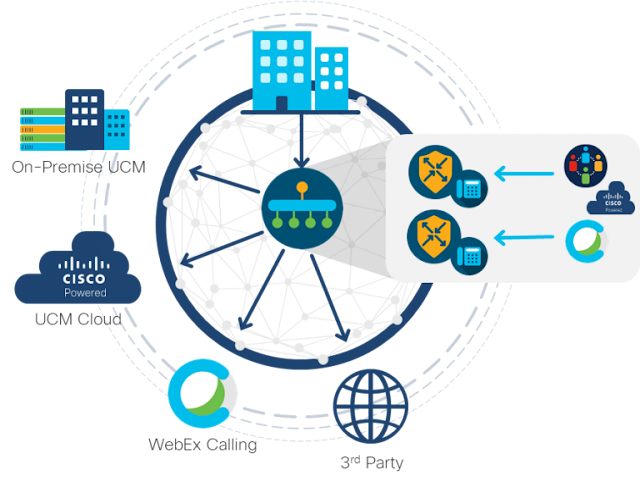
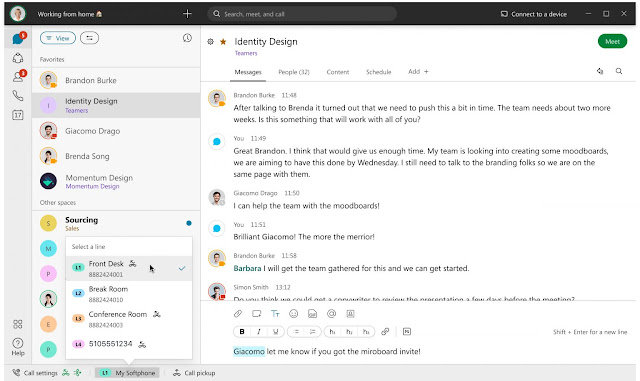
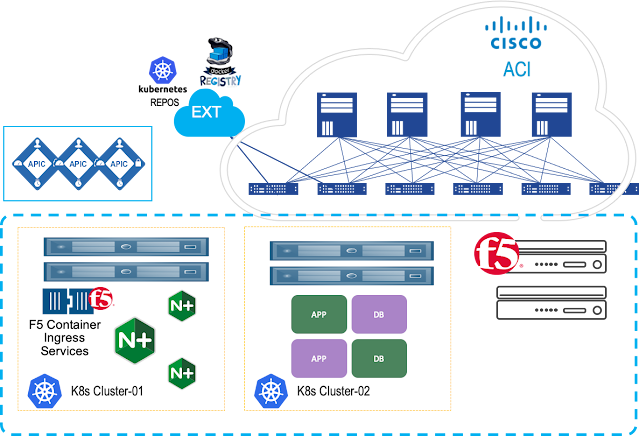
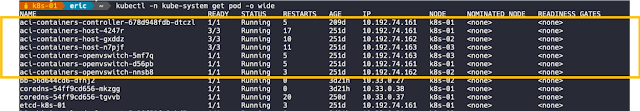
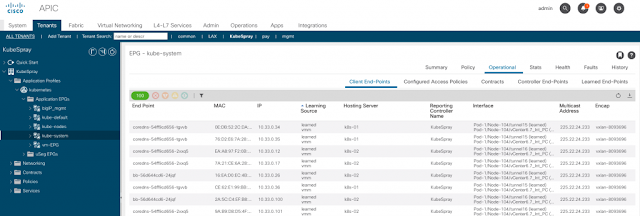
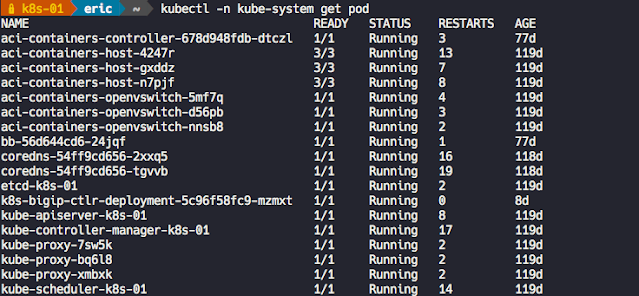
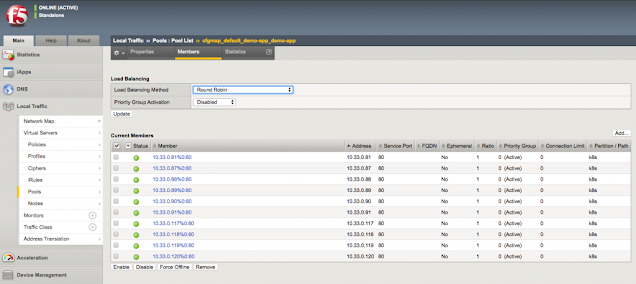
Having a Cisco edge platform with integrated UC enables communications while it simplifies, segments, and secures your connectivity.
Cisco is the only vendor to natively integrate analog, digital and IP telephony interfaces directly into the Customer Premise Equipment (CPE)
Reduced OpEx and CapEx
With both UC and SD-WAN within a single CPE, there are less support and licensing costs, as well as eliminating the cost of the UC hardware
VoIP Solution Investment Protection
Many customers have large deployments of IP phones and other VoIP solutions. Integration of UC/Voice on Cisco edge devices ensures that existing equipment investments can be leveraged since they are supported in the cloud with Cisco SD-WAN.
