works because it uses business intent to define how a network should run. Then it defines policies and configurations to ensure the network operates as intended. Then—and here’s the real power—Cisco DNA Center automatically pushes those polices and configurations throughout the network. Even a geographically distributed network.
There are several aspects of the new workforce environment that require this higher level of automation: deployments, complexity, consistent experience, configuration changes, security, and software maintenance. Let’s take a closer look at each.
Deployments
As enterprises scramble to support work from home, the number of new device deployments—for remote access, security, and routing—has exploded. The number and overnight turnaround makes managing the deployments manually nearly impossible. An IT department with a dozen techs can’t scale up to instantaneously deploy thousands or tens of thousands of remote deployments over one weekend. And, I’ve heard story after story of that’s exactly what Cisco DNA enabled.
Complexity
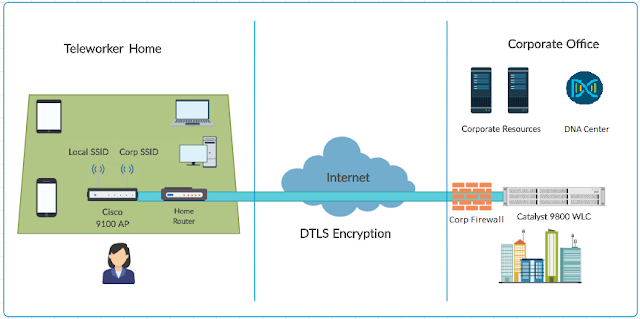
Complexity is likely to grow as organizations adapt to a more remote workplace. This is because of two factors—distribution and control. First, as workers work from home, the number of points of connection will become more distributed. And, second, the organization has less control over the technology in those home office environments. Sure, you can send virtual office routers, but you won’t have control over the ISP or wiring in the house. This makes access policy more difficult to implement and enforce – and configurations more difficult to establish and manage.
It’s just not realistic to assume that any IT department would have the manual resources to tackle this complexity. That’s where Cisco DNA automation comes in. You can establish different configurations for remote offices, headquarters, even different ISPs, then use Cisco DNA Center to automatically configure all of the necessary devices to support that remote access.
Consistent Experience
One of the things I keep hearing about the shift to working remotely is that employees don’t see their home office as workplace lite. It’s their new office. To deliver the same level of productivity, employees need to have an experience that’s consistent with the one they had in the campus or branch. That means consistent application access and performance, even while working from their new home office.
Sure, some of this consistent experience is dependent on the network devices used in the remote office. But consistent configurations and access policies are even more important. Again, with the number of home office locations exploding, there is no way for an IT department to manually provision all of these offices for optimal experience. And, if they try, the manual effort is guaranteed to introduce configuration errors that diminish the expected application and access experience and create potential security vulnerabilities.
Configuration Changes
While remote workplaces will be a big part of future collaboration, so will change. Employees may more frequently migrate between remote and campus environments. And enterprises may need to continually change configurations, policies and access permissions to accommodate this new demand for flexibility.
Through the configurations templates and automated deployment already discussed, Cisco DNA Center helps you easily make these changes. More importantly, because of the intent-based templates, those changes, regardless of how quickly they need to be deployed, will maintain the same level of consistency and application support as the initial deployment.
Security
With the expanded threat surface created by more remote work environments, security is a huge concern going forward. Vulnerabilities may be introduced into the network during rollout and management through deployment glitches, missed security patches and non-integrated security applications. The automation capabilities of Cisco DNA Center help with all three.
For deployments, the automated nature of the Cisco DNA deployments uses consistent configurations templates and significantly reduces manual errors, thereby greatly minimizing the introduction of security vulnerabilities through incomplete or inaccurate deployments.
Going further, Cisco DNA Center has security integrated into its automation capabilities. First, all applications are under constant attack and require effective security patch management to quickly address vulnerabilities. Cisco security advisories are made available from within Cisco DNA Center. The highest level threats for devices on your network rise to the top of the list where you can directly download and deploy the new patches to all affected devices.
In addition, Cisco DNA Center integrates several Cisco security solutions right into the solution dashboard. Stealthwatch and Umbrella can be deployed directly from within Cisco DNA Center. And rogue and adaptive wireless intrusion prevention is built right into the solution. As a result, security and network management, both in greater demand in this new environment, can be more effectively managed through the automation capabilities of Cisco DNA Center.
Software Maintenance
In the best of times, maintaining current versions of system software for all of your network devices can be a challenge. But when those devices are distributed across thousands or tens of thousands of remote worksites, the challenge is no longer possible with manual updates.
Again, Cisco DNA Center automation capabilities help you overcome this challenge. Cisco DNA Center can actively discover all the system software versions on your network devices, highlight those that are inconsistent or out of compliance, and even push the correct, up-to-date image to the identified network devices. All automatically from your Cisco DNA Center dashboard and regardless of location. In fact, you can even define different configurations by location and keep those up to date as well.
The bottom line is no one really knows the exact shape of the future workforce environment. But Cisco DNA Center automation capabilities all support the agility, flexibility, and remote access that will help you adapt as we all move forward.