Reduced Complexity
Cisco vManage can orchestrate scalable and consistent UC configurations across the entire enterprise via templates and policies can prioritize specific applications links, with fallback capability in case of link failure or degradation.
Telephony Survivability
Prevents internal and external IP phone outages using Cisco unified SIP SRST enabling the edge device as the fall back IP PBX with access to the PSTN.
Middle-mile Optimization
Cisco is the only vendor extensively partnering with colocation and SDCI Partners for optimization with cloud applications (Cisco WebEx, UCM Cloud and more). Cisco’s Cloud OnRamp functionality provides optimal performance for UC applications hosted in a SaaS cloud.
Ensuring security and communication integrity
Cisco SD-WAN also integrates best-of-breed security with cloud-based Cisco Umbrella or Cisco’s on-premise security portfolio, thereby ensuring the security and integrity of your network and Unified Communications.
The Distinguishing Features of Cisco
Cisco’s rich feature set in this integrated solution meets the most demanding needs of the enterprise. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key features:
Application Visibility
Application visibility is an essential element for any SD-WAN solution, not only from a monitoring standpoint, but also for analytics and policy construction. Traditionally, policies for the WAN required administrators to use IP Addressing, Ports, Layer 4 Protocol, DSCP value, and more to define traffic that should receive any special treatment. This worked in the past, but as applications evolved, policy cannot be built on these criteria. In our multi-cloud world, applications are far more dynamic and often cannot neatly fit within the confines of legacy rules. Cisco’s SD-WAN solution addresses this by utilizing both Qosmos and Network Based Application Recognition (NBAR2) to identify the applications to which it is forwarding traffic. Deep-Packet-Inspection (DPI) engines are invoked directly in the Data Plane and evaluate every packet. By using a complex formula of Layer 3, 4 and 7 information, the engines are capable of identifying which WAN application a particular packet belongs to. The data can then be used within a policy to provide intelligent routing for these applications. If an administrator wants to provide priority to Unified Communications traffic such as a videoconference, they are no longer required to specify DSCP values, ports or IP Addresses. They simply select the Unified Communications Application Family. Qosmos and NBAR2 will do the rest!
Application-Aware Routing
Cisco application-aware routing computes the optimal paths for data traffic, helping assure service levels for UC applications as well as voice traffic. These paths are calculated by tracking characteristics including packet loss, latency, and jitter in the data plane tunnels between edge devices. Cloud OnRamp automates the selection of best performing path to cloud-based UC services, including the choice of DIA for remote locations.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Automation of QoS deployments using Cisco vManage to simplify and assure best quality for voice and video. QoS prioritizes bandwidth for UC and voice traffic. The SD-WAN overlay network examines packets that enter at the edge of the network, while the edge devices are configured to provision QoS. The data traffic will then flow automatically over IPsec connections between edge devices.
You can also modify the packet forwarding flow with centralized and localized data policies. The centralized data policy enables control over traffic based on the address, port, and Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) fields in the packet’s IP header. The localized data policy controls the flow of traffic into and out of the edge devices’ interfaces.
Each interface has eight queues on edge devices, numbered 0 to 7. Queue 0 is reserved for both control traffic and low-latency queuing (LLQ) traffic; you must configure any class mapped to queue 0 to use LLQ. All control traffic is transmitted. Queues 1 to 7 are available for data traffic.
Per-VPN topology
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide segmentation and enhanced security in the SD-WAN overlay, much like Virtual Routing and Forwarding instances (VRFs). Each VPN is isolated and has its own forwarding table. Each Interface or sub-interface is explicitly configured under a single VPN, using labels in OMP route attributes and the packet encapsulation to identify it. You can create a separate VPN topology for UC traffic (full mesh).
Packet Duplication and Forward Error Correction
Forward Error Correction (FEC) and Packet Duplication enhancements were added to Cisco SD-WAN. Packet Duplication creates a copy of critical application flows across the SD-WAN fabric. FEC drastically improves audio/video quality over a lossy link such as an internet connection by adding correction packets to the flow. If packet loss occurs, these duplicated/FEC flows can be recovered from a secondary link. This does however come with the requirement of up to doubling the bandwidth allocated for a given application. However, for Unified Communications flows, this may be acceptable when considering these traffic flows are generally smaller. Also, CODEC selection can also help to alleviate the burden that Packet Duplication/FEC incurs.
Data Policy-Traffic Engineering
Data policies affect the flow of data traffic through the network based on fields in the IP packet headers and VPN membership. You can use centralized data policies for application firewalls, service chains, traffic engineering, QoS, and Cflowd. Localized data policies allow you to configure data traffic handling at a specific site, including ACLs, QoS, mirroring, and policing. A centralized data policy such as QoS classification or app-route policies may also impact handling on edge devices. You may also route voice traffic based on data policy with Cisco SD-WAN.
Geo-Redundancy
UC traffic routed through geo-redundant network links enable failover and fallback protections.
In today’s business environment, it’s never been more important to reduce costs. Cisco now offers a robust, integrated UC and secure SD-WAN solution on a single platform to both reduce CapEx and decrease support and licensing costs that reduce OpEx.
We are all doing more with less. Cisco vManage helps reduce complexity with the addition of UC orchestration with configuration via templates and policies for consistency across an enterprise datacenter, network operations center of colocation facility.
With middle-mile optimization and telephony survivability, Cisco offers the business resiliency and options to maximize your performance now, and for future needs.
Integrating UC with Cisco SD-WAN provides benefits regardless of if you are a Multi-national conglomerate with many datacenters, a service provider or a Branch of One.